Abstract
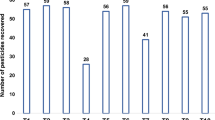
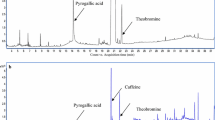
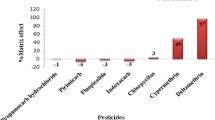
An analytical method was developed and validated for the determination of ten pesticides in sewage sludge coming from an agro-food industry. The method was based on the application of Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe (QuEChERS) extraction for solid sewage sludge and SPE extraction for sludge aqueous phase, followed by liquid chromatography (LC) coupled to hybrid quadrupole/linear ion trap mass spectrometry (QqLIT-MS). The QuEChERS method was reported 14 years ago and nowadays is mainly applied to the analysis of pesticides in food. More recent applications have been reported in other matrices as sewage sludge, but the complexity of the matrix makes necessary the optimization of the cleanup step to improve the efficiency of the analysis. With this aim, several dispersive solid-phase extraction cleanup sorbents were tested, choosing C18 + PSA as a d-SPE sorbent. The proposed method was satisfactorily validated for most compounds investigated, showing recoveries higher than 80% in most cases, with the only exception of prochloraz (71%) at low concentration level. Limits of quantification were lower than 40 ng l−1 in the aqueous phase and below 40 ng g−1 in the solid phase for the majority of the analytes. The method was applied to solid sludge and the sludge aqueous phase coming from an agro-food industry which processes fruits and vegetables.

Application of LC/MS/MS advanced analytical techniques for determination of pesticides contained in sewage sludge



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Köck-Schulmeyer M, Villagrasa M, López de Alda M, Céspedes-Sánchez R, Ventura F, Barceló D. Occurrence and behavior of pesticides in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental impact. Sci Total Environ. 2013;458–460:466–76.
Masiá A, Vásquez K, Campo J, Picó Y. Assessment of two extraction methods to determine pesticides in soils, sediments and sludges. Application to the Túria River basin. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1378:19–31.
Olofsson U, Brorström-Lundén E, Kylin H, Haglund P. Comprehensive mass flow analysis of Swedish sludge contaminants. Chemosphere. 2013;90(1):28–35.
Karas P, Metsoviti A, Zisis V, Ehaliotis C, Omirou M, Papadopoulou ES, et al. Dissipation, metabolism and sorption of pesticides used in fruit-packaging plants: towards an optimized depuration of their pesticide-contaminated agro-industrial effluents. Sci Total Environ. 2015;530:129–39.
Sánchez Pérez JA, Carra I, Sirtori C, Agüera A, Esteban B. Fate of thiabendazole through the treatment of a simulated agro-food industrial effluent by combined MBR/Fenton processes at μg/l scale. Water Res. 2014;51:55–63.
Rivas G, Casas López JL, Esteban B, Sánchez Pérez JA. Controlling pH in biological depuration of industrial wastewater to enable micropollutant removal using a further advanced oxidation process. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2014;89:1274–82.
Jiménez M, Maldonado MI, Rodríguez EM, Hernández-Ramírez A, Saggioro E, Carra I, et al. Supported TiO2 solar photocatalysis at semi-pilot scale: degradation of pesticides found in citrus processing industry wastewater, reactivity and influence of photogenerated species. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2015;90:149–57.
Agüera A, Sirtori C, Esteban B, Cabrera A, Carra I, Sánchez Pérez JA (2013) Identification of biorecalcitrant micropollutants in food industry. Removal alternatives and characterization of generated transformation products, proc. Micropol & Ecohazard Zurich, Abstract IWA–11603.
Tadeo JL, Sánchez-Brunete C, Albero B, García-Valcárcel AI. Determination of pesticide residues in sewage sludge: a review. J AOAC Int. 2010;93:1692–702.
European Committee for Standardization, Lebensmittel P, Aliments Q (2008) CEN15662:2008 Foods of plant origin—determination of pesticide residues using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS following acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and cleanup by dispersive SPE—QuEChERS-method. 24:1–83.
Bruzzoniti MC, Checchini L, De Carlo RM, Orlandini S, Rivoira L, Del Bubba M. QuEChERS sample preparation for the determination of pesticides and other organic residues in environmental matrices: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406:4089–116.
Peysson W, Vulliet E. Determination of 136 pharmaceuticals and hormones in sewage sludge using quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction followed by analysis with liquid chromatography-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1290:46–61.
Ferhi S, Bourdat-Deschamps M, Daudin J-J, Houot S, Nélieu S. Factors influencing the extraction of pharmaceuticals from sewage sludge and soil: an experimental design approach. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:6153–68.
Bourdat-Deschamps M, Leang S, Bernet N, Daudin J-J, Nélieu S. Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceuticals in aqueous environmental samples by online solid-phase extraction-ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: optimisation and matrix effects reduction by quick, easy, cheap, effective. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1349:11–23.
Rossini D, Ciofi L, Ancillotti C, Checchini L, Bruzzoniti MC, Rivoira L, et al. Innovative combination of QuEChERS extraction with on-line solid-phase extract purification and pre-concentration, followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and their metaboli. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;935:269–81.
