Abstract
Although some α-glucosidases from the α-amylase family (glycoside hydrolase family GH13) have been studied extensively, their exact number, organization on the chromosome, and orthology/paralogy relationship were unknown. This was true even for important disease vectors where gut α-glucosidase is known to be receptor for the Bin toxin used to control the population of some mosquito species. In some cases orthologs from related species were studied intensively, while potentially important paralogs were omitted. We have, therefore, used a bioinformatics approach to identify all family GH13 α-glucosidases from the selected species from Metazoa (including three mosquito species: Aedes aegypti, Anopheles gambiae, and Culex quinquefasciatus) as well as from Fungi in an effort to characterize their arrangement on the chromosome and evolutionary relationships among orthologs and among paralogs. We also searched for pseudogenes and genes coding for enzymatically inactive proteins with a possible new function. We have found GH13 α-glucosidases mostly in Arthropoda and Fungi where they form gene families, as a result of multiple lineage-specific gene duplications. In mosquito species we have identified 14 α-glucosidase (Aglu) genes of which only five have been biochemically characterized so far, two are putative pseudogenes and the rest remains uncharacterized. We also revealed quite a complex evolutionary history of the eukaryotic α-glucosidases probably involving multiple losses of genes or horizontal gene transfer from bacteria.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSR:
-
Conserved sequence region
- GH:
-
Glycoside hydrolase
- GPI:
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- MP:
-
Maximum parsimony
- MY:
-
Million years
- MYA:
-
Million years ago
- NJ:
-
Neighbor-joining
References
Abascal F, Zardoya R, Posada D (2005) ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 21:2104–2105
Alam MS, Nakashima S, Deyashiki Y, Banno Y, Hara A, Nozawa Y (1996) Molecular cloning of a gene encoding acid alpha-glucosidase from Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Eukaryot Microbiol 43:295–303
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Ashford DA, Smith WA, Douglas AE (2000) Living on a high sugar diet: the fate of sucrose ingested by a phloem-feeding insect, the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. J Insect Physiol 46:335–341
Barnett JA (1976) The utilization of sugars by yeasts. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 32:125–234
Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Clark K, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW (2012) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 40(Database issue):D48–D53
Birney E, Clamp M, Durbin R (2004) Genewise and genomewise. Genome Res 14:988–995
Broer S, Wagner CA (2002) Structure-function relationships of heterodimeric amino acid transporters. Cell Biophys 36:155–168
Brosius J (1999) RNAs from all categories generate retrosequences that may be exapted as novel genes or regulatory elements. Gene 238:115–134
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37(Database issue):D233–D238
Charron MJ, Dubin RA, Michels CA (1986) Structural and functional analysis of the MAL1 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 6:3891–3899
Chillaron J, Roca R, Valencia A, Zorzano A, Palacin M (2001) Heteromeric amino acid transporters: biochemistry, genetics, and physiology. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:995–1018
Chintapalli VR, Wang J, Dow JAT (2007) Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat Genet 39:715–720
Cohen JD, Goldenthal MJ, Buchferer B, Marmur J (1984) Mutational analysis of the MAL1 locus of Saccharomyces: identification and functional characterization of three genes. Mol Gen Genet 196:208–216
Cristofoletti PT, Ribeiro AF, Deraison C, Rahbé Y, Terra WR (2003) Midgut adaptation and digestive enzyme distribution in a phloem feeding insect, the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. J Insect Physiol 49:11–24
Da Lage JL, Renard E, Chartois F, Lemeunier F, Cariou ML (1998) Amyrel, a paralogous gene of the amylase gene family in Drosophila melanogaster and the Sophophora subgenus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6848–6853
Da Lage JL, Maczkowiak F, Cariou ML (2000) Molecular characterization and evolution of the amylase multigene family of Drosophila ananassae. J Mol Evol 51:391–403
Da Lage JL, Feller G, Janecek S (2004) Horizontal gene transfer from Eukarya to bacteria and domain shuffling: the alpha-amylase model. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:97–109
