Abstract
Rationale
The discriminative stimulus effects of a combination of acute morphine followed by naltrexone have been described in rats.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to extend observations to a non-human primate.
Methods
Eight squirrel monkeys were trained in a discrete-trial avoidance/escape procedure to discriminate morphine (1.7 mg/kg, IM, 4 h) followed by naltrexone (0.1 mg/kg, IM, 0.25 h) (MOR→NTX) versus saline (1.0 ml/kg, IM, 4 h) followed by naltrexone (0.1 mg/kg, IM, 0.25 h) (SAL→NTX).
Results
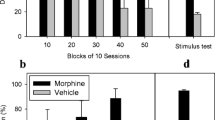
Seven subjects acquired the discrimination in an average of 108±14 sessions. MOR→NTX-appropriate responding increased as an orderly function of increasing dose of morphine (0.56–1.7 mg/kg) and of naltrexone (0.01–10 mg/kg). The discrimination was also dependent upon interval between morphine and naltrexone administration. The MOR→NTX cue was fully generalized to the combination of levorphanol (0.3 mg/kg) followed by naltrexone, but not to the non-opioid stereoisomer of levorphanol, dextrorphan (0.3 and 3.0 mg/kg) or the kappa-opioid-receptor-selective agonist U69,593 (0.3 mg/kg) followed by naltrexone. Naltrexone administered 15 min before morphine dose-dependently blocked MOR→NTX-appropriate responding.
Conclusions
This is the first non-rodent study of the discriminative effects of MOR→NTX. MOR→NTX produces a unique interoceptive stimulus that is pharmacologically selective, requires occupation of opioid receptors, presumably mu, for some minimum period of time, and is reversible. This discrimination procedure might provide new insights into the early drug-receptor interactions that underlie the development of physical dependence upon morphine-like drugs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JU, Holtzman SG (1990) Pharmacologic characterization of the sensitization to the rate-decreasing effects of naltrexone induced by acute opioid pretreatment in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:483–489
Barjavel MJ, Scherrmann JM, Bhargava HN (1995) Relationship between morphine analgesia and cortical extracellular fluid levels of morphine and its metabolites in the rat: a microdialysis study. Br J Pharmacol 116:3205–3210
Berkowitz BA (1976) The relationship of pharmacokinetics to pharmacological activity: morphine, methadone and naloxone. Clin Pharmacokinet 1:219–230
Bickel WK, Stitzer ML, Liebson IA, Bigelow GE (1988) Acute physical dependence in man: effects of naloxone after brief morphine exposure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:126–132
Bigler D, Christensen CB, Eriksen J, Jensen NH (1990) Morphine, morphine-6-glucuronide and morphine-3-glucuronide concentrations in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid during long-term high- dose intrathecal morphine administration. Pain 41:15–18
DeRossett SE, Holtzman SG (1986) Discriminative stimulus effects of the opioid antagonist diprenorphine in the squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:437–444
Dykstra LA (1983) Development of enhanced sensitivity to naloxone. Life Sci 33:2079–2089
Easterling KW, Holtzman SG (1997) Intracranial self-stimulation in rats: sensitization to an opioid antagonist following acute or chronic treatment with mu opioid agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:188–199
Easterling KW, Holtzman SG (1999) Discriminative stimulus effects of naltrexone after a single dose of morphine in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:1269–1277
Easterling KW, Plovnick RM, Holtzman SG (2000) Acute opioid but not benzodiazepine dependence in rats responding for intracranial self-stimulation. Psychopharmacology 148:263–271
Eisenberg RM (1982) Short-term tolerance to morphine: effects of diazepam, phenobarbital, and amphetamine. Life Sci 30:1615–1623
France CP, Morse WH (1989) Pharmacological characterization of supersensitivity to naltrexone in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:928–936
France CP Woods JH (1985) Opiate agonist-antagonist interactions: application of a three-key drug discrimination procedure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 234:81–89
Gellert VF, Holtzman SG (1979) Discriminative stimulus effects of naltrexone in the morphine-dependent rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 211:596–605
Goldberg SR, Morse WH, Goldberg DM (1981) Acute and chronic effects of naltrexone and naloxone on schedule-controlled behavior of squirrel monkeys and pigeons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 216:500–509
Got P, Baud FJ, Sandouk P, Diamant-Berger O, Scherrmann JM (1994) Morphine disposition in opiate-intoxicated patients: relevance of nonspecific opiate immunoassays. J Anal Toxicol 18:189–194
Hartvig P, Bergstrom K, Lindberg B, Lundberg PO, Lundqvist H, Langstrom B, Svard H, Rane A (1984) Kinetics of 11C-labeled opiates in the brain of rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:250–255