Schenck FJ, Hobbs JE. Evaluation of the quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe (QuEChERS) approach to pesticide residue analysis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2004;73(1):24–30.
Wang L, Huang X, Wang D, Chen Y, Xu D, Zhou Y. Determination of 32 sulfonylurea herbicide residues in sweet corns and green soybeans by QuEChERS-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Se Pu. 2015;33:501–7.
Nieto-García AJ, Romero-González R, GarridoFrenich A. Multi-pesticide residue analysis in nutraceuticals from grape seed extracts by gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Food Control. 2015;47:369–80.
Morris BD, Schriner RB. Development of an automated column solid-phase extraction cleanup of QuEChERS extracts, using a zirconia-based sorbent, for pesticide residue analyses by LC-MS/MS. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63(21):5107–19.
Li Y, Kelley RA, Anderson TD, Lydy MJ. Development and comparison of two multi-residue methods for the analysis of select pesticides in honey bees, pollen, and wax by gas chromatography-quadrupole mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2015;140:81–7.
Melero JA, Sánchez-Vázquez R, Vasiliadou IA, MartínezCastillejo F, Bautista LF, Iglesias J, et al. Municipal sewage sludge to biodiesel by simultaneous extraction and conversion of lipids. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;103:111–8.
Rivas G, Esteban B, Ponce-Robles L, Casas López JL, Agüera A, Sánchez Pérez JA. Fate of micropollutants during sewage sludge disintegration by low-frequency ultrasound. Chem Eng J. 2015;280:575–87.
Ortega-Gómez E, Esteban B, Ballesteros Martín MM, Fernández Ibáñez P, Sánchez Pérez JA. Inactivation of natural enteric bacteria in real municipal wastewater by solar photo-Fenton at neutral pH. Water Res. 2014;63:316–24.
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Štajnbaher D, Schenck FJ. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int. 2003;86:412–31.
Lehotay SJ. Determination of pesticide residues in foods by acetonitrile extraction and partitioning with magnesium sulfate: collaborative study. J AOAC Int. 2007;90:485–520.
Herrero P, Borrull F, Pocurull E, Marcé RM. A quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction method followed by liquid chromatography-(Orbitrap) high resolution mass spectrometry to determine benzotriazole, benzothiazole and benzenesulfonamidederivates in sewage sludge. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1339:34–41.
Rajski T, Lozano A, Uclés A, Ferrer C, Fernández-Alba AR. Determination of pesticide residues in high oil vegetal commodities by using various multi-residue methods and clean-ups followed by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1304:109–20.
Lozano A, Kiedrowska B, Scholten J, De Kroon M, De Kok A, Fernández-Alba AR. Miniaturisation and optimisation of the Dutch mini-Luke extraction method for implementation in the routine multi-residue analysis of pesticides in fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. 2016;192:668–81.
Ghanem A, Bados P, Perreau F, Benabdallah R, Plagellat C, De Alencastro LF, et al. Multiresidue analysis of atrazine, diuron and their degradation products in sewage sludge by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008;391(1):345–52.
García-Valcárcel AI, Tadeo JL. A combination of ultrasonic assisted extraction with LC-MS/MS for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in sludge. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;641(1):345–52.
Baugros J-B, Cren-Olivé C, Giroud B, Gauvrit J-Y, Lantéri P, Grenier-Loustalot M-F. Optimisation of pressurised liquid extraction by experimental design for quantification of pesticides and alkyl phenols in sludge, suspended materials and atmospheric fallout by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216(25):4941–9.
SANTE/11945/2015. Guidance document on analytical quality control and method validation procedures for pesticides residues analysis in food and feed. Available from: http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/docs/plant_pesticides_mrl_guidelines_wrkdoc_11945_en.pdf]. Accessed 14th Nov 2016
García-Valcárcel AI, Tadeo JL. Determination of azoles in sewage sludge from Spanish wastewater treatment plants by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci. 2011;34(11):1228–35.
Wluka A-K, Rüdel H, Pohl K, Schwarzbauer J. Analytical method development for the determination of eight biocides in various environmental compartments and application for monitoring purposes. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2016;23(21):21894–907.
Campo J, Masiá A, Blasco C, Picó Y. Occurrence and removal efficiency of pesticides in sewage treatment plants of four Mediterranean River Basins. J Hazard Mater. 2013;263:146–57.
Barbosa MO, Moreira NFF, Ribeiro AR, Pereira MFR, Silva AMT. Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants: an overview of the watch list of EU decision 2015/495. Water Res. 2016;94:257–79.
European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) no 485/2013 of 24 May 2013 amending Implementing Regulation (EU) no 540/2011, as regards the conditions of approval of the active substances clothianidin, thiamethoxam and imidacloprid, and prohibiting the use and. Off J Eur Union. 2013;139:12–26.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Junta de Andalucía (Andalusian Regional Government in Spain) (RNM-1739) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) for funding this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponce-Robles, L., Rivas, G., Esteban, B. et al. Determination of pesticides in sewage sludge from an agro-food industry using QuEChERS extraction followed by analysis with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 6181–6193 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0558-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0558-5