Abstract
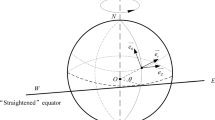
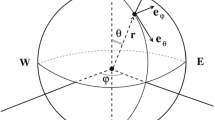
This paper is concerned with the construction of a new exact solution to the geophysical fluid dynamics governing equations for inviscid and incompressible fluid in the equatorial region. This solution represents a steady purely-azimuthal flow with a free-surface. The novel aspect of the solution we derive is that the flow it prescribes accommodates a general fluid stratification: the density may vary both with depth, and with latitude. The solution is presented in the terms of spherical coordinates, hence at no stage do we invoke approximations by way of simplifying the geometry in the governing equations. Following the construction of our explicit solution, we employ functional analytic considerations to prove that the pressure at the free-surface defines implicitly the shape of the free-surface distortion in a unique way, exhibiting also the expected monotonicity properties. Finally, using a short-wavelength stability analysis we prove that certain flows defined by our exact solution are stable for a specific choice of the density distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayly, B.J.: Three-dimensional instabilities in quasi-two dimensional inviscid flows. In: Miksad, R.W., et al. (eds.) Nonlinear Wave Interactions in Fluids, pp. 71–77. ASME, New York (1987)
Berger, M.S.: Nonlinearity and Functional Analysis. Academic Press, New York (1977)
Chen, R.M., Walsh, S., Wheeler, M.: Existence and qualitative theory for stratified solitary water waves. Ann. Inst. H. Poincaré Anal. Non Linéaire 35(2), 517–576 2018
Constantin, A.: On the modelling of equatorial waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 39, L05602 (2012)
Constantin, A., Germain, P.: Instability of some equatorially trapped waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 118, 2802–2810 (2013)
Constantin, A., Johnson, R.S.: The dynamics of waves interacting with the equatorial undercurrent. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 109(4), 311–358 (2015)
Constantin, A., Johnson, R.S.: An exact, steady, purely azimuthal equatorial flow with a free surface. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 46(6), 1935–1945 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1175/JPO-D-15-0205.1
Constantin, A., Johnson, R.S.: An exact, steady, purely azimuthal flow as a model for the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 46, 3585–3594 (2016)
Constantin, A., Ivanov, R.I.: A Hamiltonian approach to wave-current interactions in two-layer fluids. Physics of Fluids 27, 086603 (2015)
Constantin, A., Ivanov, R.I., Martin, C.I.: Hamiltonian formulation for wave-current interactions in stratified rotational flows. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal 221, 1417–1447 (2016)
Constantin, A., Johnson, R.S.: A nonlinear, three-dimensional model for ocean flows, motivated by some observations of the Pacific Equatorial Undercurrent and thermocline. Phys. Fluids 29, 056604 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4984001
Cushman-Roisin, B., Beckers, J.-M.: Introduction to Geophysical Fluid Dynamics: Physical and Numerical Aspects. Academic Press, Waltham (2011)
Escher, J., Matioc, A.-V., Matioc, B.-V.: On stratified steady periodic water waves with linear density distribution and stagnation points. J. Diff. Equ. 251, 2932–2949 (2011)
Fedorov, A.V., Brown, J.N.: Equatorial waves. In: Steele, J. (ed), Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences, pp. 3679–3695. Academic Press, New York, 2009
Friedlander, S., Vishik, M.M.: Instability criteria for the flow of an inviscid incompressible fluid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 2204–2206 (1991)
Genoud, F., Henry, D.: Instability of equatorial water waves with an underlying current. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 16, 661–667 (2014)
Gill, A.: Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics. Academic Press, New York (1982)
Henry, D., Hsu, H.-C.: Instability of internal equatorial water waves. J. Differential Equations 258(4), 1015–1024 (2015)
Henry, D., Martin, C.I.: Exact, purely azimuthal stratified equatorial flows in cylindrical coordinates. Dyn. Partial Differ. Equ. 15, 337–349 2018
Henry, D., Martin, C.-I.: Free-surface, purely azimuthal equatorial flows in spherical coordinates with stratification. J. Differential Equations, to appear
Henry, D., Matioc, A.-V.: Global bifurcation of capillary-gravity-stratified water waves. Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh Sect. A 144(4), 775–786 (2014)
Henry, D., Matioc, B.-V.: On the existence of steady periodic capillary-gravity stratified water waves. Ann. Sc. Norm. Super. Pisa Cl. Sci. (5) 12(4), 955–974 2013
Ionescu-Kruse, D.: On the short-wavelength stabilities of some geophysical flows. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 376, 20170090 (2018)
Ionescu-Kruse, D.: Local stability for an exact steady purely azimuthal flow which models the antarctic circumpolar current. J. Math Fluid Mech. 20, 569–579 (2018)
Ionescu-Kruse, D., Martin, C.I.: Local stability for an exact steady purely azimuthal equatorial flow. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 20, 27–34 (2018)
Izumo, T.: The equatorial current, meridional overturning circulation, and their roles in mass and heat exchanges during the El Niño events in the tropical Pacific Ocean. Ocean Dyn. 55, 110–123 (2005)
Johnson, G.C., McPhaden, M.J., Firing, E.: Equatorial Pacific ocean horizontal velocity, divergence, and upwelling. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 31, 839–849 (2001)
Johnson, R.S.: Application of the ideas and techniques of classical fluid mechanics to some problems in physical oceanography. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 376, 20170092 (2018)
Kessler, W.S., McPhaden, M.J.: Oceanic equatorial waves and the 1991–93 El Niño. J. Climate 8, 1757–1774 (1995)
Lifschitz, A., Hameiri, E.: Local stability conditions in fluid dynamics. Phys. Fluids 3, 2644–2651 (1991)
Martin, C.I.: On the existence of free-surface azimuthal equatorial flows. Appl. Anal. 96(7), 1207–1214 (2017)
Matioc, B.-V.: Global bifurcation for water waves with capillary effects and constant vorticity. Monatsh. Math. 174(3), 459–475 (2014)
Maslowe, S.A.: Critical layers in shear flows. Ann. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 18, 405–432 (1986)
McCreary, J.P.: Modeling equatorial ocean circulation. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 17, 359–409 (1985)
Vallis, G.K.: Atmospheric and oceanic fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press (2006)
Walsh, S.: Stratified steady periodic water waves. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 41, 1054–1105 (2009)
Walsh, S.: Steady stratified periodic gravity waves with surface tension II: global bifurcation. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 34(8), 3287–3315 (2014)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) under the research grant 13/CDA/2117. The authors would like to thank the reviewer for constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Figalli
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henry, D., Martin, C.I. Exact, Free-Surface Equatorial Flows with General Stratification in Spherical Coordinates. Arch Rational Mech Anal 233, 497–512 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00205-019-01362-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00205-019-01362-z