Abstract
Key message
A novel downy mildew resistance gene, Pl 18 , was introgressed from wild Helianthus argophyllus into cultivated sunflower and genetically mapped to linkage group 2 of the sunflower genome. The new germplasm, HA-DM1, carrying Pl 18 has been released to the public.
Abstract
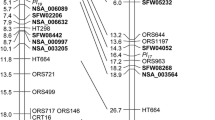
Sunflower downy mildew (DM) is considered to be the most destructive foliar disease that has spread to every major sunflower-growing country of the world, except Australia. A new dominant downy mildew resistance gene (Pl 18 ) transferred from wild Helianthus argophyllus (PI 494573) into cultivated sunflower was mapped to linkage group (LG) 2 of the sunflower genome using bulked segregant analysis with 869 simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Phenoty** 142 BC1F2:3 families derived from the cross of HA 89 and H. argophyllus confirmed the single gene inheritance of resistance. Since no other Pl gene has been mapped to LG2, this gene was novel and designated as Pl 18. SSR markers CRT214 and ORS203 flanked Pl 18 at a genetic distance of 1.1 and 0.4 cM, respectively. Forty-six single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers that cover the Pl 18 region were surveyed for saturation map** of the region. Six co-segregating SNP markers were 1.2 cM distal to Pl 18 , and another four co-segregating SNP markers were 0.9 cM proximal to Pl 18 . The new BC2F4-derived germplasm, HA-DM1, carrying Pl 18 has been released to the public. This new line is highly resistant to all Plasmopara halstedii races identified in the USA providing breeders with an effective new source of resistance against downy mildew in sunflower. The molecular markers that were developed will be especially useful in marker-assisted selection and pyramiding of Pl resistance genes because of their close proximity to the gene and the availability of high-throughput SNP detection assays.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albourie JM, Tourvieille J, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D (1998) Resistance to metalaxyl in isolates of the sunflower pathogen Plasmopara halstedii. Eur J Plant Pathol 104:2335–2342
Anderson LK, Doyle GG, Brigham B, Carter J, Hooker KD et al (2003) High-resolution crossover maps for each bivalent of Zea mays using recombination nodules. Genetics 165:849–865
Bachlava E, Radwan OE, Abratti G, Tang S, Gao W, Heesacker AF, Bazzalo ME, Zambelli A, Leon AJ, Knapp SJ (2011) Downy mildew (Pl 8 and Pl 14 ) and rust (R Adv ) resistance genes reside in close proximity to tandemly duplicated clusters of non-TIR-like NBS-LRR-encoding genes on sunflower chromosomes 1 and 13. Theor Appl Genet 122:1211–1221
Bert PF, Tourvielle De Labrouhe D, Philippon J, Mouzeyar S, Jouan I, Nicolas P, Vear F (2001) Identification of a second linkage group carrying genes controlling resistance to downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 103:992–997
Blackman BK, Scascitelli M, Kane N, Luton H, Rasmussen DA, Byr RA, Lentz DL, Rieseberg LH (2011) Sunflower domestication alleles support single domestication center in eastern North America. PNAS 108:14360–14365
Bouzidi MF, Badaoui S, Cambon F, Vear F, De Labrouhe DT, Nicolas P, Mouzeyar S (2002) Molecular analysis of a major locus for resistance to downy mildew in sunflower with specific PCR-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:592–600
Bowers JE, Bachlava E, Brunick RL, Rieseberg LH, Knapp SJ et al (2012) Development of a 10,000 locus genetic map of the sunflower genome based on multiple crosses. Genes Genomes Genetics 2:721–729
Brahm L, Röcher T, Friedt W (2000) PCR-based markers facilitating marker assisted selection in sunflower for resistance to downy mildew. Crop Sci 40:676–682
