Abstract
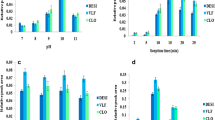
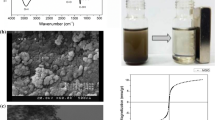
Ionic liquid-modified magnetic polymeric microspheres (ILMPM) were prepared based on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) and ionic liquids (ILs) incorporated into a polymer. The composites were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction, and vibrating magnetometer, which indicated that ILMPM had a regularly spherical shape and strong magnetic property. The obtained ILMPM were successfully applied as a special adsorbent of magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction (MDSPE) for the rapid extraction and isolation of sulfamonomethoxine sodium and sulfachloropyrazine sodium in urine. The factors that affected extraction efficiency, such as adsorption conditions, desorption conditions, washing and elution solvents, and pH of the sample solution, were optimized. Under the optimum condition, good linearity in the range of 0.005–2.0 μg g−1 (r ≥ 0.9996) was obtained for the two sulfonamides (SAs); the average recoveries at three spiked levels ranged from 86.9 to 102.1 %, with relative standard deviations of ≤4.3 %. The presented ILMPM-MDSPE method combined the advantages of ILs, MNPs, and MDSPE and therefore could be potentially applied for rapid screening of SAs in urine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen L, Liu J, Zeng Q, Wang H, Yu A, Zhang H, Ding L (2009) Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the separation of tetracycline antibiotics from egg and tissue samples. J Chromatogr A 1216:3710–3719
Xu X, Su R, Zhao X, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Li D, Li X, Zhang H, Wang Z (2011) Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and derivatization of sulfonamides in river water, honey, milk, and animal plasma. Anal Chim Acta 707:92–99
Gehring TA, Griffin B, Williams R, Geiseker C, Rushing LG, Siitonen PH (2006) Multiresidue determination of sulfonamides in edible catfish, shrimp and salmon tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography with post column derivatization and fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B 840:132–138
Fuh MRS, Chu SY (2003) Quantitative determination of sulfonamide in meat by solid-phase extraction and capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chim Acta 499:215–221
Wen Y, Zhang M, Zhao Q, Feng YQ (2005) Monitoring of five sulfonamide antibacterial residues in milk by in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 53:8468–8473
Rezazadeh M, Yamini Y, Seidi S, Ebrahimpour B (2013) Electromembrane surrounded solid phase microextraction: a novel approach for efficient extraction from complicated matrices. J Chromatogr A 1280:16–22
Song XY, Shi YP, Chen J (2013) Carbon nanotubes reinforced hollow fiber solid phase microextraction for the determination of strychnine and brucine in urine. Talanta 116:188–194
Posyniak A, Zmudzki J, Mitrowska K (2005) Dispersive solid-phase extraction for the determination of sulfonamides in chicken muscle by liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1087:259–264
Kishida K, Furusawa N (2001) Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of residual sulfonamides in chicken. J Chromatogr A 937:49–55
Barfi B, Asghari A, Rajabi M, Barfi A, Saeidi I (2013) Simplified miniaturized ultrasound-assisted matrix solid phase dispersion extraction and high performance liquid chromatographic determination of seven flavonoids in citrus fruit juice and human fluid samples: hesperetin and naringenin as biomarkers. J Chromatogr A 1311:30–40
Rallis GN, Sakkas VA, Boumba VA, Vougiouklakis T, Albanis TA (2012) Determination of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in post-mortem human lung by matrix solid-phase dispersion with the aid of response surface methodology and desirability function. J Chromatogr A 1227:1–9
Wen YY, Li JH, Zhang WW, Chen LX (2011) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with capillary electrophoresis for simultaneous determination of sulfonamides with the aid of experimental design. Electrophoresis 32:2131–2138
Lin CY, Huang SD (2008) Application of liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid-chromatography for the determination of sulfonamides in water. Anal Chim Acta 612:37–43
Zhu X, Cai J, Yang J, Su Q, Gao Y (2006) Films coated with molecular imprinted polymers for the selective stir bar sorption extraction of monocrotophos. J Chromatogr A 1131:37–44
Yan H, Qiao F, Row KH (2007) Molecularly imprinted-matrix solid-phase dispersion for selective extraction of five fluoroquinolones in eggs and tissue. Anal Chem 79:8242–8248
He Z, Liu D, Li R, Zhou Z, Wang P (2012) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water samples by Fe3O4@dioctadecy ldimethyl ammonium chloride@silica magnetic particles. Anal Chim Acta 747:29–35
Wang X, Wang L, He X, Zhang Y, Chen L (2009) A molecularly imprinted polymer-coated nanocomposite of magnetic nanoparticles for estrone recognition. Talanta 78:327–332
Liu J, Qiao SZ, Hu QH, Lu GQ (2011) Magnetic nanocomposites with mesoporous structures: synthesis and applications. Small 7:425–443
Hu Y, Liu R, Zhang Y, Li G (2009) Improvement of extraction capability of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads in aqueous media via dual-phase solvent system. Talanta 79:576–582
Hu Y, Li Y, Liu R, Tan W, Li G (2011) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads prepared by microwave heating for selective enrichment of β-agonists in pork and pig liver samples. Talanta 84:462–470
Sun L, Chen LG, Sun X, Du XB, Yue YS, He DQ, Xu HY, Zeng QL, Wang H, Ding L (2009) Analysis of sulfonamides in environmental water samples based on magnetic mixed hemimicelles solid-phase extraction coupled with HPLC-UV detection. Chemosphere 77:1306–1312
Sun L, Sun X, Du XB, Yue YS, Chen LG, Xu HY, Zeng QL, Wang H, Ding L (2010) Determination of sulfonamides in soil samples based on alumina-coated magnetite nanoparticles as adsorbents. Anal Chim Acta 665:185–192
