Abstract
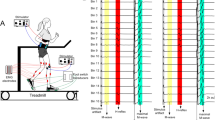
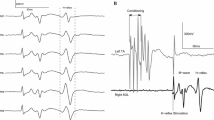
The soleus H-reflex modulation pattern was investigated in ten spinal cord intact subjects during treadmill walking at varying levels of body weight support (BWS), and nine spinal cord injured (SCI) subjects at a BWS level that promoted the best step** pattern. The soleus H-reflex was elicited by tibial nerve stimulation with a single 1-ms pulse at an intensity that the M-waves ranged from 4 to 8% of the maximal M-wave (Mmax). During treadmill walking, the H-reflex was elicited every four steps, and stimuli were randomly dispersed across the gait cycle which was divided into 16 equal bins. EMGs were recorded with surface electrodes from major left and right hip, knee, and ankle muscles. M-waves and H-reflexes at each bin were normalized to the Mmax elicited at 60–100 ms after the test reflex stimulus. For every subject, the integrated EMG area of each muscle was established and plotted as a function of the step cycle phase. The H-reflex gain was determined as the slope of the relationship between H-reflex and soleus EMG amplitudes at 60 ms before H-reflex elicitation for each bin. In spinal cord intact subjects, the phase-dependent H-reflex modulation, reflex gain, and EMG modulation pattern were constant across all BWS (0, 25, and 50) levels, while tibialis anterior muscle activity increased with less body loading. In three out of nine SCI subjects, a phase-dependent H-reflex modulation pattern was evident during treadmill walking at BWS that ranged from 35 to 60%. In the remaining SCI subjects, the most striking difference was an absent H-reflex depression during the swing phase. The reflex gain was similar for both subject groups, but the y-intercept was increased in SCI subjects. We conclude that the mechanisms underlying cyclic H-reflex modulation during walking are preserved in some individuals after SCI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbruzzese G (2002) The medical management of spasticity. Eur J Neurol 9:30–34
Barbeau H, Wainberg M, Finch L (1987) Description and application of a system for locomotor rehabilitation. Med Biol Eng Comput 25:341–344
Barbeau H, Ladoucer M, Mirbagheri MM, Kearney RE (2002) The effect of locomotor training combined with functional electrical stimulation in chronic spinal cord injured subjects: walking and reflex studies. Brain Res Rev 40:274–291
Behrman AL, Harkema SJ (2000) Locomotor training after human spinal cord injury: a series of case studies. Phys Ther 80:688–700
Capaday C, Stein RB (1986) Amplitude modulation of the soleus H-reflex in the human during walking and standing. J Neurosci 6:1308–1313
Capaday C, Stein RB (1987) Difference in the amplitude of the human soleus H-reflex during walking and running. J Physiol (Lond) 392:513–522
Capaday C, Lavoie BA, Barbeau H, Schneider C, Bonnard M (1999) Studies on the corticospinal control of human walking. I. Responses to focal transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex. J Neurophysiol 81:129–139
Chalmers GR, Knutzen KM (2000) Soleus Hoffmann-reflex modulation during walking in healthy elderly and young adults. J Gerontol Biol Sci 55:570–579
Cosgnach S, Quevedo J, Fedirchuk B, McCrea D (1999) Tonic presynaptic reduction of monosynaptic Ia EPSPs during fictive locomotion. Ann NY Acad Sci 860:505–507
Crenna P, Frigo C (1987) Excitability of the soleus H-reflex arc during walking and step** in man. Exp Brain Res 66:49–60
Crone C, Hultborn H, Mazieres L, Morin C, Nielsen J, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1990) Sensitivity of monosynaptic test reflexes to facilitation and inhibition as a function of the test reflex: a study in man and the cat. Exp Brain Res 81:35–45
Curtis DR, Gynther BD, Lacey G, Beattie DT (1997) Baclofen: reduction of presynaptic calcium influx in the cat spinal cord in vivo. Exp Brain Res 113:520–533
Dietz V (1998) Evidence for a load receptor contribution to the control of posture and locomotion. Neurosci Behav Reviews 22:495–499