Da Lage JL, Danchin EG, Casane D (2007) Where do animal α-amylases come from? An interkingdom trip. FEBS Lett 581:3927–3935
Darboux I, Nielsen-LeRoux C, Charles JF, Pauron D (2001) The receptor of Bacillus sphaericus binary toxin in Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) midgut: molecular cloning and expression. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:981–990
Dennis JA, Moran C, Healy PJ (2000) The bovine alpha-glucosidase gene: coding region, genomic structure, and mutations that cause bovine generalized glycogenosis. Mammalian Genome 11:206–212
Dillon RJ, El Kordy E (1997) Carbohydrate digestion in sandflies: α-glucosidase activity in the midgut of Phlebotomus langeroni. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 116:35–40
Downing N (1978) Measurements of the osmotic concentrations of stylet sap, haemolymph and honeydew from an aphid under osmotic stress. J Exp Biol 77:247–250
Durand A, Hughes R, Roussel A, Flatman R, Henrissat B, Juge N (2005) Emergence of a subfamily of xylanase inhibitors within glycoside hydrolase family 18. FEBS J 272:1745–1755
Eck RV, Dayhoff MO (1966) Atlas of protein sequence and structure. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Silver Springs
Eliason DA (1963) Feeding adult mosquitoes in solid sugars. Nature 200:289
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Ferreira LM, Romão TP, de Melo-Neto OP, Silva-Filha MH (2010) The orthologue to the Cpm1/Cqm1 receptor in Aedes aegypti is expressed as a midgut GPI-anchored α-glucosidase, which does not bind to the insecticidal binary toxin. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40:604–610
Fisher DB, Wright JP, Mittler TE (1984) Osmoregulation by the aphid Myzus persicae: a physiological role for honeydew oligosaccharides. J Insect Physiol 30:387–393
Foley DH, Bryan JH, Yeates D, Saul A (1998) Evolution and systematics of Anopheles: insights from a molecular phylogeny of Australasian mosquitoes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 9:262–275
Gabrisko M, Janecek S (2009) Looking for the ancestry of the heavy-chain subunits of heteromeric amino acid transporters rBAT and 4F2hc within the GH13 α-amylase family. FEBS J 276:7265–7278
Gabrisko M, Janecek S (2011) Characterization of maltase clusters in the genus Drosophila. J Mol Evol 72:104–118
Gaunt MW, Miles MA (2002) An insect molecular clock dates the origin of the insects and accords with palaeontological and biogeographic landmarks. Mol Biol Evol 19:748–761
Geber A, Williamson PR, Rex JH, Sweeney EC, Bennett JE (1992) Cloning and characterization of a Candida albicans maltase gene involved in sucrose utilization. J Bacteriol 174:6992–6996
Gomez SM, Eiglmeier K, Segurens B, Dehoux P, Couloux A, Scarpelli C, Wincker P, Weissenbach J, Brey PT, Roth CW (2005) Pilot Anopheles gambiae full-length cDNA study: sequencing and initial characterization of 35,575 clones. Genome Biol 6:R39
Graveley BR, Brooks A, Carlson JW et al (2011) The developmental transcriptome of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 471:473–479
Grimaldi D, Engel MS (2005) Evolution of the insects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Han EK, Cotty F, Sottas C, Jiang H, Michels CA (1995) Characterization of AGT1 encoding a general α-glucoside transporter from Saccharomyces. Mol Microbiol 17:1093–1107
Hehre EJ, Hamilton DM, Carlson AS (1949) Synthesis of a polysaccharide of the starch-glycogen class from sucrose by a cell-free, bacterial enzyme system (amylosucrase). J Biol Chem 177:267–279
Henikoff S, Wallace JC (1988) Detection of protein similarities using nucleotide sequence databases. Nucleic Acids Res 16:6191–6204
Hennig M, Pfeffer-Hennig S, Dauter Z, Wilson KS, Schlesier B, Nong VH (1995) Crystal structure of narbonin at 1.8 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 51:177–189
Hennig M, Jansonius JN, Terwisscha van Scheltinga AC, Dijkstra BW, Schlesier B (1996) Crystal structure of concanavalin B at 1.65 Å resolution. An “inactivated” chitinase from seeds of Canavalia ensiformis. J Mol Biol 254:237–246
Hermans MM, Kroos MA, van Beeumen J, Oostra BA, Reuser AJ (1991) Human lysosomal alpha-glucosidase. Characterization of the catalytic site. J Biol Chem 266:13507–13512
Hoefsloot LH, Hoogeveen-Westerveld M, Reuser AJ, Oostra BA (1991) Characterization of the human lysosomal alpha-glucosidase gene. Biochem J 272:493–497
Honeybee Genome Sequencing Consortium (2006) Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nature 443:931–949
Huber RE, Thompson DJ (1973) Studies on a honey bee sucrase exhibiting unusual kinetics and transglucolytic activity. Biochemistry 12:4011–4020