Zhang Y, Liu R, Hu Y, Li G (2009) Microwave heating in preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads for trace triazines analysis in complicated samples. Anal Chem 81:967–976
**g T, **a H, Guan Q, Lu W, Dai Q, Niu J, Lim JM, Hao Q, Lee YI, Zhou Y, Mei S (2011) Rapid and selective determination of urinary lysozyme based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers extraction followed by chemiluminescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 692:73–79
Guo L, Deng Q, Fang G, Gao W, Shuo W (2011) Preparation and evaluation of molecularly imprinted ionic liquids polymer as sorbent for on-line solid-phase extraction of chlorsulfuron in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:6271–6277
Bideau JL, Viau L, Vioux A (2011) Ionogels, ionic liquid based hybrid materials. Chem Soc Rev 40:907–925
Zhou X, Li ZJ, Yuan R, Liu HZ (2006) A novel room temperature ionic liquid extraction spectrophotometric determination of trace germanium in natural water with methybenzeneazosalicylfluorone. Anal Lett 39:863–877
Meindersma GW, Podt AJG, de Haan AB (2005) Selection of ionic liquids for the extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from aromatic/aliphatic mixtures. Fuel Process Technol 87:59–70
Ye CL, Zhou QX, Wang XM (2006) Headspace liquid-phase microextraction using ionic liquid as extractant for the preconcentration of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and its metabolites at trace levels in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 572:165–171
Marszałł MP, Markuszewski MJ, Kaliszan RJ (2006) Separation of nicotinic acid and its structural isomers using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquid as a buffer additive by capillary electrophoresis. Pharm Biomed Anal 41:329–332
Herrera-Herrera AV, Hernández-Borges J, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ (2009) Fluoroquinolone antibiotic determination in bovine, ovine and caprine milk using solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection with ionic liquids as mobile phase additives. J Chromatogr A 1216:7281–7287
Ho TD, Yu HL, Cole WTS, Anderson JL (2012) Ultraviolet photoinitiated on-fiber copolymerization of ionic liquid sorbent coatings for headspace and direct immersion solid-phase microextraction. Anal Chem 84:9520–9528
Ho TD, Joshi MD, Silver MA, Anderson JL (2012) Selective extraction of genotoxic impurities and structurally alerting compounds using polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings in solid-phase microextraction: alkyl halides and aromatics. J Chromatogr A 1240:29–44
Vidal L, Riekkola ML, Canals A (2012) Ionic liquid-modified materials for solid-phase extraction and separation: a review. Anal Chim Acta 715:19–41
Tian M, Bi W, Row KH (2011) Molecular imprinting in ionic liquid-modified porous polymer for recognitive separation of three tanshinones from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:2495–2502
Zhang R, Li N, Wang C, Bai Y, Ren R, Gao S, Yu W, Zhao T, Zhang H (2011) Ionic liquid foam floatation coupled with solid phase extraction for separation and determination of hormones by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 704:98–109
Jiang HL, Ying LY, Zhou SC, Ying M, Shen W, Qiu DH (2011) Chromatographic determination of biogenic amines in wines after treatment with ionic liquids as novel media. J Sep Sci 34:1055–1062
Tao Y, Liu JF, Hu XL, Li HC, Wang T, Jiang GB (2009) Hollow fiber supported ionic liquid membrane microextraction for determination of sulfonamides in environmental water samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1216:6259–6266
Han J, Wang Y, Liu Y, Li YF, Lu Y, Yan YS, Ni L (2013) Ionic liquid-salt aqueous two-phase extraction based on salting-out coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of sulfonamides in water and food. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:1245–1255
Galán-Cano F, Alcudia-León MC, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M (2013) Ionic liquid coated magnetic nanoparticles for the gas chromatography/mass spectrometric determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in waters. J Chromatogr A 1300:134–140
Shi X, Meng Y, Liu J, Sun A, Li D, Yao C, Lu Y, Chen J (2011) Group-selective molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction for the simultaneous determination of six sulfonamides in aquaculture products. J Chromatogr B 879:1071–1076
Arvand M, Alirezanejad F (2011) Sulfamethoxazole-imprinted polymeric receptor as ionophore for potentiometric transduction. Electroanalysis 23:1948–1957
Evgenév MI, Garmonov SY, Shakirova LS, Levinson FS (2000) Spectrophotometric and chromatographic determination of sulfanilamides in biological fluids and pharmaceuticals. J Anal Chem 55:799–805
Iammarino M, Palermo C, Nardiello D, Muscarella M (2011) Optimization and validation of a confirmatory method for determination of ten sulfonamides in feeds by LC and UV-diode array detection. Chromatographia 73:75–82
Kong X, Gao R, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2012) Synthesis and characterization of the core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (Fe3O4@MIPs) adsorbents for effective extraction and determination of sulfonamides in the poultry feed. J Chromatogr A 1245:8–16
Maciel JC, Andrad PL, Neri DFM, Carvalho LB Jr, Cardoso CA, Calazans GMT, Aguiar JA, Silva MPC (2012) Preparation and characterization of magnetic levan particles as matrix for trypsin immobilization. J Magn Magn Mater 324:1312–1316
Acknowledgments
The project was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21175031, 31301464) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei (B2012201052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Gao, M., Yang, C. et al. Ionic liquid-modified magnetic polymeric microspheres as dispersive solid phase extraction adsorbent: a separation strategy applied to the screening of sulfamonomethoxine and sulfachloropyrazine from urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 2669–2677 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7665-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7665-3