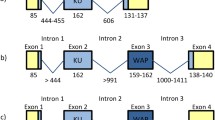
Abstract
Kunitz-type domains are ubiquitously found in natural systems as serine protease inhibitors or animal toxins in venomous animals. Kunitz motif is a cysteine-rich peptide chain of ~ 60 amino acid residues with alpha and beta fold, stabilized by three conserved disulfide bridges. An extensive dataset of amino acid variations is found on sequence analysis of various Kunitz peptides. Kunitz peptides show diverse biological activities like inhibition of proteases of other classes and/or adopting a new function of blocking or modulating the ion channels. Based on the amino acid residues at the functional site of various Kunitz-type inhibitors, it is inferred that this ‘flexibility within the structural rigidity’ is responsible for multiple biological activities. Accelerated evolution of functional sites in response to the co-evolving molecular targets of the hosts of venomous animals or parasites, gene sharing, and gene duplication have been discussed as the most likely mechanisms responsible for the functional heterogeneity of Kunitz-domain inhibitors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen JF (2010) Structure and mechanism in salivary proteins from blood-feeding arthropods. Toxicon 56(7):1120–1129
Ascenzi P, Bocedi A, Bolognesi M et al (2003) The bovine basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz inhibitor): a milestone protein. Curr Protein Pept Sci 4(3):231–251
Azarkan M, Martinez-Rodriguez S, Buts L, Baeyens-Volant D, Garcia-Pino A (2011) The plasticity of the β-trefoil fold constitutes an evolutionary platform for protease inhibition. J Biol Chem 286(51):43726–43734
Báez A, Salceda E, Fló M et al (2015) α-Dendrotoxin inhibits the ASIC current in dorsal root ganglion neurons from rat. Neurosci Lett 606:42–47
Ben Khalifa N, Tyteca D, Courtoy PJ et al (2012) Contribution of Kunitz protease inhibitor and transmembrane domains to amyloid precursor protein homodimerization. Neurodegener Dis 10(1–4):92–95
Bonaldo P, Colombatti A (1989) The carboxyl terminus of the chicken α3 chain of collagen VI is a unique mosaic structure with glycoprotein Ib-like, fibronectin type III, and Kunitz modules. J Bio Cem 264(34):20235–20239
Broze GJ Jr, Girard TJ (2012) Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: structure-function. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 17:262–280
Buchanan A, Revell JD (2015) Novel therapeutic proteins and peptides. In: Manmohan S, Maya S (eds) Novel approaches and strategies for biologics, vaccines and cancer therapies. Academic Press, Cambridge, ISBN 9780124166035, pp. 483–509.
Cescon M, Gattazzo F, Chen P, Bonaldo P (2015) Collagen VI at a glance. J Cell Sci 128:3525–3531
Chang LS, Chung C, Huang HB, Lin SR (2001) Purification and characterization of a chymotrypsin inhibitor from the venom of Ophiophagus hannah (king cobra). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 283:862–867
Chapin JC, Hajjar KA (2015) Fibrinolysis and the control of blood coagulation. Blood Rev 29(1):17–24
Chen P, Cescon M, Bonaldo P (2013a) Collagen VI in cancer and its biological mechanisms. Trends in Mol Med 19(7):410–417
Chen Z, Luo F, Feng J, Yang W et al (2013b) Genomic and structural characterization of Kunitz-type peptide LmKTT-1a highlights diversity and evolution of scorpion potassium channel toxins. PLoS ONE 8(4):e60201
Cleynen I, Juni P, Bekkering GE, Nuesch E et al (2011) Genetic evidence supporting the association of protease and protease inhibitor genes with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review. PLoS ONE 6(9):e24106
Cohen I, Coban M, Shahar A, Sankaran B et al (2019) Disulfide engineering of human Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitors enhances proteolytic stability and target affinity toward mesotrypsin. J Biol Chem 294(13):5105–5120
Cotabarren J, Lufrano D, Graciela Parisi M et al (2020) Biotechnological, biomedical and agronomical applications of plant protease inhibitors with high stability: a systematic review. Plant Sci 292:110398
De Magalhães MTQ, Mambelli FS, Santos BPO, Morais SB, Oliveira SC (2018) Serine protease inhibitors containing a Kunitz domain: their role in modulation of host inflammatory responses and parasite survival. Microbes Infect 20(9–10):606–609
De Souza JG, Morais KL, Anglés-Cano E et al (2016) Promising pharmacological profile of a Kunitz-type inhibitor in murine renal cell carcinoma model. Oncotarget 7(38):62255–62266