Dietz V, Faist M, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1990) Amplitude modulation of the quadriceps H-reflex in the human during the early stance phase of gait. Exp Brain Res 79:221–224
Dietz V, Colombo G, Jensen L, Baumgartner L (1995) Locomotor capacity of spinal cord in paraplegic patients. Ann Neurol 37:574–582
Dietz V, Wirz M, Colombo G, Curt A (1998) Locomotor capacity and recovery of spinal cord function in paraplegic patients: a clinical and electrophysiological evaluation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 109:140–153
Dietz V, Muller R, Colombo G (2002) Locomotor activity in spinal man: significance of afferent input from joint and load receptors. Brain 125:2626–2634
Dobkin BH, Harkema SJ, Requejo PS, Edgerton VR (1995) Modulation of locomotor-like EMG activity in subjects with complete and incomplete spinal cord injury. J Neurol Rehab 9:183–190
Dobkin B, Barbeau H, Deforge D, Ditunno J, Elashoff R, Apple D, Basso M, Behrman A, Harkema S, Saulino M, Scott M (2007) The evolution of walking-related outcomes over the first 12 weeks of rehabilitation for incomplete traumatic spinal cord injury: the multicenter randomized spinal cord injury locomotor trial. Neurorehab Neural Repair 21:25–35
Drew T, Cabana T, Rossignol S (1996) Responses of medullary reticulospinal neurones to stimulation of cutaneous limb nerves during locomotion in intact cats. Exp Brain Res 111:153–168
Duysens J, Clarac F, Cruse H (2000) Load-regulating mechanisms in gait and posture: comparative aspects. Physiol Rev 80:83–133
Dyhre-Poulsen P, Simonesen EB, Voigt M (1991) Dynamic control of muscle stiffness and H reflex modulation during hop** and jum** in man. J Physiol (Lond) 437:287–304
Dyhre-Poulsen P, Simonsen EB (2002) H reflexes recorded during locomotion. Adv Exp Med Biol 508:377–383
Faist M, Dietz V, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1996) Modulation, probably presynaptic in origin, of monosynaptic Ia excitation during human gait. Exp Brain Res 109:441–449
Faist M, Ertel M, Berger W, Dietz V (1999) Impaired modulation of quadriceps tendon jerk reflex during spastic gait: differences between spinal and cerebral lesions. Brain 122:567–579
Ferris DP, Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Farley CT, Dyhre-Poulsen P (2001) Soleus H-reflex gain in humans walking and running under simulated reduced gravity. J Physiol (Lond) 530:167–180
Field-Fote EC, Lindley SD, Sherman AL (2005) Locomotor training approaches for individuals with spinal cord injury: a preliminary report of walking-related outcomes. J Neurol Phys Ther 29:127–137
Gossard JP, Cabelguen JM, Rossignol S (1990) Phase-dependent modulation of primary afferent depolarization in single cutaneous primary afferents evoked by peripheral stimulation during fictive locomotion in the cat. Brain Res 537:14–23
Grillner S, Wallen P (1985) Central pattern generators for locomotion, with special reference to vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci 8:233–261
Halliday DM, Conway BA, Christensen LO, Hansen NL, Petersen NP, Nielsen JB (2003) Functional coupling of motor units is modulated during walking in human subjects. J Neurophysiol 89:960–968
Hansen NL, Hansen S, Christensen LO, Petersen NT, Nielsen JB (2001) Synchronization of lower limb motor unit activity during walking in human subjects. J Neurophysiol 86:1266–1276
Hansen NL, Conway BA, Halliday DM, Hansen S, Pyndt HS, Biering-Sorensen F, Nielsen JB (2005) Reduction of common synaptic drive to ankle dorsiflexor motoneurons during walking in patients with spinal cord lesion. J Neurophysiol 94:934–942
Harkema SJ, Hurley SL, Patel UK, Requejo PS, Dobkin BH, Edgerton VR (1997) Human lumbosacral spinal cord interprets loading during step**. J Neurophysiol 77:797–811
Hodapp M, Klisch C, Mall V, Vry J, Berger W, Faist M (2007) Modulation of soleus H-reflexes during gait in children with cerebral palsy. J Neuropshysiol 98:3263–3268
Hultborn H, Conway BA, Gossard JP, Brownstone R, Fedirchuk B, Schomburg ED, Enriquez-Denton M, Perrrault MC (1998) How do we approach the locomotor network in the mammalian spinal cord? Ann NY Acad Sci 860:70–82
