Abstract
In 1963, selenosis occurred in Yutangba Village, Enshi City, China. Subsequently, local residents migrated to a new area of Yutangba to avoid high selenium (Se) exposure. In this study, 19 soil samples, 43 food samples, 60 hair samples and 58 plasma samples from local residents were randomly collected in New Yutangba Village. The mean total Se concentrations in cultivated soil samples were 1753.6 ± 742.8 µg/kg (n = 14). The estimated daily Se intake in New Yutangba Village decreased to 63.2 ± 39.8 µg/day, slightly higher than the recommended dietary Se intake for adults in China (60 µg/day). The mean Se concentrations in hair and plasma samples were 549.7 ± 165.2 µg/kg (n = 60) and 98.4 ± 32.1 µg/L (n = 58), respectively. The result indicated that appropriate activities, such as relocation, consuming a mixture of local foods and market foods containing low Se concentration, could effectively reduce the risk of high Se exposure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajaj M, Eiche E, Neumann T, Winter J, Gallert C (2011) Hazardous concentrations of selenium in soil and groundwater in North-West India. J Hazard Mater 189(3):640–646
Berthold HK, Michalke B, Krone W, Guallar E, Gouni-Berthold I (2012) Influence of serum selenium concentrations on hypertension: the Lipid Analytic Cologne cross-sectional study. J Hypertens 30(7):1328–1335
Chang C, Yin R, Zhang H, Yao L (2019) Bioaccumulation and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil–rice system in a typical seleniferous area in central China. Environ Toxicol Chem 38:1577–1584
Chen DJ (2012) Selenium geochemical characteristics in Zoige area. Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, pp 48–53
Chen SQ, Peng ZS, He XH, Huang W, Liao ML, Wu RP, Liu JH, Zhu YF, Mou ZH, Tian E, **e WM (2018) Investigation on blood and nail selenium of residents in environment with different selenium levels in Enshi, Hubei province. J Environ Hyg 8(1):18–23 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Chinese Society of Nutrition (2016) Dietary reference intakes of Chinese residents. Acta Nutr Sin. (in Chinese)
Combs GF Jr. (2015) Biomarkers of selenium status. Nutrients 7(4):2209–2236
Combs GF Jr., Watts JC, Jackson MI, Johnson LK, Zeng H, Scheett AJ, Uthus EO, Schomburg L, Hoeg A, Hoefig CS, Davis CD, Milner JA (2011) Determinants of selenium status in healthy adults. Nutr J 10:75
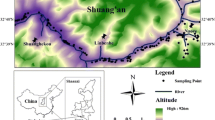
Cui Z, Huang J, Peng Q, Yu D, Wang S, Liang D (2017) Risk assessment for human health in a seleniferous area, Shuang’an, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(21):17701–17710
Dinh QT, Cui Z, Huang J, Tran TAT, Wang D, Yang W, Zhou F, Wang M, Yu D, Liang D (2018) Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: a review. Environ Int 112:294–309
Fairweather-Tait SJ, Bao Y, Broadley MR, Collings R, Ford D, Hesketh JE, Hurst R (2011) Selenium in human health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(7):1337–1383
Flohé L, Brigelius-Flohé R (2006) Selenoproteins of the glutathione system, Chap. 15. In: Hatfield DL, Berry MJ, Gladyshev VN (eds) Selenium: its molecular biology and role in human health. Springer, New York, pp 161–172
Fordyce FM, Zhang GD, Green K, Liu XP (2000) Soil, grain and water chemistry in relation to human selenium-responsive diseases in Enshi District, China. Appl Geochem 15(1):117–132
Gao J, Liu Y, Huang Y, Lin ZQ, Banuelos GS, Lam MHW, Yin XB (2011) Daily selenium intake in a moderate selenium deficiency area of Suzhou, China. Food Chem 126(3):1088–1093
Gao H, Hagg S, Sjogren P, Lambert PC, Ingelsson E, van Dam RM (2014) Serum selenium in relation to measures of glucose metabolism and incidence of Type 2 diabetes in an older Swedish population. Diabetic Med 31(7):787–793
Hansen JC, Deutch B, Pedersen HS (2004) Selenium status in Greenland Inuit. Sci Total Environ 331(1–3):207–214
Hill KE, **a Y, Akesson B, Boeglin ME, Burk RF (1996) Selenoprotein P concentration in plasma is an index of selenium status in selenium-deficient and selenium-supplemented Chinese subjects. J Nutr 126(1):138–145
Hira CK, Partal K, Dhillon K (2004) Dietary selenium intake by men and women in high and low selenium areas of Punjab. Public Health Nutr 7(1):39–43
Huang QG, Li DW, Zhu XS, Yuan WW, Zhang DY, Zhang ZZ (2010) Investigation of Keshan disease in Wanyuan in 2008. J Prev Med Inf 26:409–410 (in Chinese)
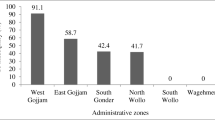
Huang Y, Wang Q, Gao J, Lin Z, Banuelos GS, Yuan L, Yin X (2013) Daily dietary selenium intake in a high selenium area of Enshi. China Nutr 5(3):700–710
Hybsier S, Schulz T, Wu Z, Demuth I, Minich WB, Renko K, Rijntjes E, Kohrle J, Strasburger CJ, Steinhagen-Thiessen E, Schomburg L (2017) Sex-specific and inter-individual differences in biomarkers of selenium status identified by a calibrated ELISA for selenoprotein P. Redox Biol 11:403–414
Janghorbani M, **a Y, Ha P, Whanger PD, Butler JA, Olesik JW, Grunwald E (1999) Effect of dietary selenium restriction on selected parameters of selenium status in men with high life-long intake. J Nutr Biochem 10(10):564–572