Heishman SJ, Stitzer ML, Bigelow GE, Liebson IA (1989) Acute opioid physical dependence in postaddict humans: naloxone dose effects after brief morphine exposure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:127–134
Holtzman SG (1985) Discriminative stimulus effects of morphine withdrawal in the dependent rat: suppression by opiate and nonopiate drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 233:80–86
Holtzman SG (1990) Discriminative stimulus effects of drugs: relationship to potential for abuse. In: Adler MW, Cowan A (eds) Modern methods in pharmacology, testing and evaluation of drugs of abuse. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 193–210
June HL, Stitzer ML, Cone E (1995) Acute physical dependence: time course and relation to human plasma morphine concentrations. Clin Pharmacol Ther 57:270–280
Kosersky DS, Harris RA, Harris LS (1974) Naloxone-precipitated jum** activity in mice following the acute administration of morphine. Eur J Pharmacol 26:122–124
Krystal JH, Redmond DE Jr (1983) A preliminary description of acute physical dependence on morphine in the vervet monkey. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:289–291
Mansour A, Khachaturian H, Lewis ME, Akil H, Watson SJ (1988) Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci 11:308–314
Martin WR (1983) Pharmacology of opioids. Pharmacol Rev 35:283–323
Olive MF, Bertolucci M, Evans CJ, Maidment NT (1995) Microdialysis reveals a morphine-induced increase in pallidal opioid peptide release. Neuroreport 6:1093–1096
Oliveto AH, Picker MJ, Dykstra LA (1991) Acute and chronic morphine administration: effects of mixed-action opioids in rats and squirrel monkeys responding under a schedule of food presentation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:8–18
Pitts RC, Dykstra LA (1994) Antinociceptive and response rate-altering effects of kappa opioid agonists, spiradoline, enadoline and U69,593, alone and in combination with opioid antagonists in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:1501–1508
Powell KR, Holtzman SG (1999) Differential antagonism of the rate-decreasing effects of kappa-opioid receptor agonists by naltrexone and norbinaltorphimine. Eur J Pharmacol 377:21–28
Ramabadran K (1983) Naloxone-precipitated abstinence in mice, rats and gerbils acutely dependent on morphine. Life Sci 33:385–388
Schaefer GJ, Holtzman SG (1977) Discriminative effects of morphine in the squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 201:67–75
Schlen H Bentley GA (1980) The possibility that a component of morphine-induced analgesia is contributed indirectly via the release of endogenous opioids. Pain 9:73–84
Schnur P (1991) Acute morphine dependence in the hamster. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:711–713
Schulteis G, Markou A, Gold LH, Stinus L, Koob GF (1994) Relative sensitivity to naloxone of multiple indices of opiate withdrawal: a quantitative dose-response analysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:1391–1398
Shannon HE, Holtzman SG (1976) Evaluation of the discriminative effects of morphine in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 198:54–65
Stitzer ML, Wright C, Bigelow GE, June HL, Felch LJ (1991) Time course of naloxone-precipitated withdrawal after acute methadone exposure in humans. Drug Alcohol Depend 29:39–46
Valentino RJ, Herling S, Woods JH (1983) Discriminative stimulus effects of naltrexone in narcotic-naive and morphine-treated pigeons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:307–313
Wang D, Raehal KM, Bilsky EJ, Sadee W (2001) Inverse agonists and neutral antagonists at mu opioid receptor (MOR): possible role of basal receptor signaling in narcotic dependence. J Neurochem 77:1590–1600
Wang Z, Bilsky EJ, Porreca F, Sadee W (1994) Constitutive mu opioid receptor activation as a regulatory mechanism underlying narcotic tolerance and dependence. Life Sci 54:L339–L350
White DA, Holtzman SG (2001) Acute opioid pretreatment potentiates naltrexone-induced drinking suppression in water-deprived rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:156–164
Young AM (1986) Effects of acute morphine pretreatment on the rate-decreasing and antagonist activity of naloxone. Psychopharmacology 88:201-208
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Kelly R. Powell for conducting the preliminary experiments that led the way to this study. This research was supported by NIH grants DA00541 and K05 DA00008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, D.A., Holtzman, S.G. Discriminative stimulus effects of acute morphine followed by naltrexone in the squirrel monkey. Psychopharmacology 167, 203–210 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1367-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1367-9