Abstract
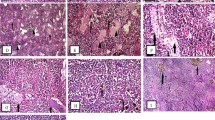
Two sampling sites contaminated with high aqueous metal concentrations in the vicinity of metal-related factories (site2) and 7 km downstream (site3) were selected along river Nile. These sites were compared to reference fish farm (site1) that fed on unpolluted water source. Bioaccumulation of metals (Cu, Zn, Pb, Fe, Mn and Cd) in Oreochromis niloticus showed a tissue-specific pattern with high rate of accumulation in gills, liver and kidney. The lowest concentrations of almost all metals were observed in muscle. The accumulated pattern was confirmed by histopathological examination of gills, liver and kidneys. Tissues from site2 and 3 revealed various histopathological alterations ranging from compensatory histological changes to histological damage. Evaluation of human health hazard using metals hazard index values in skin and muscle showed that all metals were in the safe limits for human intake except in the case of zinc and cadmium in skin at subsistence consumption level.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Mousa MAA, Ahmad MH, Sakr SFM (2007) The use of calcium pre-exposure as a protective agent against environmental copper toxicity for juvenile Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquaculture 264:236–246
Al-Yousuf MH, El-Shahawi MS, Al-Ghais SM (2000) Trace metals in liver, skin and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex. Sci Total Environ 256:87–94
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, New York
Atli G, Canli M (2010) Response of antioxidant system of fresh water fish Oreochromis niloticus to acute and chronic metal (Cd, Cu, Cr, Zn, Fe) exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1884–1889
Bernet D, Schmidt H, Meier W, Burkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T (1999) Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J Fish Dis 22:25–34
Bhagwant S, Elahee KB (2002) Pathologic gill lesions in two edible lagoon fish species, Mulloidichthys flavolineatus and Mugil cephalus, from the Bay of Poudre d’Or, Mauritius, Western Indian Ocean. J Mar Sci 1:35–42
Campbell PGC, Giguère A, Bonneris E, Hare L (2005) Cadmium handling strategies in two chronically indigenous freshwater organisms: the yellow perch (Perca flavescens) and the floater mollusc (Pyganodon grandis). Aquat Toxicol 72:83–97
CCME (1999) Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: summary table. Canadian environmental quality guidelines. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg
Copat C, Bella F, Castaing M, Fallico R, Sciacca S, Ferrante M (2012) Heavy metals concentrations in fish from sicily (Mediterranean sea) and evaluation of possible health risks to consumers. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:78–83
FAO/WHO (2006) A model for establishing upper levels of intake for nutrients and related substances. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization, FAO/WHO Nutrient Risk Assessment Workshop, 2–6 May 2005, WHO Headquarters, Geneva
Ferguson HW (1989) Text book of systemic pathology of fish, 1st edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames Iowa, Canada
Karadede H, Seyit A, Erhan Ü (2004) Heavy metals in mullet, Liza abu, and catfish, Silurus triostegus, from the Atatürk Dam Lake (Euphrates), Turkey. Environ Int 30:183–188
Kotze P, Preez HH, Van Vuren JHJ (1999) Bioaccumulation of copper and zinc in Oreochromis mossambicus and Clarias gariepinus, from the Olifants river, Mpumalanga, South Africa. Water SA 25:99–100
Luoma SN, Cain DJ, Rainbow PS (2010) Calibrating biomonitors to ecological disturbance: a new technique for explaining metal effects in natural waters. Integr Environ Assess Manag 6:199–209
Malik N, Biswas AK, Qureshi TA, Borana K, Virha R (2010) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish tissues of a freshwater lake of Bhopal. Environ Monit Assess 160:267–276
Manahan SE (1991) Water pollution environment chemistry, 1st edn. Lewis Publishers, London
Mohamed FAS (2009) Histopathological studies on Tilapia zilli and Solea vulgaris from lake Qarun, Egypt. World J Fish Mar Sci 1:29–39
Nsikak UB, Joseph PE, Akan BW, David EB (2007) Mercury accumulation in fishes from tropical aquatic ecosystems in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Curr Sci 92:781–785
Oliveira-Ribeiro CA, Belger L, Pelletiter E, Rouleau C (2002) Histopathological evidence of inorganic mercury and methylmercury toxicity in the arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Environ Res 90:217–225
Omar WA, Zaghloul KH, Abdel-Khalek AA, Abo-Hegab S (2013) Risk assessment and toxic effects of metal pollution in two cultured and wild fish species from highly degraded aquatic habitats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:753–764
Onsanit S, Ke CH, Wang XH, Wang KJ, Wang WX (2010) Trace elements in two marine fish cultured in fish cages in Fujian province, China. Environ Pollut 158:1334–1342
Ptashynski MD, Pedlar RM, Evans RE, Baron CL, Klaverkamp JF (2002) Toxicology of dietary nickel in lake whitefish (Coregonus clupeaformis). Aquatic Toxicol 58:229–247
Qiao-qiao C, Guang-wei Z, Langdon A (2007) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fishes from Taihu Lake, China. J Environ Sci 19:1500–1504
Rainbow PS (2007) Trace metal bioaccumulation: models, metabolic availability and toxicity. Environ Int 33:576–582
SAS (2006) SAS/STAT User’s Guide, Version 9.1, SAS Institute Inc., Statistical Analysis System, Cary, NC, USA
Thophon S, Kruatrachue M, Upatham ES, Pokethitiyook P, Sahaphong S, Jaritkhuan S (2003) Histopathological alterations of white seabass, Lates calcarifer, in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environ Pollut 121:307–320
Turkmen A, Turkmen M, Tepe Y, Mazlum Y, Oymael S (2006) Metal concentrations in Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) and Mullet (Mugil cephalus) in Iskenderun Bay, Northern East Mediterranean, Turkey. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 77:186–193
Uluturhan E, Kucuksezgin F (2007) Heavy metal contaminations in Red Pandora (Pagellus erythrinus) tissues from the Eastern Aegean Sea, Turkey. Water Res 41:1185–1192
U.S.EPA (2000) Guidance for assessing chemical contaminant data for use in fish advisories. Vol 2, Risk assessment and fish consumption limits (3rd ed.), United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, Office of Science and Technology and Office of Water, (EPA/823/B-97/009)
van Dyk JC, Pieterse GM, van Vuren JHJ (2007) Histological changes in the liver of Oreochromis mossambicus (Cichlidae) after exposure to cadmium and zinc. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66:432–440
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Khalek, A.A. Risk Assessment, Bioaccumulation of Metals and Histopathological Alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Facing Degraded Aquatic Conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94, 77–83 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1400-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1400-9