Jian ZS, Yu XT, Huang J (2007) The study of the dietary structure and nutrient of residents in iodine deficiency area. J Public Health Prev Med 1:59–60
Long Z, Yuan L, Hou Y, Banuelos GS, Liu Y, Pan L, Liu X, Yin X (2018) Spatial variations in soil selenium and residential dietary selenium intake in a selenium-rich county, Shitai, Anhui, China. J Trace Elem Med Biol 50:111–116
Mao DJ, Zheng BS, Su HC (1997) The medical geography characteristics of Se-poisoning in Yutangba. Endem Dis Bull 12:59–61 (in Chinese)
Martens DA, Suarez DL (1997) Selenium speciation of soil/sediment determined with sequential extractions and hydride generation atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Environ Sci Technol 31(1):133–139
Navarro-Alarcon M, Cabrera-Vique C (2008) Selenium in food and the human body: a review. Sci Total Environ 400(1–3):115–141
Pedrosa LFC, Motley AK, Stevenson TD, Hill KE, Burk RF (2012) Fecal selenium excretion is regulated by dietary selenium intake 1. Biol Trace Elem Res 149:377–381
Qin HB, Zhu JM, Liang L, Wang MS, Su H (2013) The bioavailability of selenium and risk assessment for human selenium poisoning in high-Se areas, China. Environ Int 52:66–74
Rasmussen LB, Hollenbach B, Laurberg P, Carle A, Hog A, Jorgensen T, Vejbjerg P, Ovesen L, Schomburg L (2009) Serum selenium and selenoprotein P status in adult Danes – 8-year followup. J Trace Elem Med Biol 23(4):265–271
Stroud JL, Broadley MR, Foot I, Fairweather-Tait SJ, Hart DJ, Hurst R, Knott P, Mowat H, Norman K, Scott P, Tucker M, White PJ, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2010) Soil factors affecting selenium concentration in wheat grain and the fate and speciation of Se fertilisers applied to soil. Plant Soil 332(1–2):19–30
Tan JA (1989) The Atlas of Endemic diseases and their environments in the People’s Republic of China. Science Press, China
Ullah H, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ali MU, Abbas Q, Munir MAM, Mian MM (2018) Developmental selenium exposure and health risk in daily foodstuffs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:291–306
**a YM, Hill KE, Byrne DW, Xu JY, Burk RF (2005) Effectiveness of selenium supplements in a low-selenium area of China. Am J Clin Nutr 81(4):829–834
**a Y, Hill KE, Li P, Xu J, Zhou D, Motley AK, Wang L, Byrne DW, Burk RF (2010) Optimization of selenoprotein P and other plasma selenium biomarkers for the assessment of the selenium nutritional requirement: a placebo-controlled, double-blind study of selenomethionine supplementation in selenium-deficient Chinese subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 92(3):525–531
Yan MS, Zhang MZ, Tang J, Gong YY, Dong P, Liu JF (2012) Selenium content distribution in surface soil of Chongqing North Fujian and its agricultural economic significance. J Earth Environ 40(4):589–594
Yang GQ, Wang SZ, Zhou RH, Sun SZ, Man RE (1981) Research on the etiology of an endemic disease characterized by loss of nails and hair in Enshi county. J Chin Acad Med 3(Suppl 2):1–6 (in Chinese)
Yuan LX, Zhu YY, Lin ZQ, Banuelos G, Li W, Yin XB (2013) A novel selenocystine-accumulating plant in selenium-mine drainage area in Enshi, China. Plos One 8:6
Zhao B, Zhou SB, Wu X (2018) Distribution and accumulation of selenium in plants and health risk assessment from a selenium-rich area in China. Pol J Environ Stud 27(6):2873–2882
Zhu J, Zheng B (2001) Distribution of selenium in a mini-landscape of Yutangba, Enshi, Hubei Province, China. Appl Geochem 16(11–12):1333–1344
Zhu J, Wang N, Li S, Li L, Su H, Liu C (2008) Distribution and transport of selenium in Yutangba, China: impact of human activities. Sci Total Environ 392(2–3):252–261
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Bureau of Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture (Grant No. XYJ2018000080), Guangxi Innovation Special Project (Grant Nos. GKAA17202026, AA17202027-3, AA17202038-1, AA17202010, AA17202044-1, AA17202019-2), Shanxi Keypoint Research and Invention Program (Grant No. 201703D211001), Special Plan of Scientific Research for Shanxi Agriculture Valley Construction of China (Grant No. SXNGJSKYZX201706), and the Natural Selenium Biofortification Program (NBP) by the International Society for Selenium Research (ISSR). Thanks for the local CDC for collecting blood samples. Thanks should go to Ning Zhang and Xu Tian for sampling and questionnaire serveying. Thanks for students from School of Public Health in Soochow University for questionnaire investigation. We also thank International Science Editing (http://www.internationalscienceediting.com) for editing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Z., **ang, J., Song, J. et al. Soil Selenium Concentration and Residents Daily Dietary Intake in a Selenosis Area: A Preliminary Study in Yutangba Village, Enshi City, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 105, 798–805 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02983-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02983-x