Abstract
Rational
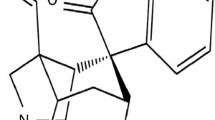
Neuropathic pain is frequently comorbid with sleep disturbances. Paeoniflorin, a main active compound of total glucosides of paeony, has been well documented to exhibit neuroprotective bioactivity.
Objective
The present study evaluated effects of paeoniflorin on neuropathic pain and associated insomnia and the mechanisms involved.
Methods
The analgesic and hypnotic effects of paeoniflorin were measured by mechanical threshold and thermal latency, electroencephalogram (EEG) and electromyogram, and c-Fos expression in a neuropathic pain insomnia model.
Results
The data revealed that paeoniflorin (50 or 100 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly increased the mechanical threshold and prolonged the thermal latency in partial sciatic nerve ligation (PSNL) mice. Meanwhile, paeoniflorin increased non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep amount and concomitantly decreased wakefulness time. However, pretreatment with l,3-dimethy-8-cyclopenthylxanthine, an adenosine A1 receptor (R, A1R) antagonist, abolished the analgesic and hypnotic effects of paeoniflorin. Moreover, paeoniflorin at 100 mg/kg failed to change mechanical threshold and thermal latency and NREM sleep in A1R knockout PSNL mice. Immunohistochemical study showed that paeoniflorin inhibited c-Fos overexpression induced by PSNL in the anterior cingulate cortex and ventrolateral periaqueductal gray.
Conclusions
The present findings indicated that paeoniflorin exerted analgesic and hypnotic effects via adenosine A1Rs and might be of potential use in the treatment of neuropathic pain and associated insomnia.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MN, Kumar S, Rai S, Methippara M, Szymusiak R, McGinty D (2009) Role of adenosine A(1) receptor in the perifornical-lateral hypothalamic area in sleep-wake regulation in rats. Brain Res 1304:96–104
Anastassiou E, Iatrou CA, Vlaikidis N, Vafiadou M, Stamatiou G, Plesia E, Lyras L, Vadalouca A (2011) Impact of pregabalin treatment on pain, pain-related sleep interference and general well-being in patients with neuropathic pain: a non-interventional, multicentre, post-marketing study. Clin Drug Investig 31:417–426
Argoff CE (2007) The coexistence of neuropathic pain, sleep, and psychiatric disorders: a novel treatment approach. Clin J Pain 23:15–22
Bagley EE, Vaughan CW, Christie MJ (1999) Inhibition by adenosine receptor agonists of synaptic transmission in rat periaqueductal grey neurons. J Physiol 516:219–225
Baron R, Binder A, Wasner G (2010) Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol 9:807–819
Barros TA, de Freitas LA, Filho JM, Nunes XP, Giulietti AM, de Souza GE, dos Santos RR, Soares MB, Villarreal CF (2010) Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties of 7-hydroxycoumarin in experimental animal models: potential therapeutic for the control of inflammatory chronic pain. J Pharm Pharmacol 62:205–213
Benington JH, Kodali SK, Heller HC (1995) Stimulation of A1 adenosine receptors mimics the electroencephalographic effects of sleep deprivation. Brain Res 692:79–85
Cartmell SM, Gelgor L, Mitchell D (1991) A revised rotarod procedure for measuring the effect of antinociceptive drugs on motor function in the rat. J Pharmacol Methods 26:149–159
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Chen CR, Zhou XZ, Luo YJ, Huang ZL, Urade Y, Qu WM (2012) Magnolol, a major bioactive constituent of the bark of Magnolia officinalis, induces sleep via the benzodiazepine site of GABA(A) receptor in mice. Neuropharmacology 63:1191–1199
Cheng JT, Wang CJ, Hsu FL (1999) Paeoniflorin reverses guanethidine-induced hypotension via activation of central adenosine A1 receptors in Wistar rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26:815–816
Chokroverty S (2000) Diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders caused by co-morbid disease. Neurology 54:S8–S15
Dunham NW, Miya TS (1957) A note on a simple apparatus for detecting neurological deficit in rats and mice. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc 46:208–209
Essawy SS, Elbaz AA (2013) Role of adenosine receptors in the anti-nociceptive effects of allopurinol in mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17:1857–1863