James AA, Blackmer K, Racioppi JV (1989) A salivary gland-specific, maltase-like gene of the vector mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Gene 75:73–83
Janecek S (1995) Close evolutionary relatedness among functionally distantly related members of the (α/β)8-barrel glycosyl hydrolases suggested by the similarity of their fifth conserved sequence region. FEBS Lett 377:6–8
Janecek S (2002) How many conserved sequence regions are there in the α-amylase family? Biologia 57(Suppl. 11):29–41
Janecek S, Blesak K (2011) Sequence-structural features and evolutionary relationships of family GH57 α-amylases and their putative α-amylase-like homologues. Protein J 30:429–435
Janecek S, Svensson B, Henrissat B (1997) Domain evolution in the α-amylase family. J Mol Evol 45:322–331
Janecek S, Svensson B, MacGregor EA (2007) A remote but significant sequence homology between glycoside hydrolase clan GH-H and family GH31. FEBS Lett 581:1261–1268
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem Sci 23:403–405
Jeffs PS, Holmes EC, Ashburner M (1994) The molecular evolution of the alcohol dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase-related genes in the Drosophila melanogaster species subgroup. Mol Biol Evol 11:287–304
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Jones DC, Mehlert A, Güther ML, Ferguson MA (2005) Deletion of the glucosidase II gene in Trypanosoma brucei reveals novel N-glycosylation mechanisms in the biosynthesis of variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem 280:35929–35942
Juge N, Payan F, Williamson G (2004) XIP-I, a xylanase inhibitor protein from wheat: a novel protein function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1696:203–211
Kalume DE, Okulate M, Zhong J, Reddy R, Suresh S, Deshpande N, Kumar N, Pandey A (2005) A proteomic analysis of salivary glands of female Anopheles gambiae mosquito. Proteomics 5:3765–3777
Kimura A, Takewaki S, Matsui H, Kubota M, Chiba S (1990) Allosteric properties, substrate specificity, and subsite affinities of honeybee α-glucosidase I. J Biochem 107:762–768
Krzywinski J, Grushko OG, Besansky NJ (2006) Analysis of the complete mitochondrial DNA from Anopheles funestus: an improved dipteran mitochondrial genome annotation and a temporal dimension of mosquito evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:417–423
Kubota M, Tsuji M, Nishimoto M et al (2004) Localization of α-glucosidases I, II and III in organs of European honeybee, Apis mellifera L., and origin of α-glucosidase in honey. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:2346–2352
Kunita R, Nakabayashi O, Wu JY, Hagiwara Y, Mizutani M, Pennybacker M, Chen YT, Kikuchi T (1997) Molecular cloning of acid alpha-glucosidase cDNA of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) and the lack of its mRNA in acid maltase deficient quails. Biochim Biophys Acta 1362:269–278
Kuriki T, Imanaka T (1999) The concept of the α-amylase family: structural similarity and common catalytic mechanism. J Biosci Bioeng 87:557–565
Lawson D, Arensburger P, Atkinson P et al (2009) VectorBase: a data resource for invertebrate vector genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D583–D587
Lodge JA, Maier T, Liebl W, Hoffmann V, Sträter N (2003) Crystal structure of Thermotoga maritima α-glucosidase AglA defines a new clan of NAD+-dependent glycosidases. J Biol Chem 278:19151–19158
Long M, Wang W, Zhang J (1999) Origin of new genes and source for N-terminal domain of the chimerical gene, **g-wei, in Drosophila. Gene 238:135–141
MacGregor EA, Janecek S, Svensson B (2001) Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the α-amylase family of enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1546:1–20
Maczkowiak F, Da Lage JL (2006) Origin and evolution of the Amyrel gene in the α-amylase multigene family of Diptera. Genetica 128:145–158
Marinotti O, James AA (1990) An α-glucosidase in the salivary glands of the vector mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem 20:619–623
Marinotti O, de Brito M, Moreira CK (1996) Apyrase and α-glucosidase in the salivary glands of Aedes albopictus. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 113:675–679
Martiniuk F, Ellenbogen A, Hirschhorn R (1985) Identity of neutral alpha-glucosidase AB and the glycoprotein processing enzyme glucosidase II. Biochemical and genetic studies. J Biol Chem 260:1238–1242
Matsui H, Iwanami S, Ito H, Mori H, Honma M, Chiba S (1997) Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding alpha-glucosidase from sugar beet. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:875–880