Chen J, Hu J, Jan CC (2006) Molecular map** of a nuclear male-sterility gene in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) using TRAP and SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 113:122–127
de Romano AB, Romano C, Bulos M, Altieri E, Sala C (2010) A new gene for resistance to downy mildew in sunflower. In: Proceedings of Int Symposium “Sunflower breeding on resistance to diseases”, Krasnodar, Russia, June 23–24, 2010 pp 142–147
Dußle CM, Hahn V, Knapp SJ, Bauer E (2004) Pl Arg from Helianthus argophyllus is unlinked to other known downy mildew resistance genes in sunflower. Theor Appl Genet 109:1083–1086
Faris JD, Haen KM, Gill BS (2000) Saturation map** of a gene-rich recombination hot spot region in wheat. Genetics 154:823–835
Feng J, Liu Z, Cai XW, Jan CC (2013) Toward a molecular cytogenetic map for cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) by landed BAC/BIBAC clones. Genes Genome Genet 3:31–40
Fick GN, Zimmer DE (1974) RHA271, RHA273 and RHA274 sunflower parental lines for producing downy mildew resistant hybrids. Available: http://library.ndsu.edu/repository/handle/10365/9694. Accessed 4 Jan 2016
Franchel J, Bouzidi MF, Bronner G, Vear F, Nicolas P, Mouzeyar S (2013) Positional cloning of a candidate gene for resistance to the sunflower downy mildew, Plasmopara halstedii race 300. Theor Appl Genet 126:359–367
Gascuel Q, Martinez Y, Boniface M-C, Vear F, Pichon M, Godiard L (2014) The sunflower downy mildew pathogen Plasmopara halstedii. Mol Plant Path. doi:10.1111/mpp.12164
Gedil MA, Slabaugh MB, Berry S, Segers B, Peleman J, Michelmore R, Miller JF, Gulya T, Knapp SJ (2001) Candidate disease resistance genes in sunflower cloned using conserved nucleotide binding site motifs: genetic map** and linkage to downy mildew resistance gene Pl1. Genome 44:205–212
Gill KS, Gill BS, Endo TR, Boyko EV (1996a) Identification and high-density map** of gene-rich regions in chromosome group 5 of wheat. Genetics 143:1001–1012
Gill KS, Gill BS, Endo TR, Taylor T (1996b) Identification and high-density map** of gene rich regions in chromosome group 1 of wheat. Genetics 144:1883–1891
Gilley MA, Markell SG, Gulya TJ, Misar CG (2015) Prevalence and virulence of Plasmopara halstedii (downy mildew) in sunflowers in 2014. In: Proceeding 37th Sunflower Research Forum. Fargo ND http://www.sunflowernsa.com/uploads/research/1245/gilley.downy.mildew.poster_2015.pdf. Accessed 7–8 Jan 2015
Gulya TJ (2001) Field and greenhouse evaluations of new fungicides for the control of metalaxyl-resistant sunflower downy mildew. In: Proceeding 23rd Sunflower Research Workshop. Fargo, ND. January 17–18, 2001. pp 29–34 (121516)
Gulya TJ (2002) Efficacy of single and two-way fungicide seed treatments for the control of metalaxyl-resistant strains of Plasmopara halstedii (sunflower downy mildew). In: The BCPC Conference—Pests & Diseases 2002. British Crop Protection Council. Proceedings Brighton Crop Protection Conference, November 18–21, 2002, Brighton, UK. pp 575–580
Gulya TJ (2005) Evaluation of wild annual Heliathus species for resistance to downy mildew and Sclerotinia stalk rot. In: Proceeding 27th Sunflower Research Forum. Fargo ND http://www.sunflowernsa.com/uploads/research/265/GulyaWildHelianthus_studies_05.pdf. Accessed 12–13 Jan 2005
Gulya TJ (2007) Distribution of Plasmopara halstedii races from sunflower around the world. Advances in Downy Mildew Research. In: Lebeda A, Spencer-Phillips PTN (eds) In: Proceedings of 2nd International Downy Mildew Symposium. Palcky University, vol 3. Olomouc and JOLA, Czech Republic 2–6 July 2007, pp 121–134
Gulya TJ, Miller JF, Viranyi F, Sackston WE (1991) Proposed internationally standardized methods for race identification of Plasmopara halstedii. Helia 14(15):11–20
