Abstract
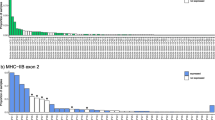
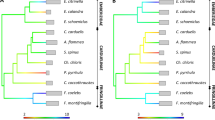
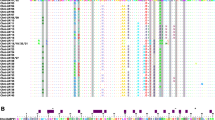
During the last decade, the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) has received much attention in the fields of evolutionary and conservation biology because of its potential implications in many biological processes. New insights into the gene structure and evolution of MHC genes can be gained through study of additional lineages of birds not yet investigated at the genomic level. In this study, we characterized MHC class II B genes in five families of birds of prey (Accipitridae, Pandionidae, Strigidae, Tytonidae, and Falconidae). Using PCR approaches, we isolated genomic MHC sequences up to 1300 bp spanning exons 1 to 3 in 26 representatives of each raptor lineage, finding no stop codons or frameshift mutations in any coding region. A survey of diversity across the entirety of exon 2 in the lesser kestrel Falco naumanni reported 26 alleles in 21 individuals. Bayesian analysis revealed 21 positively selected amino acid sites, which suggests that the MHC genes described here are functional and probably expressed. Finally, through interlocus comparisons and phylogenetic analysis, we also discuss genetic evidence for concerted and transspecies evolution in the raptor MHC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernatchez L, Landry C (2003) MHC studies in nonmodel vertebrates: what have we learned about natural selection in 15 years? J Evol Biol 16:363–377
Bonneaud C, Sorci G, Morin V, Westerdahl H, Zoorob R, Wittzell H (2004) Diversity of Mhc class I and IIB genes in house sparrows (Passer domesticus). Immunogenetics 55:855–865
Bos DH, DeWoody JA (2005) Molecular characterization of major histocompatibility complex class II alleles in wild tiger salamanders (Ambystoma tigrinum). Immunogenetics 57:775–781
Bourlet Y, Behar G, Guillemot F, Frechin N, Billault A, Chausse A-M, Zoorob R, Auffrey C (1988) Isolation of major histocompatibility complex class II (B-L) b chain sequences: comparison with mammalian a chains and expression in lymphoid organs. EMBO J 7:1031
Bradley RD, Hillis DM (1996) Recombinant DNA sequences generated by PCR amplification. Mol Biol Evol 14:592–593
Brooke M, Birkhead M (1991) The Cambridge encyclopedia of ornithology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Brown JH, Jardetzky TS, Gorga JC, Stern LJ, Urban RG, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1993) Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature 364:33–39
Brown JL, Eklund A (1994) Kin recognition and the major histocompatibility complex: An integrative review. Am Nat 143:435–461
Consuegra S, Megens HJ, Leon K, Stet RJM, Jordan WC (2005) Patterns of variability at the major histocompatibility class II alpha locus in Atlantic salmon contrast with those at the class I locus. Immunogenetics 57:16–24
Drouin G, Prat F, Ell M, Clarke GDP (1999) Detecting and characterizing gene conversion events in multigene family members. Mol Biol Evol 16:1369–1390
Edwards SV, Wakeland EK, Potts WK (1995a) Contrasting histories of avian and mammalian Mhc genes revealed by class II B sequences from songbirds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 12200–12204
Edwards SV, Grahn M, Potts WK (1995b) Dynamics of Mhc evolution in birds and crocodilians: amplification of class II genes with degenerate primers. Mol Ecol 4: 719–729
Edwards SV, Potts WK (1996) Polymorphism of genes in the major histocompatiblility complex: implications for conservation genetics of vertebrates. In: Smith TB, Wayne RK (eds) Molecular genetic approaches in conservation. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 214–237
Edwards SV, Chesnut K, Satta Y, Wakeland EK (1997) Ancestral polymorphism of MHC class II genes in mice: implications for balancing selection and the mammalian molecular clock. Genetics 146:655–668
Edwards SV, Gasper J, Stone M (1998) Genomics and polymorphism of Agph-DAB1, an Mhc class II B gene in red-winged blackbirds (Agelaius phoenicus). Mol Biol Evol 15:236–250
Edwards SV, Hess CM, Gaspar J, Garrigan D (1999) Toward and evolutionary genomics of the avian MHC. Immunol Rev 167:119–132
Edwards SV, Nusser J, Gasper J (2000) Characterization and evolution of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes in non-model organisms, with examples from birds. In: Baker AJ (ed) Molecular methods in ecology. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 168–207