Fredholm BB, IJerzman AP, Jacobson KA, Linden J, Muller CE, International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (2011) LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors—an update. Pharmacol Rev 63:1–34
Gao X, Lu Q, Chou G, Wang Z, Pan R, **a Y, Hu H, Dai Y (2014) Norisoboldine attenuates inflammatory pain via the adenosine A1 receptor. Eur J Pain 18:939–948
Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, Xu Q, Peng W, Liu W, Jensen TK, Pei Y, Wang F, Han X, Chen JF, Schnermann J, Takano T, Bekar L, Tieu K, Nedergaard M (2010) Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci 13:883–888
Gong QJ, Li YY, **n WJ, Wei XH, Cui Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Liu CC, Liu XG (2010) Differential effects of adenosine A1 receptor on pain-related behavior in normal and nerve-injured rats. Brain Res 1361:23–30
Huang ZL, Qu WM, Eguchi N, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA, Fredholm BB, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (2005) Adenosine A2A, but not A1, receptors mediate the arousal effect of caffeine. Nat Neurosci 8:858–859
Huang ZL, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (2011) The role of adenosine in the regulation of sleep. Curr Top Med Chem 11:1047–1057
Huang ZL, Zhang Z, Qu WM (2014) Roles of adenosine and its receptors in sleep-wake regulation. Int Rev Neurobiol 119:349–371
** L, Zhang LM, **e KQ, Ye Y, Feng L (2011) Paeoniflorin suppresses the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in endotoxin-treated human monocytic cells. Br J Pharmacol 164:694–703
Johansson B, Halldner L, Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA, Poelchen W, Gimenez-Llort L, Escorihuela RM, Fernandez-Teruel A, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Xu XJ, Hardemark A, Betsholtz C, Herlenius E, Fredholm BB (2001) Hyperalgesia, anxiety, and decreased hypoxic neuroprotection in mice lacking the adenosine A1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:9407–9412
Kovacs KJ (2008) Measurement of immediate-early gene activation- c-fos and beyond. J Neuroendocrinol 20:665–672
Kukkar A, Bali A, Singh N, Jaggi AS (2013) Implications and mechanism of action of gabapentin in neuropathic pain. Arch Pharm Res 36:237–251
Kuribara H, Higuchi Y, Tadokoro S (1977) Effects of central depressants on rota-rod and traction performances in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 27:117–126
Lautenbacher S, Kundermann B, Krieg JC (2006) Sleep deprivation and pain perception. Sleep Med Rev 10:357–369
Lee YW, Yaksh TL (1996) Pharmacology of the spinal adenosine receptor which mediates the antiallodynic action of intrathecal adenosine agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:1642–1648
Lee B, Shin YW, Bae EA, Han SJ, Kim JS, Kang SS, Kim DH (2008) Antiallergic effect of the root of Paeonia lactiflora and its constituents paeoniflorin and paeonol. Arch Pharm Res 31:445–450
Li Y, van den Pol AN (2008) Mu-opioid receptor-mediated depression of the hypothalamic hypocretin/orexin arousal system. J Neurosci 28:2814–2819
Li XY, Ko HG, Chen T, Descalzi G, Koga K, Wang H, Kim SS, Shang Y, Kwak C, Park SW, Shim J, Lee K, Collingridge GL, Kaang BK, Zhuo M (2010) Alleviating neuropathic pain hypersensitivity by inhibiting PKMzeta in the anterior cingulate cortex. Science 330:1400–1404
Lima FO, Souza GR, Verri WA Jr, Parada CA, Ferreira SH, Cunha FQ, Cunha TM (2010) Direct blockade of inflammatory hypernociception by peripheral A1 adenosine receptors: involvement of the NO/cGMP/PKG/KATP signaling pathway. Pain 151:506–515
Liu ZW, Gao XB (2007) Adenosine inhibits activity of hypocretin/orexin neurons by the A1 receptor in the lateral hypothalamus: a possible sleep-promoting effect. J Neurophysiol 97:837–848
Liu DZ, **e KQ, Ji XQ, Ye Y, Jiang CL, Zhu XZ (2005) Neuroprotective effect of paeoniflorin on cerebral ischemic rat by activating adenosine A1 receptor in a manner different from its classical agonists. Br J Pharmacol 146:604–611
Liu DF, Wei W, Song LH (2006a) Protective effect of paeoniflorin on immunological liver injury induced by bacillus Calmette-Guerin plus lipopolysaccharide: modulation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 MRNA. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33:332–339
Liu DZ, Zhao FL, Liu J, Ji XQ, Ye Y, Zhu XZ (2006b) Potentiation of adenosine A1 receptor agonist CPA-induced antinociception by paeoniflorin in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 29:1630–1633