Gulya TJ, Draper M, Harbour J, Holen C, Knodel J, Lamey A, Mason P (1999) Metalaxyl resistance in sunflower downy mildew in North America. In: Proceedings of 21st Sunflower Res. Workshop. Fargo ND, January 14–15, 1999. pp 118–123
Gulya TJ, Markell S, McMullen M, Harveson B, Osborne L (2011) New virulent races of downy mildew: distribution, status of DM resistant hybrids, and USDA sources of resistance. In: Proceedings of 33th Sunflower Research Forum. Fargo ND https://www.sunflowernsa.com/uploads/resources/575/gulya_virulentracesdownymildew.pdf. Accessed 12–13 Jan 2011
Harter AV, Gardner KA, Falush D, Lentz DL, Bye RA, Rieseberg LH (2004) Origin of extent domesticated sunflowers in eastern North America. Nature 430:201–205
Hulke BS, Miller JF, Gulya TJ, Vick BA (2010) Registration of the oilseed sunflower genetic stocks HA 458, HA 459, and HA 460 possessing genes for resistance to downy mildew. J Plant Reg 4:93–97
Jan CC, Rutger JN (1988) Mitomycin C- and streptomycin-induced male sterility in cultivated sunflower. Crop Sci 28:792–795
Künzel G, Korzun L, Meister A (2000) Cytologically integrated physical RFLP maps for the barley genome based on translocation breakpoints. Genetics 154:397–412
Leppik EE (1966) Origin and specialization of Plasmopara halstedii complex on compositae. FAO Plant Prot Bull 14:72–76
Liu Z, Gulya TJ, Seiler GJ, Vick BA, Jan CC (2012) Molecular map** of the Pl16 downy mildew resistance gene from HA-R4 to facilitate marker-assisted selection in sunflower. Theor Appl Genet 125:121–131
Marek L, Barb J, Constable J, Seiler GJ (2014) An exciting new wild sunflower species: Helianthus winteri. In: Proceeding 36th Sunflower Research Forum. Fargo ND http://www.sunflowernsa.com/uploads/resources/703/h.winteri_marek2014_revised.pdf. Accessed 8–9 Jan 2014
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Miller JF, Gulya TJ (1987) Inheritance of resistance to race 3 downy mildew in sunflower. Crop Sci 27:210–212
Miller JF, Gulya TJ (1988) Registration of 6 downy mildew resistant sunflower germplasm lines. Crop Sci 28:1040–1041
Miller JF, Gulya TJ (1991) Inheritance of resistance to race 4 of downy mildew derived from interspecific crosses in sunflower. Crop Sci 31:40–43
Molinero-Ruiz ML, Melero-Vara JM, Dominguez J (2003) Inheritance of resistance to two races of sunflower downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) in two Helianthus annuus L. lines. Euphytica 131:47–51
Mouzeyar S, Roeckel-Drevet P, Gentzbittel L, Philippon J, de Labrouhe DT, Vear F, Nicolas P (1995) RFLP and RAPD map** of the sunflower Pl1 locus for resistance to Plasmopara halstedii race 1. Theor Appl Genet 91:733–737
Moyers BT, Rieseberg LH (2013) Divergence in gene expression is uncoupled from divergence in coding sequence in a secondarily woody sunflower. Inter J Plant Sci 174(7):1079–1089
Mulpuri S, Liu Z, Feng J, Gulya TJ, Jan CC (2009) Inheritance and molecular map** of a downy mildew resistance gene, Pl13 in cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 119:795–803
Pegadaraju V, Nipper R, Hulke BS, Qi LL, Schultz Q (2013) De novo sequencing of the sunflower genome for SNP discovery using the RAD (Restriction site Associated DNA) approach. BMC Genom 14:556
Qi LL, Hulke BS, Vick BA, Gulya TJ (2011) Molecular map** of the rust resistance gene R 4 to a large NBS-LRR cluster on linkage group 13 of sunflower. Theor Appl Genet 123:351–358
Qi LL, Gulya TJ, Hulke BS, Vick BA (2012) Chromosome location, DNA markers and rust resistance of the sunflower gene R5. Mol Breeding 30:745–756
Qi LL, Long YM, Gulya TJ, Block CC, Hulke BS (2013) Genetic resistance of cultivated sunflower to Sclerotinia stalk rot introduced from wild Helianthus. In: the 15th International Scleortinia Workshop, August 20–24, 2013, Wuhan, Hubei, China. pp 66