Ekblom R, Grahn M, Höglund J (2003) Patterns of polymorphism in the MHC class II of a non-passerine bird, the great snipe (Gallinago media). Immunogenetics 54:734–741
Gasper JS, Shiina T, Inoko H, Edwards SV (2001) Songbird genomics: Analysis of 45 kb upstream of a polymorphic MHC class II gene in red-winged blackbirds (Agelaius phoeniceus). Genomics 75:26–34
Grimholt U, Larsen S, Nordmo R, et al. (2003) MHC polymorphism and disease resistance in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): facing pathogens with single expressed major histocompatibility class I and class II loci. Immunogenetics 55:210–219
Gemmell NJ, Akiyama S (1996) An efficient method for the extraction of DNA from vertebrate tissues. Trends Genet 12:338–339
Guillemot F, Kaufman JF, Skjoedt K, Auffray C (1989) The major histocompatibility complex in the chicken. Trends Genet 5:300–304
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hedrick PW (1999) Balancing selection and MHC. Genetica 104:207–214
Hedrick PW (2001) Conservation genetics: where are we now? Tree 16:629–636
Hess CM, Gasper J, Hoekstra HE, Hill CE, Edwards SV (2000) MHC class II pseudogene and genomic signature of a 32-kb cosmid in the house finch (Carpodacus mexicanus). Genome Res 10:613–623
Hess CM, Edwards SV (2002) The evolution of major histocompatibility genes in birds. Bioscience 52:423–431
Hunt HD, Goto RM, Foster DN, Bacon LD, Miller MM (2006) At least one YMHCI molecule in the chicken is alloimmunogenic and dynamically expressed on spleen cells during development. Immunogenetics 58:297–307
Huson H, Bryant D (2006) Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol Biol Evol 23:254–267
Jarvi SI, Tarr CL, McIntosh CE, Atkinson CT, Fleischer RC (2004) Natural selection of the major histocompatibility complex (Mhc) in Hawaiian honeycreepers (Drepanidinae). Mol Ecol 13:2157–2168
Kaufman J, Salomonsen J (1997) The “minimal essential MHC” revisited: Both peptide-binding and cell surface expression level of MHC molecules are polymorphisms selected by pathogens in chickens. Hereditas 127:67–73
Kaufman J, Milne S, Göbel T, Walker BA, Jacob JP, Auffrey C, Zoorob R, Beck S (1999) The chicken B locus is a minimal-essential major histocompatibility complex. Nature 401:923–925
Kaufman J (2000) The simple chicken major histocompatibility complex: life and death in the face of pathogens and vaccines. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Biol Sci 355:1077–1084
Klein J (1987) Origin of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism – the transspecies hypothesis. Human Immunol 19:155–162
Klein J (1986) Natural history of the major histocompatibility complex. Wiley, New York
Klein J, Bontrop RE, Dawkins RL, Erlich HA, Gyllensten UB, Heise ER, Jones PP, Parham P, Wakeland EK, Watkins DI (1990) Nomenclature for the major histocompatibility complexes of different species: a proposal. Immunogenetics 31:217–219
Knapp LA, Ha JC, Sackett GP (1996) Parental MHC antigen sharing and pregnancy wastage in captive pigtailed macaques. J Reprod Immunol 32:73–78
Martinshon JT, Sousa AB, Guethlein LA, Howard JC (1999) The gene conversion hypothesis of MHC evolution: A review. Immunogenetics 50:168–200
Meyerhans A, Vartanian JP, Wain-Hobson S (1990) DNA recombination during PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 18:1687–1690
Miller MM, Shiina T, Goto R, Inoko H (2003) Rfp-Y, the second cluster of MHC loci in the chicken, contains large families of distinctive NK lectin-like and class Ib loci. Faseb J 17:C161–C161
Miller HC, Lambert DM (2004) Gene duplication and gene conversion in class II MHC genes of New Zealand robins (Petroicidae). Immunogenetics 56:178–191
Miller HC, Belov K, Daugherty CH (2005) Characterisation of MHC class II genes from an ancient reptile lineage, Sphenodon (tuatara). Immunogenetics 57:883–891
Musolf K, Meyer-Lucht Y, Sommer S (2004) Evolution of MHC-DRB class II polymorphism in the genus Apodemus and a comparison of DRB sequences within the family Muridae (Mammalia: Rodentia). Immunogenetics 56:420–426
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7799–7806
Nielsen R, Yang A (1998) Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics 148:929–936
Otting N, de Groot NG, Doxiadis GG, Bontrop RE (2002) Extensive Mhc-DQB variation in humans and non-human primate species. Immunogenetics 54:230–239