Liu HQ, Zhang WY, Luo XT, Ye Y, Zhu XZ (2006c) Paeoniflorin attenuates neuroinflammation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease by activation of adenosine A1 receptor. Br J Pharmacol 148:314–325
Liu YY, Yin D, Chen L, Qu WM, Chen CR, Laudon M, Cheng NN, Urade Y, Huang ZL (2014) Piromelatine exerts antinociceptive effect via melatonin, opioid, and 5HT1A receptors and hypnotic effect via melatonin receptors in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231:3973–3985
Maione S, de Novellis V, Cappellacci L, Palazzo E, Vita D, Luongo L, Stella L, Franchetti P, Marabese I, Rossi F, Grifantini M (2007) The antinociceptive effect of 2-chloro-2′-C-methyl-N6-cyclopentyladenosine (2′-Me-CCPA), a highly selective adenosine A1 receptor agonist, in the rat. Pain 131:281–292
Morgado C, Terra PP, Tavares I (2010) Neuronal hyperactivity at the spinal cord and periaqueductal grey during painful diabetic neuropathy: effects of gabapentin. Eur J Pain 14:693–699
Narita M, Ozaki S, Ise Y, Yajima Y, Suzuki T (2003) Change in the expression of c-fos in the rat brain following sciatic nerve ligation. Neurosci Lett 352:231–233
Narita M, Niikura K, Nanjo-Niikura K, Furuya M, Yamashita A, Saeki M, Matsushima Y, Imai S, Shimizu T, Asato M, Kuzumaki N, Okutsu D, Miyoshi K, Suzuki M, Tsukiyama Y, Konno M, Yomiya K, Matoba M, Suzuki T (2011) Sleep disturbances in a neuropathic pain-like condition in the mouse are associated with altered GABAergic transmission in the cingulate cortex. Pain 152:1358–1372
Nozaki C, Le Bourdonnec B, Reiss D, Windh RT, Little PJ, Dolle RE, Kieffer BL, Gaveriaux-Ruff C (2012) delta-Opioid mechanisms for ADL5747 and ADL5859 effects in mice: analgesia, locomotion, and receptor internalization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 342:799–807
O’Brien EM, Waxenberg LB, Atchison JW, Gremillion HA, Staud RM, McCrae CS, Robinson ME (2010) Negative mood mediates the effect of poor sleep on pain among chronic pain patients. Clin J Pain 26:310–319
Oishi Y, Huang ZL, Fredholm BB, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (2008) Adenosine in the tuberomammillary nucleus inhibits the histaminergic system via A1 receptors and promotes non-rapid eye movement sleep. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:19992–19997
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, San Diego
Poon A, Sawynok J (1998) Antinociception by adenosine analogs and inhibitors of adenosine metabolism in an inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia model in the rat. Pain 74:235–245
Qu WM, Yue XF, Sun Y, Fan K, Chen CR, Hou YP, Urade Y, Huang ZL (2012) Honokiol promotes non-rapid eye movement sleep via the benzodiazepine site of the GABA(A) receptor in mice. Br J Pharmacol 167:587–598
Rainnie DG, Grunze HC, McCarley RW, Greene RW (1994) Adenosine inhibition of mesopontine cholinergic neurons: implications for EEG arousal. Science 263:689–692
Raymond I, Nielsen TA, Lavigne G, Manzini C, Choiniere M (2001) Quality of sleep and its daily relationship to pain intensity in hospitalized adult burn patients. Pain 92:381–388
Rocha-Gonzalez HI, Ramirez-Aguilar M, Granados-Soto V, Reyes-Garcia JG, Torres-Lopez JE, Huerta-Cruz JC, Navarrete A (2014) Antineuropathic effect of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rodents. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:129
Roehrs T, Roth T (2005) Sleep and pain: interaction of two vital functions. Semin Neurol 25:106–116
Sawynok J, Liu XJ (2003) Adenosine in the spinal cord and periphery: release and regulation of pain. Prog Neurobiol 69:313–340
Sowa NA, Voss MK, Zylka MJ (2010) Recombinant ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) has long lasting antinociceptive effects that are dependent on adenosine A1 receptor activation. Mol Pain 6:20
Stenberg D, Litonius E, Halldner L, Johansson B, Fredholm BB, Porkka-Heiskanen T (2003) Sleep and its homeostatic regulation in mice lacking the adenosine A1 receptor. J Sleep Res 12:283–290
Svenningsson P, Hall H, Sedvall G, Fredholm BB (1997) Distribution of adenosine receptors in the postmortem human brain: an extended autoradiographic study. Synapse 27:322–335
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R, Nurmikko T, Serra J (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70:1630–1635
