Abstract
Key message
The genetic basis of GLS resistance was dissected using two DH populations sharing a common resistant parent. A major QTL repeatedly detected in multiple developmental stages and environments was fine mapped in a backcross population.
Abstract
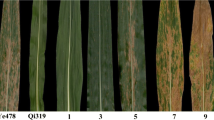
Grey leaf spot (GLS), caused by Cercospora zeae-maydis or Cercospora zeina, is a highly destructive foliar disease worldwide. However, the mechanism of resistance against GLS is not well understood. To study the inheritance of this resistance, we developed two doubled haploid (DH) populations sharing a common resistant parent. The two DH populations were grown in two locations representing the typical maize-growing mountain area in Southwest China for 2 years. GLS disease severity was investigated 2 or 3 times until maturity in the 2 years, and the area under the disease progress curve was calculated. Two high-density linkage maps were constructed by genoty**-by-sequencing. A total of 22 quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were detected for GLS resistance, with most QTLs being repeatedly detected in different stages, locations and years. The confidence intervals of two major QTLs (qGLS_Y2-2 and qGLS_Z2-1) on chromosome 2 from the two DH populations overlapped with each other and were integrated into one consensus QTL (qGLS_YZ2-1). Using highly resistant and highly susceptible plants from a BC3 population, we fine mapped this genetic locus to a genomic region of 2.4 Mb. Using a panel of 255 inbred lines from breeding programmes, we detected associations between markers in the qGLS_YZ2-1 region and GLS resistance. The peak marker (ID-B1) will be very useful for marker-assisted breeding for GLS resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcade A, Labourdette A, Falque M, Mangin B, Chardon F, Charcosset A, Joets J (2004) BioMercator: integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20:2324–2326
Asea G, Vivek B, Bigirwa G, Lipps PE, Pratt RC (2009) Validation of consensus quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to multiple foliar pathogens of maize. Phytopathology 99:540–547
Balint-Kurti PJ, Wisser R, Zwonitzer JC (2008) Use of an advanced intercross line population for precise map** of quantitative trait loci for gray leaf spot resistance in maize. Crop Sci 48:1696–1704
Benson J, Poland J, Benson BM, Stromberg EL, Nelson RJ (2015) Resistance to gray leaf spot of maize: genetic architecture and mechanisms elucidated through nested association map** and near-isogenic line analysis. PLoS Genet 11:e1005045
Berger DK, Carstens M, Korsman J, Middleton F, Kloppers FJ, Tongoona P, Myburg AA (2014) Map** QTL conferring resistance in maize to gray leaf spot disease caused by Cercospora zeina. BMC Genet 15:60
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association map** of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635
Brunelli KR, Dunkle LD, Sobrinho CA, Fazza AC, Camargo LEA (2008) Molecular variability in the maize grey leaf spot pathogens in Brazil. Genet Mol Biol 31:938–942
Bubeck D, Goodman M, Beavis W, Grant D (1993) Quantitative trait loci controlling resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Crop Sci 33:838–847
Campbell CL, Madden LV (1990) Introduction to plant disease epidemiology. Wiley, New York, p 532
Chung C, Poland J, Kump KL, Benson J, Longfellow J, Walsh E, Balint-kurti PJ, Nelson RJ (2011) Targeted discovery of quantitative trait loci for resistance to northern leaf blight and other diseases of maize. Theor Appl Genet 123:307–326
Clements MJ, Dudley JW, White DG (2000) Quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to gray leaf spot of corn. Phytopathology 90:1018–1025
Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Groenewald M, Caldwell P, Braun U, Harrington TC (2006) Species of Cercospora associated with grey leaf spot of maize. Stud Mycol 55:189–197
Dunkle LD, Levy M (2000) Genetic relatedness of African and United States populations of Cercospora zeae-maydis. Phytopathology 90:486–490
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland J, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, Mitchell SE (2011) A robust simple genoty**-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6:e19379
Gordon SG, Bartsch M, Matthies I, Gevers HO, Lipps PE, Pratt RC (2004) Linkage of molecular markers to Cercospora zeae-maydis resistance in maize. Crop Sci 44:628–636
He W, Yang L, Leng Y, Zhang B, Yang J, Li L, Chen Y, Kang J, Tang H, Deng L, Wu Y, Cao M, Rong T (2018) QTL map** for resistance of maize to grey leaf spot. J Phytopathol 166:167–176
Hwang S, Wang H, Gossen BD, Chang KF, Turnbull GD, Howard RJ (2006) Impact of foliar diseases on photosynthesis, protein content and seed yield of alfalfa and efficacy of fungicide application. Eur J Plant Pathol 115:389–399
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis. Crop Sci 25:192–194
Latterell FM, Rossi AE (1983) Gray leaf spot of corn: a disease on the move. Plant Dis 67:842–847
Lehmensiek A, Esterhuizen AM, Van Staden D, Nelson SW, Retief AE (2001) Genetic map** of gray leaf spot (GLS) resistance genes in maize. Theor Appl Genet 103:797–803
Lennon JR, Krakowsky MD, Goodman MM, Flintgarcia S, Balint-kurti PJ (2016) Identification of alleles conferring resistance to gray leaf spot in maize derived from its wild progenitor species teosinte. Crop Sci 56:209–218
Lipps PE (1998) Gray leaf spot: a global threat to corn production. APSNet Featur. https://doi.org/10.1094/APSnetFeature-1998-0598
Liu KJ, Xu XD (2013) First report of gray leaf spot of maize caused by Cercospora zeina in China. Plant Dis 97:1656