Piertney SB, Oliver MK (2006) The evolutionary ecology of the major histocompatibility complex. Heredity 96:7–21
Richardson D, Westerdahl H (2003) A comparison of MHC diversity in two Acrocephalus species: the outbred great reed warbler and the inbred Seyshelles warbler. Mol Ecol 12:3523–3529
Richman A, Herrera LG, Nash D, Schierup MH (2003) Relative roles of mutation and recombination in generating allelic polymorphism at MHC class II locus in Peromyscus maniculatus. Genet Res 82:89–99
Robinson J, Malik A, Parham P, Bodme JG, Marsh SGE (2000) IMGT/HLA database — A sequence database for the human major histocompatibility complex. Tissue Antigens 55:280–287
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19:2496–2497
Sato A, Figueroa F, Mayer WE, Grant PR, Grant BR, Klein J (2000) Mhc class II genes of Darwin’s Finches: divergence by point mutations and reciprocal recombination. In: Kasahara M (ed) Major histocompatibility complex: evolution, structure and function. Springer, Berlin
Sawyer SA (1999) GENECONV: a computer package for the statistical detection of gene conversion. Distributed by the author, Department of Mathematics, Washington University in St. Louis. http://www.math.wustl.edu/∼sawyer
Schaschl H, Wandeler P, Suchentrunk F, Obexer-Ruff G, Goodman SJ (2006) Selection and recombination drive the evolution of MHC class II DRB diversity in ungulates. Heredity 97:427–437
Shi Y, **ao-bing W, Peng Y, Bi-hui C (2004) Cloning and sequences analysis of the second exon of MHC class II B genes in Chinese alligator, Alligator sinensis. Zool Res 25:415–421
Singh PB, Brown RE, Roser B (1987) MHC antigens in urine as olfactory recognition cues. Nature 327:161–164
Sommer S (2005) The importance of immune gene variability in evolutionary ecology and evolution. Front Zool 2:16
Tregenza T, Wedell N (2000) Genetic compatibility, mate choice and patterns of parentage: Invited review. Mol Ecol 9:1013–1027
Trowsdale J (1995) ‘Both bird and man and beast’: comparative organization of MHC genes. Immunogenetics 41:1–17
Tsuda TT, Tsuda M, Naruse T, Kawata H, Ando A, Shiina T, Fukuda M, Kurita M, LeMaho I, Kulski JK, Inoko H (2001) Phylogenetic analysis of penguin (Spheniscidae) species based on sequence variation in MHC class II genes. Immunogenetics 53:712–716
Wagner A, Blackstone N, Cartwright P, Dick M, Misof B, Snow P, Wagner G, Bartels J, Murtha M, Pendleton J (1994) Surveys of gene families using polymerase chain reaction: PCR selection and PCR drift. Syst Biol 43:250–261
Wegner KM, Kalbe M, Rauch G, Kurtz J, Schaschl H, Reusch TBH (2006) Genetic variation in MHC class II expression and interactions with MHC sequence polymporphism in three-spined sticklebacks. Mol Ecol 15:1153–1164
Westerdahl H, Wittzell H, von Schantz T (1999) Polymorphism and transcription of Mhc class I genes in a passerine bird, the great reed warbler. Immunogenetics 49:158–170
Westerdahl H, Waldenstrom J, Hansson B, Hasselquist D, von Schantz T, Bensch S (2005) Associations between malaria and MHC genes in a migratory songbird. Proc Biol Sci 272:1511–1518
Wittzell H, Bernot A, Auffrey C, Zoorob R (1999a) Concerted evolution of two Mhc class II B loci in pheasants and domestic chickens. Mol Biol Evol 16:479–490
Wittzell H, Madsen T, Westerdahl H, Shine R, von Schantz T (1999b) MHC variation in birds and reptiles. Genetica 104:301–309
Yang Z (2000) Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood (PAML), version 3.0. University College, London
Ye X, Zhu J, Velleman SG, Bacon WL, Nestor KE (1999) Analysis of genetic polymorphism in the major histocompatibility complex of Japanese quail. Poult Sci 78:8–14
Zelano B, Edwards SV (2002). An Mhc component to kin recognition and mate choice in birds: predictions, progress, and prospects. Am Nat 160:S225–S237
Zoorob R, Behar G, Kroemer G, Auffrey C (1990) Organization of a functional chicken class II B gene. Immunogenetics 31:179–187
Acknowledgments
We thank Christopher N. Balakrishnan for his comments and suggestions during the preparation of this manuscript. This study and a research visit for MA to Harvard University was supported by a grant from the MCyT (project REN2001-2310) to MA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alcaide, M., Edwards, S.V. & Negro, J.J. Characterization, Polymorphism, and Evolution of MHC Class II B Genes in Birds of Prey. J Mol Evol 65, 541–554 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-007-9033-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-007-9033-9