Tsai HY, Lin YT, Tsai CH, Chen YF (2001) Effects of paeoniflorin on the formalin-induced nociceptive behaviour in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 75:267–271
Vincenzi F, Targa M, Romagnoli R, Merighi S, Gessi S, Baraldi PG, Borea PA, Varani K (2014) TRR469, a potent A(1) adenosine receptor allosteric modulator, exhibits anti-nociceptive properties in acute and neuropathic pain models in mice. Neuropharmacology 81:6–14
Wang Q, Yue XF, Qu WM, Tan R, Zheng P, Urade Y, Huang ZL (2013) Morphine inhibits sleep-promoting neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic area via mu receptors and induces wakefulness in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:791–801
Wang TX, Yin D, Guo W, Liu YY, Li YD, Qu WM, Han WJ, Hong ZY, Huang ZL (2015) Antinociceptive and hypnotic activities of pregabalin in a neuropathic pain-like model in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 135:31–39
Wattiez AS, Libert F, Privat AM, Loiodice S, Fialip J, Eschalier A, Courteix C (2011) Evidence for a differential opioidergic involvement in the analgesic effect of antidepressants: prediction for efficacy in animal models of neuropathic pain? Br J Pharmacol 163:792–803
Wilson AR, Maher L, Morgan MM (2008) Repeated cannabinoid injections into the rat periaqueductal gray enhance subsequent morphine antinociception. Neuropharmacology 55:1219–1225
Wu YE, Li YD, Luo YJ, Wang TX, Wang HJ, Chen SN, Qu WM, Huang ZL (2015) Gelsemine alleviates both neuropathic pain and sleep disturbance in partial sciatic nerve ligation mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. doi:10.1038/aps.2015.86
Xu XH, Qiu MH, Dong H, Qu WM, Urade Y, Huang ZL (2014) GABA transporter-1 inhibitor NO-711 alters the EEG power spectra and enhances non-rapid eye movement sleep during the active phase in mice. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24:585–594
Yu HY, Liu MG, Liu DN, Shang GW, Wang Y, Qi C, Zhang KP, Song ZJ, Chen J (2007) Antinociceptive effects of systemic paeoniflorin on bee venom-induced various ‘phenotypes’ of nociception and hypersensitivity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88:131–140
Zahn PK, Straub H, Wenk M, Pogatzki-Zahn EM (2007) Adenosine A1 but not A2a receptor agonist reduces hyperalgesia caused by a surgical incision in rats: a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein-dependent process. Anesthesiology 107:797–806
Zhang XJ, Li Z, Leung WM, Liu L, Xu HX, Bian ZX (2008) The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin on neonatal maternal separation-induced visceral hyperalgesia in rats. J Pain 9:497–505
Zhang XJ, Chen HL, Li Z, Zhang HQ, Xu HX, Sung JJ, Bian ZX (2009) Analgesic effect of paeoniflorin in rats with neonatal maternal separation-induced visceral hyperalgesia is mediated through adenosine A(1) receptor by inhibiting the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) pathway. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:88–97
Zhao X, Xu Y, Zhao Q, Chen CR, Liu AM, Huang ZL (2012) Curcumin exerts antinociceptive effects in a mouse model of neuropathic pain: descending monoamine system and opioid receptors are differentially involved. Neuropharmacology 62:843–854
Zhuo M (2008) Cortical excitation and chronic pain. Trends Neurosci 31:199–207
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by grants-in-aid for scientific research from the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB711000, 2015CB856401, 2009ZX09303-006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81420108015, 81301135, 31171010, 31171049, 31121061, 31271164, J1210041, 31471064), a key laboratory program of the Education Commission of Shanghai Municipality (ZDSYS14005), the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (13ZR1403200, 14JC1400900, 13dz2260700, 13140903100), and the Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (B119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance with Ethical Standards
We declare that the experiments comply with the current laws of China.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, D., Liu, YY., Wang, TX. et al. Paeoniflorin exerts analgesic and hypnotic effects via adenosine A1 receptors in a mouse neuropathic pain model. Psychopharmacology 233, 281–293 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4108-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4108-6