Deisenhofer J, Steigemann W (1975) Crystallographic refinement of the structure of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor at l.5 Å resolution. Acta Cryst B31:238–250
Ding L, Hao J, Luo X, Chen Z (2018) Engineering varied serine protease inhibitors by converting P1 site of BF9, a weakly active Kunitz-type animal toxin. Int J Biol Macromol 120(Pt A):1190–1197
Fioretti E, Angeletti M, Citro G, Barra D, Ascoli F (1987) Kunitz-type inhibitors in human serum. Identification and characterization. J Biol Chem 262(8):3586–3589
Flight SM, Johnson LA, Du QS, Warner RL et al (2009) Textilinin-1, an alternative anti-bleeding agent to aprotinin: importance of plasmin inhibition in controlling blood loss. Br J Hematol 145:207–211
Fregonese L, Stolk J (2008) Hereditary alpha-I-antitrypsin deficiency and its clinical consequences. Orphanet J Rare Dis 3:16
Fries E, Blom AM (2000) Bikunin-not just a plasma proteinase inhibitor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32(2):125–137
Fries E, Kaczmarczyk A (2003) Inter-α-inhibitor, hyaluronan and inflammation. Acta Biochim Polon 50(3):735–742
Fry BG, Roelants K, Champagne DE, Scheib H, Tyndall JDA (2005) The toxicogenomic multiverse: convergent recruitment of proteins into animal venoms. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 10(1):483–511
Garcia-Fernandez R, Pons T, Meyer A, Perbandt M et al (2012) Structure of the recombinant BPTI/Kunitz-type inhibitor rShPI-1A from the marine invertebrate Stichodactyla helianthus. Acta Crystallogr. Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 68:1289–1293
Garcia-Fernandez R, Peigneur S, Pons T, Alvarez C et al (2016) The Kunitz-type protein ShPI-1 inhibits serine proteases and voltage-gated potassium channels. Toxins 8:110
Graur D, Li WH (1988) Evolution of protein inhibitors of serine proteinases: positive Darwinian selection or compositional effects? J Mol Evol 28:131–135
Harvey AL (1997) Recent studies on dendrotoxins and potassium ion channels. Gen Pharmacol Vasc Syst 28(1):7–12
Harvey AL (2001) Twenty years of dendrotoxins. Toxicon 39(1):15–26
Harvey AL, Robertson B (2004) Dendrotoxins: structure-activity relationships and effects on potassium ion channels. Curr Med Chem 11(23):3065–3072
Hill RE, Hastie ND (1987) Accelerated evolution in the reactive centre regions of serine protease inhibitors. Nature 326:96–99
Hynes TR, Randal M, Kennedy LA, Eigenbrot C, Kossiakoff AA (1990) X-ray crystal structure of the protease inhibitor domain of Alzheimer’s amyloid β-precursor protein. Biochemistry 29(43):10018–10022
Ikeo K, Takahashi K, Gojobori T (1992) Evolutionary origin of a Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitor domain inserted in the amyloid β precursor protein of Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Evol 34:536–543
Jefferies JR, Campbell AM, Van Rossum AJ, Barrett J, Brophy PM (2001) Proteomic analysis of Fasciola hepatica excretory-secretory products. Proteomics 1:1128–1132
Johnson SA, Rogers J, Finch CE (1989) APP-695 transcript prevalence is selectively reduced during Alzheimer’s disease in cortex and hippocampus but not in cerebellum. Neurobiol Aging 10:267–272
Johnson SA, Mc Neill T, Cordell B, Finch CE (1990) Relation of neuronal APP-751/APP-695 mRNA ratio and neuritic plaque density in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 248:854–857
Kalita B, Dutta S, Mukherjee AK (2019) RGD-independent binding of Russell’s viper venom kunitz-type protease inhibitors to platelet GPIIb/IIIa receptor. Sci Rep 9:8316
Ketterer S, Gomez-Auli A, Hillebrand LE, Petrera A et al (2016) Inherited diseases caused by mutations in cathepsin protease genes. FEBS J 284:1437–1454
Kitaguchi N, Takahashi Y, Tokushima Y, Shiojiri S, Ito H (1988) Novel precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitor activity. Nature 331:530–532
Kitaguchi N, Takahashi Y, Oishi K, Shiojiri S et al (1990) Enzyme specificity of proteinase inhibitor region in amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer’s disease: different properties compared with protease nexin I. Biochim Biophys Acta 1038:105–113
Kordis D, Gubensek F (2000) Adaptive evolution of animal toxin multigene families. Gene 261(1):43–52
Lamande SR, Morgelin M, Adams NE et al (2006) The C5 domain of the collagen VI α3(VI) chain is critical for extracellular microfibril formation and is present in the extracellular matrix of cultured cells. J Bio Chem 281(24):16607–16614
