Abstract
Key message
Seven kernel dimension QTLs were identified in wheat, and kernel thickness was found to be the most important dimension for grain weight improvement.
Abstract
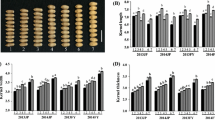
Kernel morphology and weight of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) affect both yield and quality; however, the genetic basis of these traits and their interactions has not been fully understood. In this study, to investigate the genetic factors affecting kernel morphology and the association of kernel morphology traits with kernel weight, kernel length (KL), width (KW) and thickness (KT) were evaluated, together with hundred-grain weight (HGW), in a recombinant inbred line population derived from Nanda2419 × Wangshuibai, with data from five trials (two different locations over 3 years). The results showed that HGW was more closely correlated with KT and KW than with KL. A whole genome scan revealed four QTLs for KL, one for KW and two for KT, distributed on five different chromosomes. Of them, QKl.nau-2D for KL, and QKt.nau-4B and QKt.nau-5A for KT were newly identified major QTLs for the respective traits, explaining up to 32.6 and 41.5% of the phenotypic variations, respectively. Increase of KW and KT and reduction of KL/KT and KW/KT ratios always resulted in significant higher grain weight. Lines combining the Nanda 2419 alleles of the 4B and 5A intervals had wider, thicker, rounder kernels and a 14% higher grain weight in the genotype-based analysis. A strong, negative linear relationship of the KW/KT ratio with grain weight was observed. It thus appears that kernel thickness is the most important kernel dimension factor in wheat improvement for higher yield. Map** and marker identification of the kernel dimension-related QTLs definitely help realize the breeding goals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammiraju JSS, Dholakia BB, Santra DK, Singh H, Lagu MD, Tamhankar SA, Dhaliwal HS, Rao VS, Gupta VS, Ranjekar PK (2001) Identification of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers associated with seed size in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 102:726–732
Ammiraju JSS, Dholakia BB, Jawdekar G, Santra DK, Röder MS, Singh HS, Lagu MD, Dhaliwal HS, Rao VS, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS (2004) Identification of chromosomal regions governing grain size and shape in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Genet Breed 58:91–100
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME (2006) Association map** of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME (2007) QTL analysis of kernel size and shape in two hexaploid wheat map** populations. Field Crops Res 101:171–179
Campbell KG, Bergman CJ, Gualberto DG, Anderson JA, Giroux MJ, Hareland G, Fulcher RG, Sorrells ME, Finney PL (1999) Quantitative trait loci associated with kernel traits in a soft × hard wheat cross. Crop Sci 39:1184–1195
Chastain TG, Ward KJ, Wysocki DJ (1995) Stand establishment responses of soft white winter wheat to seedbed residue and seed size. Crop Sci 35:213–218
Cui F, Zhao C, Ding A, Li J, Wang L, Li X, Bao Y, Li J, Wang H (2014) Construction of an integrative linkage map and QTL map** of grain yield-related traits using three related wheat RIL populations. Theor Appl Genet 127:659–675
Dholakia BB, Ammiraju JSS, Singh H, Lagu MD, Rörner MS, Rao VS, Dhaliwal HS, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS (2003) Molecular marker analysis of kernel size and shape in bread wheat. Plant Breed 122:392–395
Echeverry-Solarte M, Kumar A, Kianian S, Mantovani EE, McClean PE, Deckard EL, Elias E, Simsek S, Alamri MS, Schatz B, Mergoum M (2015) Genome-wide map** of spike-related and agronomic traits in a common wheat population derived from a supernumerary parent and an elite parent. Plant. Genome. doi:10.3835/plantgenome2014.12.0089
Fan C, **ng Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171
Gegas VC, Nazari A, Griffiths S, Simmonds J, Fish L, Orford S, Sayers L, Doonan JH, Snape JW (2010) A genetic framework for grain size and shape variation in wheat. Plant Cell 22:1046–1056
Jia H, Wan H, Yang S, Zhang Z, Kong Z, Xue S, Zhang L, Ma Z (2013) Genetic dissection of yield-related traits in a recombinant inbred line population created using a key breeding parent in China’s wheat breeding. Theor Appl Genet 126:2123–2139
Li Y, Fan C, **ngY, JiangY, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, **ao J (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43:1266–1269
Li Q, Zhang Y, Liu TT, Wang FF, Liu K, Chen JS, Tian JC (2015) Genetic analysis of kernel weight and kernel size in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using unconditional and conditional QTL map**. Mol Breed 35:1–15
Lin F, Kong Z, Zhu H, Xue S, Wu J, Tian D, Wei J, Zhang C, Ma Z (2004) Map** QTL associated with resistance to Fusarium head blight in the Nanda2419 × Wangshuibai population. I. Type II resistance. Theor Appl Genet 109:1504–1511
Liu R, Meng J (2003) MapDraw: a Microsoft Excel macro for drawing genetic linkage maps based on given genetic linkage data. Heraditas 25:317–321