Qi LL, Ma GJ, Long YM, Hulke BS, Markell SG (2015a) Relocation of a rust resistance gene R 2 and its marker-assisted gene pyramiding in confection sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 128:477–488
Qi LL, Long YM, Jan CC, Ma GJ, Gulya TJ (2015b) Pl 17 is a novel gene independent of known downy mildew resistance genes in the cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 128:757–767
Qi LL, Long YM, Ma GJ, Markell SG (2015c) Map saturation and SNP marker development for the rust resistance genes (R 4 , R 5 , R 13a , and R 13b ) in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Mol Breed. doi:10.10007/s11032-015-0380-8
Radwan O, Bouzidi MF, Vear F, Philippon J, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Nicolas P, Mouzeyar S (2003) Identification of non-TIR-NBS-LRR markers linked to the Pl5/Pl8 locus for resistance to downy mildew in sunflower. Theor Appl Genet 106:1438–1446
Radwan O, Bouzidi MF, Nicolas P, Mouzeyar S (2004) Development of PCR markers for the Pl 5 /Pl 8 locus for resistance to Plasmopara halstedii in sunflower, Helianthus annuus L. from complete CC-NBS-LRR sequences. Theor Appl Genet 109:176–185
Radwan O, Gandhi S, Heesacker A, Whitaker B, Taylor C, Plocik A, Kesseli R, Kozik A, Michelmore RW, Knapp SJ (2008) Genetic diversity and genomic distribution of homologs encoding NBS-LRR disease resistance proteins in sunflower. Mol Genet Genomics 280:111–125
Rahim M, Jan CC, Gulya TJ (2002) Inheritance of resistance to sunflower downy mildew races 1, 2 and 3 in cultivated sunflower. Plant Breed 121:57–60
Rashid KY, Desjardins ML, Kaminski DA (2006) Diseases of sunflower in Manitoba and Saskatchewan in 2005. Can. Plant Dis Survey 2006, 86:114–115. Available at http://phytopath.ca/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/cpds-archive/vol86/CPDS_vol_86_No_1_%281-130%292006.pdf. Accessed 4 Jan 2016
Rieseberg LH, Seiler GJ (1990) Molecular evidence and the origin and development of the domesticated sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Econ Bot 44S:79–91
Roeckel-Drevet P, Gagne G, Mouzeyar S, Gentzbittel L, Philippon J, Nicolas P, de Labrouhe DT, Vear F (1996) Colocation of downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) resistance genes in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Euphytica 91:225–228
Rogers CE, Thompson TE, Seiler GJ (1982) Sunflower species of the United States. National Sunflower Association, Bismarck, pp 4–22
Seiler GJ (1991) Registration of 13 downy mildew tolerant interspecific sunflower germplasm lines derived from wild annual species. Crop Sci 31:1714–1716
Seiler GJ (2010) Utilization of wild Heliathus species in breed for disease resistance. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium “Sunflower Breeding on Resistance to Diseases”, Krasnodar, Russia. International Sunflower Association, Paris, France. June 23–24, 2010. pp 37–51
Seiler GJ, Jan CC (2014) Wild sunflower species as a genetic resource for resistance to sunflower broomrape (Orobanche cumana Wallr.). Helia 37:129–139
Slabaugh MB, Yu JK, Tang SX, Heesacker A, Hu X, Lu GH, Bidney D, Han F, Knapp SJ (2003) Haploty** and map** a large cluster of downy mildew resistance gene candidates in sunflower using multilocus intron fragment length polymorphisms. Plant Biotechnol J 1:167–185
Talukder ZI, Gong L, Hulke BS, Pegadaraju V, Song QJ, Schultz Q, Qi LL (2014) A high-density SNP map of sunflower derived from RAD-sequencing facilitating fine-map** of the rust resistance gene R 12 . PLoS One 9(7):e98628. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098628
Tang S, Yu JK, Slabaugh MB, Shintani DK, Knapp SJ (2002) Simple sequence repeat map of the sunflower genome. Theor Appl Genet 105:1124–1136