Laskowski M, Kato I (1980) Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem 49:593–626
Laskowski M, Kato I, Ardelt W, Cook J, Denton A et al (1987a) Ovomucoid third domains from 100 avian species: isolation, sequences and hypervariability of enzyme-inhibitor contact residues. Biochemistry 26:202–221
Laskowski M, Kato I, Kohr WJ, Park SJ, Tashiro M, Whatley HE (1987b) Positive Darwinian selection in evolution of protein inhibitors of serine proteinases. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 52:545–553
Lehmann A (2008) Ecallantide (DX-88), a plasma kallikrein inhibitor for the treatment of hereditary angioedema and the prevention of blood loss in on-pump cardiothoracic surgery. Expert Opin Biol Ther 8(8):1187–1199
Lu J, Yang H, Yu H et al (2008) A novel serine protease inhibitor from Bungarus fasciatus venom. Peptides 29(3):369–374
Martins LA, Kotál J, Bensaoud C et al (2020) Small protease inhibitors in tick saliva and salivary glands and their role in tick-host-pathogen interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 1868(2):140336
Masci PP, Whitaker AN, Sparrow LG, Jersey JD, Winzor DJ et al (2000) Textilinins from Pseudonaja textilis textilis. Characterization of two plasmin inhibitors that reduce bleeding in an animal model. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 11:385–393
Molinari F, Meskanaite V, Munnich A, Sonderegger P, Colleaux L (2003) Extracellular proteases and their inhibitors in genetic diseases of the central nervous system. Hum Mol Genet 12(2):R195–R200
Morais SB, Figueiredo BC, Assis NRG et al (2018) Schistosoma mansoni SmKI-1 serine protease inhibitor binds to elastase and impairs neutrophil function and inflammation. PLoS Pathog 14(2):e1006870
Morjen M, Kallech-Ziri O, Bazaa A et al (2013) PIVL, a new serine protease inhibitor from Macrovipera lebetina transmediterranea venom, impairs motility of human glioblastoma cells. Matrix Biol 32(1):52–62
Mukherjee AK, Mackessy SP (2014) Pharmacological properties and pathophysiological significance of a Kunitz-type protease inhibitor (Rusvikunin-II) and its protein complex (Rusvikunin complex) purified from Daboia russelii russelii venom. Toxicon 89:55–66
Oliva ML, Ferreira Rda S, Ferreira JG, de Paula CA et al (2011) Structural and functional properties of kunitz proteinase inhibitors from leguminosae: a mini review. Curr Protein Pept Sci 12(5):348–357
Peigneur S, Billen B, Derua R, Waelkens E et al (2011) A bifunctional sea anemone peptide with Kunitz type protease and potassium channel inhibiting properties. Biochem Pharmacol 82:81–90
Pendlebury D, Wang R, Henin RD et al (2014) Sequence and conformational specificity in substrate recognition: several human Kunitz protease inhibitor domains are specific substrates of mesotrypsin. J Biol Chem 289(47):32783–32797
Pugia MJ, Valdes R, Jortani SA (2007) Bikunin (urinary trypsin inhibitor): structure, biological relevance, and measurement. Adv In Clin Chem 44:223–245
Ranasinghe S, McManus DP (2013) Structure and function of invertebrate Kunitz serine protease inhibitors. Dev Com Immuno 39:219–227
Ranasinghe SL, Fischer K, Gobert GN et al (2015a) Functional expression of a novel Kunitz type protease inhibitor from the human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Parasites Vectors 8:408
Ranasinghe SL, Fischer K, Gobert GN, McManus DP (2015b) A novel coagulation inhibitor from Schistosoma japonicum. Parasitology 142(14):1663–1672
Rawlings ND, Tolle DP, Barrett AJ (2004a) Evolutionary families of peptidase inhibitors. Biochem J 378:705–716
Rawlings ND, Tolle DP, Barrett AJ (2004b) MEROPS: the peptidase database. Nucleic acids Res 32:160–164
Robertson B, Owen D, Stow J, Butler C, Newland C (1996) Novel effects of dendrotoxin homologues on subtypes of mammalian Kv1 potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett 383:26–30
Robinson MW, Menon R, Donnelly SM, Dalton JP, Ranganathan S (2009) An integrated transcriptomics and proteomics analysis of the secretome of the helminth pathogen Fasciola hepatica proteins associated with invasion and infection of the mammalian host. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:1891–1907
Sabotič J, Kos J (2012) Microbial and fungal protease inhibitors—current and potential applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1351–1375