Liu Y, Wang L, Sun C, Zhang Z, Zheng Y, Qiu F (2014) Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 127:1019–1037
Lizana XC, Riegel R, Gomez LD, Herrera J, Isla A, McQueen-Mason SJ, Calderini DF (2010) Expansins expression is associated with grain size dynamics in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Exp Bot 61:1147–1157
Ma L, Li T, Hao C, Wang Y, Chen X, Zhang X (2016) TaGS5-3A, a grain size gene selected during wheat improvement for larger kernel and yield. Plant Biotechnol J. 14:1269–1280
Maphosa L, Langridge P, Taylor H, Parent B, Emebiri LC, Kuchel H, Reynolds MP, Chalmers KJ, Okada A, Edwards J, Mather DE (2014) Genetic control of grain yield and grain physical characteristics in a bread wheat population grown under a range of environmental conditions. Theor Appl Genet 127:1607–1624
Marshall D, Mares DJ, Moss HJ, Ellison F (1986) Effects of grain shape and size on milling yields in wheat. II. Experimental studies. Aust J Agr Res 37:331–342
Okamoto Y, Nguyen AT, Yoshioka M, Iehisa JC, Takumi S (2013) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling grain size and shape in the D genome of synthetic hexaploid wheat lines. Breed Sci 63:423–429
Prashant R, Kadoo N, Desale C, Kore P, Dhaliwal HS, Chhuneja P, Gupta V (2012) Kernel morphometric traits in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) are modulated by intricate QTL × QTL and genotype × environment interactions. J Cereal Sci 56:432–439
Ramya P, Chaubal A, Kulkarni K, Gupta L, Kadoo N, Dhaliwal HS, Chhuneja P, Lagu M, Gupta V (2010) QTL map** of 1000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J App Genet 51:421–429
Shewry PR, Mitchell RAC, Tosi P, Wan Y, Underwood C, Lovegrove A, Freeman J, Toole GA, Mills ENC, Ward JL (2012) An integrated study of grain development of wheat (cv. Hereward). J Cereal Sci 56:21–30
Song X, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M, Lin H (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Sun X, Wu K, Zhao Y, Kong F, Han G, Jiang H, Huang X, Li R, Wang H, Li S (2009) QTL analysis of kernel shape and weight using recombinant inbred lines in wheat. Euphytica 165:615–624
Tsilo TJ, Hareland GA, Simsek S, Chao S, Anderson JA (2010) Genome map** of kernel characteristics in hard red spring wheat breeding lines. Theor Appl Genet 121:717–730
Tyagi S, Mir RR, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2015) Interval map** and meta-QTL analysis of grain traits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 201:367–380
Wan X, Wan J, Jiang L, Wang J, Zhai H, Weng J, Wang H, Lei C, Wang J, Zhang X (2006) QTL analysis for rice grain length and fine map** of an identified QTL with stable and major effects. Theor Appl Genet 112:1258–1270
Williams K, Sorrells ME (2014) Three-dimensional seed size and shape QTL in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) populations. Crop Sci 54:98–110
Williams K, Munkvold JD, Sorrells ME (2013) Comparison of digital image analysis using elliptic Fourier descriptors and major dimensions to phenotype seed shape in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 190:99–116
Wu X, Cheng R, Xue S, Kong Z, Wan H, Li G, Huang Y, Jia H, Jia J, Zhang L, Ma Z (2014a) Precise map** of a quantitative trait locus interval for spike length and grain weight in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Breed 33:129–138
Wu W, Li C, Ma B, Shah F, Liu Y, Liao Y (2014b) Genetic progress in wheat yield and associated traits in China since 1945 and future prospects. Euphytica 196:155–168
Wu Q, Chen Y, Zhou S, Fu L, Chen J, ** of grain shape and size in the wheat population Yanda1817 × Beinong6. PLoS One 10:e0118144
** of quantitative trait loci for kernel morphology traits in a non-1BL.1RS-1BL.1RS wheat cross. Crop Pasture Sci 62:625–638
**e Q, Mayes S, Sparkes DL (2015) Carpel size, grain filling, and morphology determine individual grain weight in wheat. J Exp Bot 66:6715–6730
Yan L, Loukoianov A, Blechl A, Tranquilli G, Ramakrishna W, SanMiguel P, Bennetzen JL, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2004) The wheat VRN2 gene is a flowering repressor down-regulated by vernalization. Science 303:1640–1644
Yu K, Liu D, Wu W, Yang W, Sun J, Li X, Zhan K, Cui D, Ling H, Liu C, Zhang A (2016) Development of an integrated linkage map of einkorn wheat and its application for QTL map** and genome sequence anchoring. Theor Appl Genet. doi:10.1007/s00122-016-2791-2
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by NSFC Fund 31430064, National Key Research and Development Programs of China 2016YFD0101802 and 2016YFD0100402, JSNSF BK20130679 and BK20160714, Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Initiative for Modern Crop Production and ‘111’ project B08025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Susanne Dreisigacker.
Ruiru Cheng and Zhongxin Kong contributed equally to this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, R., Kong, Z., Zhang, L. et al. Map** QTLs controlling kernel dimensions in a wheat inter-varietal RIL map** population. Theor Appl Genet 130, 1405–1414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2896-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2896-2