Tang S, Kishore VK, Knapp SJ (2003) PCR-multiplexes for a genome-wide framework of simple sequence repeat marker loci in cultivated sunflower. Theor Appl Genet 107:6–19
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW et al (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
The Tomato Genome Consortium (2012) The tomato genome sequence provides insights into flesh fruit evolution. Nature 485:635–641
Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Lafon S, Walse P, Raulic I (2000) A new race of Plasmopara halstedii, pathogen of sunflower downy mildew. Oleagineux 7:404–405
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap ® 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen, Netherlands. http://www.kyazma.com. Accessed 4 Jan 2016
Vear F, Gentzbittel L, Philippon J, Mouzeyar S, Mestries E, Roeckel-Drevet P, de Labroube DT, Nicolas P (1997) The genetics of resistance to five races of downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:584–589
Vear F, Seriveys H, Petit A, Serre F, Boudon JP, Roche S, Walser P, Tourieille D de Labrouhe (2008) Origins of major genes for downy mildew resistance in sunflower. In: Proceedings of 17th International Sunflower Conference Cordoba, Spain, 2008, Consejeria de Agricultura y Pesca, pp 125–130
Vincourt P, As-sadi F, Bordat A, Langlade NB, Gouzy J, Pouilly N, Lippi Y, Serre F, Godiard L, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Vear F (2012) Consensus map** of major resistance genes and independent QTL for quantitative resistance to sunflower downy mildew. Theor Appl Genet 125:909–920
Viranyi F, Gulya TJ, Tourieille D L (2015) Recent changes in the pathogenic variability of Plasmopara halstedii (sunflower downy mildew) populations from different continents. Helia doi:10.1515/helia-2015-0009
Vrânceanu VL, Pirvu N, Stoenescu FM (1981) New sunflower downy mildew resistance genes and their management. Helia 4:23–27
Wieckhorst S, Bachlava E, Dußle CM, Tang S, Gao W, Saski C, Knapp SJ, Schön CC, Hahn V, Bauer E (2010) Fine map** of the sunflower resistance locus Pl ARG introduced from the wild species Helianthus argophyllus. Theor Appl Genet 121:1633–1644
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) RFLP analysis of the size of chromosomal segments retained around the Tm-2 locus of tomato during backcross breeding. Theor Appl Genet 77:353–359
Yu JK, Tang S, Slabaugh MB, Heesacker A, Cole G et al (2003) Towards a saturated molecular genetic linkage map for cultivated sunflower. Crop Sci 43:367–387
Zimmer DE (1974) Physiological specialization between races of Plasmopara halstedii in America and Europe. Phytopathol 64:1465–1467
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Loren Rieseberg for providing access to the Sunflower Genome Data Repository. We also thank Drs. Gerald Seiler and Steven Xu for critical review of the manuscript, and Angelia Hogness and Cheryl Huckle for technical assistance. This project was supported by the National Sunflower Association Agreement 12-D02, the USDA-ARS CRIS Project No. 5442-21000-039-00D, and the USDA-AMS Specialty Crop Block Grant Program 12-25-B-1689. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this report is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the US Department of Agriculture. The USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments were performed in compliance with the current laws of the USA.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Hahn.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, L.L., Foley, M.E., Cai, X.W. et al. Genetics and map** of a novel downy mildew resistance gene, Pl 18 , introgressed from wild Helianthus argophyllus into cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 129, 741–752 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2662-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2662-2