Kepple TM, Siegel KL, Stanhope SJ (1997) Relative contributions of the lower extremity joint moments to forward progression and support during gait. Gait Posture 6:1–8
Knikou M (2005) Effects of hip joint angle changes on intersegmental spinal coupling in human spinal cord injury. Exp Brain Res 167:381–393
Knikou M (2007) Hip-phase-dependent flexion reflex modulation and expression of spasms in patients with spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 204:171–181
Knikou M (2008) The H-reflex as a probe: pathways and pitfalls. J Neurosci Methods 171:1–12
Knikou M, Rymer WZ (2002) Hip angle induced modulation of H reflex amplitude, latency and duration in spinal cord injured humans. Clin Neurophysiol 113:1698–1708
Knikou M, Chaudhuri D, Kay E, Schmit BD (2006) Pre- and post-alpha motoneuronal control of the soleus H-reflex during sinusoidal hip movements in human spinal cord injury. Brain Res 1103:123–139
Knikou M, Kay E, Schmit BD (2007a) Parallel facilitatory reflex pathways from the foot and hip to flexors and extensors in the injured human spinal cord. Exp Neurol 206:146–158
Knikou M, Schmit BD, Chaudhuri D, Kay E, Rymer WZ (2007b) Soleus H-reflex excitability changes in response to sinusoidal hip stretches in the injured human spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 423:18–23
Knikou M, Angeli CA, Ferreira C, Harkema SJ (2008a) Soleus H-reflex phase-dependent modulation as a marker of locomotor recovery in the spinal-lesioned human spinal cord. Proceedings of the 38th annual meeting of the society for neuroscience, Washington DC
Knikou M, Angeli CA, Ferreira C, Harkema SJ (2008b) Neural circuits of the injured human spinal cord during assisted step**. From the bench to the bedside: the latest discoveries in SCI research, New York Academy of Sciences, NY, USA
Larsen B, Mrachacz-Kersting N, Lavoie BA, Voigt M (2006) The amplitude modulation of the quadriceps H-reflex in relation to the knee joint action during walking. Exp Brain Res 170:555–566
Lavoie BA, Devanne H, Capaday C (1997) Differential control of reciprocal inhibition during walking versus postural and voluntary motor tasks in humans. J Neurophysiol 78:429–438
Maynard FM, Bracken MB, Creasey G, Ditunno JF, Donovan WH, Ducker TB et al (1997) International standards for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 5:266–274
Meunier S, Morin C (1989) Changes in presynaptic inhibition of Ia fibres to soleus motoneurones during voluntary dorsiflexion of the foot. Exp Brain Res 76:510–518
Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1998) Cortical control of presynaptic inhibition of Ia afferents in humans. Exp Brain Res 119:415–426
Nakazawa K, Miyoshi T, Sekiguchi H, Nozaki D, Akai M, Yano H (2004) Effects of loading and unloading of lower limb joints on the soleus H-reflex in standing humans. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1296–1304
Neptune RR, Kautz SA, Zajac FE (2001) Contributions of the individual ankle plantar flexors to support, forward progression and swing initiation during walking. J Biomech 34:1387–1398
Nielsen J, Kagamihara Y (1992) The regulation of disynaptic reciprocal Ia inhibition during co-contraction of antagonistic muscles in man. J Physiol (Lond) 456:373–391
Nielsen J, Kagamihara Y (1993) The regulation of presynaptic inhibition during co-contraction of antagonistic muscles in man. J Physiol (Lond) 464:575–593
Nielsen J, Petersen N, Ballegaard M (1995) Latency of effects evoked by electrical and magnetic brain stimulation in lower limb motoneurones in man. J Physiol (Lond) 484:791–802
Norman KE, Pepin A, Ladouceur M, Barbeau H (1995) A treadmill apparatus and harness support for evaluation and rehabilitation of gait. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 76:772–778
Pearson KG, Misiaszek JE, Fouad K (1998) Enhancement and resetting of locomotor activity by muscle afferents. Ann NY Acad Sci 860:203–215
Petersen N, Christensen LOD, Sinkjaer T, Morita H, Nielsen J (1998) Evidence suggesting a transcortical pathway from muscle afferents to tibialis anterior motoneurones in man. J Physiol (Lond) 512:267–276