Matsuura Y, Kusunoki M, Harada W, Kakudo M (1984) Structure and possible catalytic residues of Taka-amylase A. J Biochem 95:697–702
McQuilton P, St Pierre SE, Thurmond J, FlyBase Consortium (2012) FlyBase 101—the basics of navigating FlyBase. Nucleic Acids Res 40(Database issue):D706–D714
Munoz-Torres MC, Reese JT, Childers CP, Bennett AK, Sundaram JP, Childs KL, Anzola JM, Milshina N, Elsik CG (2011) Hymenoptera Genome Database: integrated community resources for insect species of the order Hymenoptera. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Database issue):D658–D662
Mury FB, da Silva JR, Ferreira LS et al (2009) α-Glucosidase promotes hemozoin formation in a blood-sucking bug: an evolutionary history. PLoS One 4:e6966
Nei M, Rooney AP (2005) Concerted and birth-and-death evolution of multigene families. Annu Rev Genet 39:121–152
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7799–7806
Nishimoto M, Kubota M, Tsuji M, Mori H, Kimura A, Matsui H, Chiba S (2001) Purification and substrate specificity of honeybee, Apis mellifera L., α-glucosidase III. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:1610–1616
Nishimoto M, Mori H, Moteki T et al (2007) Molecular cloning of cDNAs and genes for three α-glucosidases from European honeybees, Apis mellifera L., and heterologous production of recombinant enzymes in Pichia pastoris. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1703–1716
Novak S, Zechner-Krpan V, Marie V (2004) Regulation of maltose transport and metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Technol Biotechnol 42:213–218
Opota O, Charles JF, Warot S, Pauron D, Darboux I (2008) Identification and characterization of the receptor for the Bacillus sphaericus binary toxin in the malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 149:419–427
Oslancova A, Janecek S (2002) Oligo-1,6-glucosidase and neopullulanase enzyme subfamilies from the α-amylase family defined by the fifth conserved sequence region. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:1945–1959
Payan F, Flatman R, Porciero S, Williamson G, Juge N, Roussel A (2003) Structural analysis of xylanase inhibitor protein I (XIP-I), a proteinaceous xylanase inhibitor from wheat (Triticum aestivum, var. Soisson). Biochem J 372:399–405
Payan F, Leone P, Porciero S et al (2004) The dual nature of the wheat xylanase protein inhibitor XIP-I: structural basis for the inhibition of family 10 and family 11 xylanases. J. Biol. Chem 279:36029–36037
Price DR, Karley AJ, Ashford DA, Isaacs HV, Pownall ME, Wilkinson HS, Gatehouse JA, Douglas AE (2007) Molecular characterisation of a candidate gut sucrase in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:307–317
Rhodes JD, Croghan PC, Dixon AFG (1997) Dietary sucrose and oligosaccharide synthesis in relation to osmoregulation in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Physiol Entomol 22:373–379
Rigden DJ (2002) Iterative database searches demonstrate that glycoside hydrolase families 27, 31, 36 and 66 share a common evolutionary origin with family 13. FEBS Lett 523:17–22
Romão TP, de Melo Chalegre KD, Key S, Ayres CF, Fontes de Oliveira CM, de Melo-Neto OP, Silva-Filha MH (2006) A second independent resistance mechanism to Bacillus sphaericus binary toxin targets its α-glucosidase receptor in Culex quinquefasciatus. FEBS J 273:1556–1568
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Savard J, Tautz D, Richards S, Weinstock GM, Gibbs RA, Werren JH, Tettelin H, Lercher MJ (2006) Phylogenomic analysis reveals bees and wasps (Hymenoptera) at the base of the radiation of Holometabolous insects. Genome Res 16:1334–1338
Sikora J, Urinovská J, Majer F, Poupetová H, Hlavatá J, Kostrouchová M, Ledvinová J, Hrebícek M (2010) Bioinformatic and biochemical studies point to AAGR-1 as the ortholog of human acid alpha-glucosidase in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biochem 341:51–63
Silva-Filha MH, Nielsen-LeRoux C, Charles JF (1999) Identification of the receptor for Bacillus sphaericus crystal toxin in the brush border membrane of the mosquito Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 29:711–721
Skov LK, Mirza O, Henriksen A, De Montalk GP, Remaud-Simeon M, Sarçabal P, Willemot RM, Monsan P, Gajhede M (2001) Amylosucrase, a glucan-synthesizing enzyme from the alpha-amylase family. J Biol Chem 276:25273–25278
Snyder M, Davidson N (1983) Two gene families clustered in a small region of the Drosophila genome. J Mol Biol 166:101–118
Souza-Neto JA, Machado FP, Lima JB, Valle D, Ribolla PE (2007) Sugar digestion in mosquitoes: identification and characterization of three midgut α-glucosidases of the neo-tropical malaria vector Anopheles aquasalis (Diptera: Culicidae). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 147:993–1000
