Abstract
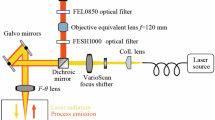
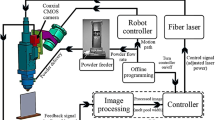
This paper presents a hybrid control system that is able to improve dimensional accuracy of geometrically complex parts manufactured by direct metal deposition process. The melt pool height is monitored by three high-speed charged couple device cameras in a triangulation setup. The melt pool temperature is monitored by a dual-color pyrometer. A two-input single-output hybrid control system including a master height controller and a slave temperature controller is used to control both height growth and melt pool temperature at each deposition layer. The height controller is a rule-based controller and the temperature controller uses a generalized predictive control algorithm with input constraints. When the melt pool height is above a prescribed layer thickness, the master height controller blocks control actions from the temperature controller and decreases laser power to avoid over-building. When the melt pool height is below the prescribed layer thickness, the temperature controller bypasses the height controller and dynamically adjusts laser power to control the melt pool temperature. This hybrid controller is able to achieve stable layer growth by avoiding both over-building and under-building through heat input control. A complex 3-D turbine blade with improved geometrical accuracy is demonstrated using the hybrid control system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu JC, Li LJ (2007) Effects of process variables on laser direct formation of thin wall. Opt Laser Technol 39(2):231–236. doi:10.1016/j.optlastec.2005.08.012
Cao X, **ao M, Jahazi M, Fournier J, Alain M (2008) Optimization of processing parameters during laser cladding of ZE41A-T5 magnesium alloy castings using Taguchi method. Mater Manuf Processes 23(3–4):413–418. doi:10.1080/10426910801940391
Meriaudeau F, Truchetet F (1996) Control and optimization of the laser cladding process using matrix cameras and image processing. J Laser Appl 8(6):317–324
Toyserkani E, Khajepour A (2006) A mechatronics approach to laser powder deposition process. Mechatronics 16(10):631–641. doi:10.1016/j.mechatronics.2006.05.002
Iravani-Tabrizipour M, Toyserkani E (2007) An image-based feature tracking algorithm for real-time measurement of clad height. Mach Vision Appl 18(6):343–354
Asselin M, Toyserkani E, Iravani-Tabrizipour M, Khajepour A (2005) Development of trinocular CCD-based optical detector for real-time monitoring of laser cladding. 2005 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automations. Conference Proceedings 1–4:1190–1196
Han L, Liou FW, Phatak KM (2004) Modeling of laser cladding with powder injection. Metall Mater Trans B-Proc Metall Mater Proc Sci 35(6):1139–1150
Iravani-Tabrizipour M, Toyserkani E (2007) An image-based feature tracking algorithm for real-time measurement of clad height. Mach Vis Appl 18:343–354. doi:10.1007/s00138-006-0066-7
Davis TA, Shin YC (2011) Vision-based clad height measurement. Mach Vision Appl 22(1):129–136. doi:10.1007/s00138-009-0240-9
Bi GJ, Gasser A, Wissenbach K, Drenker A, Poprawe R (2006) Investigation on the direct laser metallic powder deposition process via temperature measurement. Appl Surf Sci 253(3):1411–1416. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.02.025
Bi GJ, Schurmann B, Gasser A, Wissenbach K, Poprawe R (2007) Development and qualification of a novel laser-cladding head with integrated sensors. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(3–4):555–561. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.05.010
Doubenskaia M, Bertrand P, Smurov I (2004) Optical monitoring of Nd: YAG laser cladding. Thin Solid Films 453:477–485. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2003.11.184
Hu DM, Kovacevic R (2003) Sensing, modeling and control for laser-based additive manufacturing. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(1):51–60
Mazumder J, Dutta D, Kikuchi N, Ghosh A (2000) Closed loop direct metal deposition: art to part. Opt Lasers Eng 34(4–6):397–414
Koch J, Mazumder J (2000) Apparatus and methods for monitoring and controlling multi-layer laser cladding. US Patent 6,122,564, September 19
Tang L, Ruan JZ, Landers RG, Liou F (2008) Variable powder flow rate control in laser metal deposition processes. J Manufac Sci Eng Trans ASME. doi:10.1115/1.2953074
Fathi A, Khajepour A, Durali M, Toyserkani E (2008) Geometry control of the deposited layer in a nonplanar laser cladding process using a variable structure controller. J Manufact Sci Eng-Trans ASME. doi:10.1115/1.2823085
Fathi A, Khajepour A, Toyserkani E, Durali M (2007) Clad height control in laser solid freeform fabrication using a feedforward PID controller. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 35:280–292. doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0721-1
Liu JC, Li LJ (2004) In-time motion adjustment in laser cladding manufacturing process for improving dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the formed part. Opt Laser Technol 36(6):477–483. doi:10.1016/j.optlastec.2003.12.003
Zeinali M, Khajepour A (2010) Height control in laser cladding using adaptive sliding mode technique: theory and experiment. J Manufac Sci Eng-Trans ASME. doi:10.1115/1.4002023
Salehi D, Brandt M (2006) Melt pool temperature control using LabVIEW in Nd: YAG laser blown powder cladding process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 29(3–4):273–278. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-2514-3
Fox MDT, Hand DP, Su DN, Jones JDC, Morgan SA, McLean MA, Steen WM (1998) Optical sensor to monitor and control temperature and build height of the laser direct-casting process. Appl Opt 37(36):8429–8433
Qi H, Azer M, Singh P (2010) Adaptive toolpath deposition method for laser net shape manufacturing and repair of turbine compressor airfoils. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 48(1–4):121–131. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-2265-7
Hua Y, Choi J (2005) Adaptive direct metal/material deposition process using a fuzzy logic-based controller. J Laser Appl 17(4):200–210
Mazumder J, Dutta B (2009) Rapid, ultra precision direct metal deposition technology, Technical Report to Advanced Technology Program National Institute of Standards and Technology, Technology Administration, US Department of Commerce
Li YX, Ma J (1997) Study on overlap** in the laser cladding process. Surf Coat Tech 90(1–2):1–5
Ordys AW, Clarke DW (1993) A state-space description for GPC controllers. Int J Syst Sci 24(9):1727–1744
Hsiao FH, Chen CW, Liang YW, Xu SD, Chiang WL (2005) T-S fuzzy controllers for nonlinear interconnected systems with multiple time delays. IEEE T Circuits-I 52(9):1883–1893. doi:10.1109/Tcsi.2005.852492
Chen CW (2009) Modeling and control for nonlinear structural systems via a NN-based approach. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):4765–4772. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2008.06.062
Chen CY, Lin JW, Lee WI, Chen CW (2010) Fuzzy control for an oceanic structure: a case study in time-delay TLP system. J Vib Control 16(1):147–160. doi:10.1177/1077546309339424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, L., Bagavath-Singh, V., Dutta, B. et al. Control of melt pool temperature and deposition height during direct metal deposition process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58, 247–256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3395-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3395-2