Petersen N, Morita H, Nielsen J (1999) Modulation of reciprocal inhibition between ankle extensors and flexors during walking in man. J Physiol (Lond) 520:605–619
Phadke CP, Wu SS, Thompson FJ, Behrman AL (2006) Soleus H-reflex modulation in response to change in percentage of leg loading in standing after incomplete spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett 403:6–10
Phadke CP, Wu SS, Thompson FJ, Behrman AL (2007) Comparison of soleus H-reflex modulation after incomplete spinal cord injury in 2 walking environments: treadmill with body weight support and overground. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88:1606–1613
Pratt CA, Jordan LM (1987) Ia inhibitory interneurons and Renshaw cells as contributors to the spinal mechanisms of fictive locomotion. J Neurophysiol 57:56–71
Schneider C, Lavoie BA, Capaday C (2000) On the origin of the soleus H-reflex modulation pattern during human walking and its task-dependent differences. J Neurophysiol 83:2881–2890
Schubert M, Curt A, Jensen L, Dietz V (1997) Corticospinal input in human gait: modulation of magnetically evoked motor responses. Exp Brain Res 115:234–246
Simonsen EB, Dyhre-Poulsen P (1999) Amplitude of the human soleus H-reflex during walking and running. J Physiol (Lond) 515:929–939
Sinkjær T, Andersen JB, Larsen B (1996a) Soleus stretch reflex modulation during gait in humans. J Neurophysiol 76:1112–1120
Sinkjær T, Andersen JB, Nielsen JF (1996b) Impaired stretch reflex and joint torque modulation during spastic gait in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol 243:566–574
Sinkjær T, Andersen JB, Ladouceur M, Christensen LO, Nielsen JB (2000) Major role for sensory feedback in soleus EMG activity in the stance phase of walking in man. J Physiol (Lond) 523:817–827
Stewart JE, Barbeau H, Gauthier S (1991) Modulation of locomotor patterns and spasticity in spinal cord injured patients. Can J Neurol Sci 18:321–332
Visintin M, Barbeau H (1989) The effects of body weight support on the locomotor pattern of spastic paretic patients. Can J Neurol Sci 16:315–325
Wernig A, Muller S (1992) Laufband locomotion with body weight support improved walking in persons with severe spinal cord injuries. Paraplegia 30:229–238
Winchester P, McColl R, Querry R, Foreman N, Mosby J, Tansey K, Williamson J (2005) Changes in supraspinal activation patterns following robotic locomotor therapy in motor incomplete spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 19:313–324
Wirz M, Colombo G, Dietz V (2001) Long term effects of locomotor training in spinal humans. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71:93–96
Wirz M, Zemon DH, Rupp R, Scheel A, Colombo G, Dietz V, Hornby TG (2005) Effectiveness of automated locomotor training in patients with chronic incomplete spinal cord injury: a multicenter trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:672–680
Yang JF, Whelan PJ (1993) Neural mechanisms that contribute to cyclical modulation of the soleus H-reflex in walking in humans. Exp Brain Res 95:547–556
Yang JF, Fung J, Edamura M, Blunt R, Stein RB, Barbeau H (1991) H-reflex modulation during walking in spastic paretic subjects. Can J Neurosci 18:443–452
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the clinical research team of the Frazier Rehab Institute, and the research participants for their valuable contribution. We are grateful to Dr. Poul Dyhre-Poulsen for his significant contribution to this study and would like to acknowledge the support provided by the Neurological Institute of Kentucky. This work was supported by the New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH)/Wadsworth Center, Spinal Cord Injury Research Board, Grant No. SCIRB24 to Maria Knikou.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knikou, M., Angeli, C.A., Ferreira, C.K. et al. Soleus H-reflex modulation during body weight support treadmill walking in spinal cord intact and injured subjects. Exp Brain Res 193, 397–407 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1636-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1636-x