Stam MR, Danchin EG, Rancurel C, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2006) Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: towards improved functional annotations of α-amylase-related proteins. Protein Eng Des Sel 19:555–562
Takewaki S, Chiba S, Kimura A, Matsui H, Koike Y (1980) Purification and properties of α-glucosidases of the honey bee Apis mellifera L. Agric Biol Chem 44:731–740
Takewaki S, Kimura A, Kubota M, Chiba S (1993) Substrate specificity and subsite affinities of honeybee α-glucosidase II. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:1508–1513
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Teste MA, François JM, Parrou JL (2010) Characterization of a new multigene family encoding isomaltases in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the IMA family. J Biol Chem 285:26815–26824
Tibbot BK, Skadsen RW (1996) Molecular cloning and characterization of a gibberellin-inducible, putative alpha-glucosidase gene from barley. Plant Mol Biol 30:229–241
Van der Kaaij RM, Janecek S, van der Maarel MJ, Dijkhuizen L (2007) Phylogenetic and biochemical characterization of a novel cluster of intracellular fungal alpha-amylase enzymes. Microbiology 153:4003–4015
Vanin EF (1985) Processed pseudogenes: characteristics and evolution. Annu Rev Genet 19:253–272
Vieira CP, Vieira J, Hartl DL (1997) The evolution of small gene clusters: evidence for an independent origin of the maltase gene cluster in Drosophila virilis and Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 14:985–993
Viigand K, Tammus K, Alamäe T (2005) Clustering of MAL genes in Hansenula polymorpha: cloning of the maltose permease gene and expression from the divergent intergenic region between the maltose permease and maltase genes. FEMS Yeast Res 5:1019–1028
Vongsangnak W, Salazar M, Hansen K, Nielsen J (2009) Genome-wide analysis of maltose utilization and regulation in aspergilli. Microbiology 155:3893–3902
Walters FS, Mullin CA (1988) Sucrose-dependent increase in the oligosaccharide production and associated glycosidase activities in the potato aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae (Thomas). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 9:35–46
Wells RG, Hediger MA (1992) Cloning of a rat kidney cDNA that stimulates dibasic and neutral amino acid transport and has sequence similarity to glucosidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5596–5600
Wilkinson TL, Ashford DA, Pritchard J, Douglas AE (1997) Honeydew sugars and osmoregulation in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. J Exp Biol 200:2137–2143
Winge O, Roberts C (1950) Identification of the gene for maltose fermentation in Saccharomyces italicus. Nature 166:1114
Yamamoto K, Nakayama A, Yamamoto Y, Tabata S (2004) Val216 decides the substrate specificity of α-glucosidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 271:3414–3420
Yuan XL, van der Kaaij RM, van den Hondel C, Punt PJ, van der Maarel M, Dijkhuizen L, Ram AFJ (2008) Aspergillus niger genome-wide analysis reveals a large number of novel α-glucan acting enzymes with unexpected expression profiles. Mol Genet Genomics 279:545–561
Zhang Z, Inomata N, Yamazaki T, Kishino H (2003) Evolutionary history and mode of the amylase multigene family in Drosophila. J Mol Evol 57:702–709
Zheng L, Whang LH, Kumar V, Kafatos FC (1995) Two genes encoding midgut-specific maltase-like polypeptides from Anopheles gambiae. Exp Parasitol 81:272–283
Zona R, Chang-Pi-Hin F, O’Donohue MJ, Janecek S (2004) Bioinformatics of the glycoside hydrolase family 57 and identification of catalytic residues in amylopullulanase from Thermococcus hydrothermalis. Eur J Biochem 271:2863–2872
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Dr. Stefan Janecek, my supervisor, for all his support and encouragement. This work was supported by the Grant No. 2/0148/11 from the Slovak Grant Agency VEGA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
239_2013_9545_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
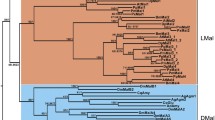
Fig. S1 Phylogenetic trees of α-glucosidases and related proteins from the α-amylase family (pdf file)Supplementary material 2 (PDF 398 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabriško, M. Evolutionary History of Eukaryotic α-Glucosidases from the α-Amylase Family. J Mol Evol 76, 129–145 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-013-9545-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-013-9545-4