Salier JP (1990) Inter-α-trypsin inhibitor: emergence of a family within the Kunitz-type protease inhibitor superfamily. Trends in Biochem Sci 15:435–439
Salier JP, Rouet P, Raguenez G, Daveau M (1996) The inter-α-inhibitor family: from structure to regulation. Biochem J 315:1–9
Schwarz A, Cabezas-Cruz A, Kopecky J, Valdes JJ (2014) Understanding the evolutionary structural variability and target specificity of tick salivary Kunitz peptides using next generation transcriptome data. BMC Evol Biol 14:4
Sheffield WP, Eltringham-Smith LJ, Bhakta V (2018) Fusion to human serum albumin extends the circulatory half-life and duration of antithrombotic action of the kunitz protease inhibitor domain of protease nexin 2. Cell Physiol Biochem 45(2):772–782
Shigetomi H, Onogi A, Kajiwara H et al (2010) Anti-inflammatory actions of serine protease inhibitors containing the Kunitz domain. Inflamm Res 59(9):679–687
Simeon R, Chen Z (2018) Invitro-engineered non-antibody protein therapeutics. Protein Cell 9(1):3–14
Smith D, Tikhonova IG, Jewhurst HL, Drysdale OC et al (2016) Unexpected activity of a novel Kunitz-type inhibitor: inhibition of cysteine proteases but not serine proteases. J Biol Chem 291(37):19220–19234
Strydom DJ (1973) Protease inhibitors as snake venom toxins. Nat New Biol 243:88–89
Strydom DJ (1977) Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequence of toxin Vi2, a homologue of pancreatic trypsin inhibitor, from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta 491:361–369
Thakur R, Mukherjee AK (2017) Pathophysiological significance and therapeutic applications of snake venom protease inhibitors. Toxicon 131:37–47
Vincent JP, Lazdunski M (1973) The interaction between alpha-chymotrypsin and pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz inhibitor). Kinetic and thermodynamic properties. Eur J Biochem 38:365–372
Walsh JB, Stephan W (2001) Multigene families: evolution. Encycl Life Sci 1–6:673
Wan H, Lee KS, Kim BY, Zou FM, Yoon HJ et al (2013a) A spider-derived kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor that acts as a plasmin inhibitor and an elastase inhibitor. PLoS ONE 8(1):e53343
Wan H, Lee KS, Kim BY, Zou FM et al (2013b) A spider-derived Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor that acts as a plasmin inhibitor and an elastase inhibitor. PLoS ONE 8(1):e53343
Wang FC, Bell N, Reid P, Smith LA et al (1999) Identification of residues in dendrotoxin K responsible for its discrimination between neuronal K+ channels containing Kv1.1 and 1.2a subunit. Eur J Biochem 263:222–229
Williams A, Baird LG (2003) DX-88 and HAE: a developmental perspective. Transfus Apher Sci 29(3):255–258
Wulff H, Castle NA, Pardo LA (2009) Voltage-gated potassium channels as therapeutic tragets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(12):982–1001
Yuan CH, He QY, Peng K, Diao JB, Tang X et al (2008) Discovery of a distinct superfamily of Kunitz-type toxin (KTT) from tarantulas. PLoS ONE 3:e3414
Zhao R, Dai H, Qiu S, Li T, He Y et al (2011) SdPI, the first functionally characterized Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitor from scorpion venom. PLoS ONE 6:27548
Zhuo L, Hascall VC, Kimata K (2004) Inter-α-trypsin inhibitor, a covalent protein-glycosaminoglycan-protein complex. J Biol Chem 279(37):38079–38082
Župunski V, Kordiš D (2016) Strong and widespread action of site-specific positive selection in the snake venom Kunitz/BPTI protein family. Sci Rep 6:37054
Zupunski V, Kordis D, Gubensek F (2003) Adaptive evolution in the snake venom Kunitz/BPTI protein family. FEBS Lett 547:131–136
Zweckstetter M, Czisch M, Mayer U et al (1996) Structure and multiple conformations of the Kunitz-type domain from human type VI collagen α3(VI) chain in solution. Structure 4:195–209
Acknowledgements
MM is a recipient of DST-INSPIRE Faculty fellowship award from Department of Science & Technology (DST) and Indo-Australian Career Boosting Gold Fellowship (IACBGF) from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, New Delhi. Support from Shiv Nadar University and mentorship of Dr. Shailja Singh is sincerely acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Erich Bornberg-Bauer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, M. Evolutionary Aspects of the Structural Convergence and Functional Diversification of Kunitz-Domain Inhibitors. J Mol Evol 88, 537–548 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-020-09959-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-020-09959-9