Mammadov J, Sun X, Gao Y, Ochsenfeld C, Bakker E, Ren R, Flora J, Wang X, Kumpatla SP, Meyer D (2015) Combining powers of linkage and association map** for precise dissection of QTL controlling resistance to gray leaf spot disease in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Genom 16:916–916
Maroof MAS, Yue YG, **ang ZX, Stromberg EL, Rufener GK (1996) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling resistance to gray leaf spot disease in maize. Theor Appl Genet 93:539–546
McCouch S, Cho Y, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–13
Mckenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky AM, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel SB, Daly MJ (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Meisel B, Korsman J, Kloppers FJ, Berger DK (2009) Cercospora zeina is the causal agent of grey leaf spot disease of maize in southern Africa. Eur J Plant Pathol 124:577–583
Menkir A, Ayodele M (2005) Genetic analysis of resistance to gray leaf spot of midaltitude maize inbred lines. Crop Sci 45:163–170
Munkvold GP, Martinson CA, Shriver JM, Dixon PM (2001) Probabilities for profitable fungicide use against gray leaf spot in hybrid maize. Phytopathology 91:477–484
Ngoko Z, Cardwell KF, Marasas WFO, Wingfield MJ, Ndemah R, Schulthess F (2002) Biological and physical constraints on maize production in the humid forest and western highlands of Cameroon. Eur J Plant Pathol 108:893–902
Okori P, Fahleson J, Rubaihayo P, Adipala E, Dixelius C (2003) Assessment of genetic variation among East African Cercospora zeae-maydis. Afr Crop Sci 11:75–85
Pozar G, Butruille D, Silva HD, Mccuddin Z, Penna JCV (2009) Map** and validation of quantitative trait loci for resistance to Cercospora zeae-maydis infection in tropical maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 118:553–564
Pratt RC, Gordon SG, Lipps PE, Asea G, Bigirwa G, Pixley KV (2004) Use of IPM in the control of multiple diseases in maize: strategies for selection of host resistance. Afr Crop Sci J 11:189–198
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Salvi S, Tuberosa R (2005) To clone or not to clone plant QTLs: present and future challenges. Trends Plant Sci 10(6):297–304
Shi L, Li X, Hao Z, ** of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize based on bioinformatics. Agric Sci China 6(12):1411–1419
Shi L, Lv X, Weng J, Zhu H, Liu C, Hao Z, Zhou Y, Zhang D, Li M, Ci X, Li X, Zhang S (2014) Genetic characterization and linkage disequilibrium map** of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize (Zea mays L.). Crop J 2(2):132–143
Sriwatanapongse S, **ahyon S, Vasal SK (1993) Suwan-1: Maize from Thailand to the world. Mexico, DF: CIMMYT
Tehon LR (1924) Notes on the parasitic fungi of Illinois. III. Mycologia 17:110–129
Van Os H, Stam P, Visser RGF, Van Eck HJ (2005) SMOOTH: a statistical method for successful removal of genoty** errors from high-density genetic linkage data. Theor Appl Genet 112:187–194
Wang S, Basten C, Zeng Z (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University
Ward JMJ, Stromberg EL, Nowell DC, Nutter FW (1999) Gray leaf spot: a disease of global importance in maize production. Plant Dis 83:884–895
Wu C, Ma LJ, Sun Y et al (1992) Outbreak of a new leaf spot disease of maize caused by Cercospora zeae-maydis. J Maize Sci 1992:67–68
Wu Y, Bhat PR, Close TJ, Lonardi S (2008) Efficient and accurate construction of genetic linkage maps from the minimum spanning tree of a graph. PLoS Genet 4:e1000212
Wu Z, Wang B, Chen X, Wu J, King GJ, **ao Y, Liu K (2016) Evaluation of linkage disequilibrium pattern and association study on seed oil content in Brassica napus using ddRAD sequencing. PLoS ONE 11:e0146383
** for constructing an ultrahigh-density linkage map based on population sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:10578–10583
Xu L, Zhang Y, Shao S, Chen W, Tan J, Zhu M, Zhong T, Fan X, Xu M (2014) High-resolution map** and characterization of qRgls2, a major quantitative trait locus involved in maize resistance to gray leaf spot. BMC Plant Biol 14:230
Yang Q, He Y, Kabahuma M, Chaya T, Kelly A, Borrego E, Bian Y, Kasmi FE, Yang L, Teixeira PJPL (2017) A gene encoding maize caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase confers quantitative resistance to multiple pathogens. Nat Genet 49:1364–1372
Zhang Y, Xu L, Fan X, Tan J, Chen W, Xu M (2012) QTL map** of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 125:1797–1808
Zhang X, Yang Q, Rucker E, Thomason WE, Balint-kurti PJ (2017) Fine map** of a quantitative resistance gene for gray leaf spot of maize (Zea mays L.) derived from teosinte (Z. mays ssp. parviglumis). Theor Appl Genet 130:1285–1295
Zwonitzer JC, Coles ND, Krakowsky MD, Arellano C, Holland JB, Mcmullen MD, Pratt RC, Balint-kurti PJ (2010) Map** resistance quantitative trait loci for three foliar diseases in a maize recombinant inbred line population—evidence for multiple disease resistance? Phytopathology 100:72–79
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0101205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LD, KL and YL designed the study. KL and YL supervised the study. LD, HZ, CY, WX and KM performed the experiments. LD, FY, BW and XH analysed the data. LD and KL prepared the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments were performed in compliance with the current laws of China.
Additional information
Communicated by Thomas Lubberstedt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, L., Yu, F., Zhang, H. et al. Genetic map** of quantitative trait loci and a major locus for resistance to grey leaf spot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 133, 2521–2533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03614-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03614-z