Abstract
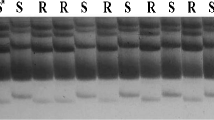
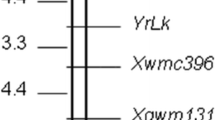
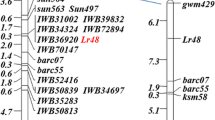
Southern corn rust (SCR), Puccinia polysora Underw, is a destructive disease in maize (Zea mays L.). Inbred line Qi319 is highly resistant to SCR. Results from the inoculation test and genetic analysis of SCR in five F2 populations and five BC1F1 populations derived from resistant parent Qi319 clearly indicate that the resistance to SCR in Qi319 is controlled by a single dominant resistant gene, which was named RppQ. Simple sequence repeat (SSR) analysis was carried out in an F2 population derived from the cross “Qi319×340”. Twenty SSR primer pairs evenly distributed on chromosome10 were screened at first. Out of them, two primer pairs, phi118 and phi 041, showed linkage with SCR resistance. Based on this result, eight new SSR primer pairs surrounding the region of primers phi118 and phi 041 were selected and further tested regarding their linkage relation with RppQ. Results indicated that SSR markers umc1,318 and umc 2,018 were linked to RppQ with a genetic distance of 4.76 and 14.59 cM, respectively. On the other side of RppQ, beyond SSR markers phi 041 and phi118, another SSR marker umc1,293 was linked to RppQ with a genetic distance of 3.78 cM. Because the five linkage SSR markers (phi118, phi 041, umc1,318, umc 2,018 and umc1,293) are all located on chromosome 10, the RppQ gene should also be located on chromosome 10. In order to fine map the RppQ gene, AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphism) analysis was carried out. A total 54 AFLP primer combinations were analyzed; one AFLP marker, AF1, from the amplification products of primer combination E-AGC/M-CAA, showed linkage with the RppQ gene in a genetic distance of 3.34 cM. Finally the RppQ gene was mapped on the short arm of chromosome 10 between SSR markers phi 041 and AFLP marker AF1 with a genetic distance of 2.45 and 3.34 cM respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Yokozeki Y, Inagaki A, Fujimura T (1996) Microsatallite DNA markers for rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 93:1071–1077
Bailey BA, Schun W, Fred-eriksen RA, Bockholt AJ (1987) Identification of slow-rusting resistance to Puccinia polysora in maize inbreds and single crosses. Plant Dis 71:518–521
Chen CX, Yang DE, Yu YJ, Wang ZL, Wang B (2003) Studies on southern corn rust and its resistance. Acta Phytopathol Sin 33:86–87
Chin ECL, Senior ML, Smith JSC (1996) Maize simple repetitive DNA sequences: abundance and allele variation. Genome 39:866–873
Duan DR, He HZ (1984) Description of a rust Puccinia polysora on corn in Hainan Island. Acta Mycol Sin 3:125–126
Futrell MC (1975) Puccinia polysora on maize associated with crop** practice and genetic homogeneity. Phytopathology 65:1041–1042
Futrell MC, Hooker AL, Scott GE (1975) Resistance on maize to corn rust, controlled by a single dominant gene. Crop Sci 15:597–599
Hillel J, Schapp T, Haberfield A, Jeffreys AJ, Plotzky Y, Cahaner A, Lave U (1990) DNA fingerprints applied to gene introgression in breeding program. Genetics 124:783–789
Hoisington DA, Khairallah MM, Gonzales-de-Leon D (1994) Laboratory protocols. CIMMYT Applied Molecular Genetics Laboratory, CIMMYT, Hisfoa, Mexico, DF
Holland JB, Uhr DV, Jeffers D, Goodman MM (1998) Inheritance of resistance to southern corn rust in tropical-by-corn-belt maize populations. Theor Appl Genet 96:232–241
Hooker AL, Yarwood CE (1966) Culture of Puccinia sorghi on detached leaves of corn and Oxalis corniculata. Phytopathology 56:536–539
Hospital F, Chevalet C, Mulsant P (1992) Using markers in gene-introgression breeding programs. Genetics 132:1199–1210
Hulbert SH, Bennetzen JL (1991) Recombination at the Rp1 locus of maize. Mol Gen Genet 226:377–382
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Etoh T (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Liu YY, Wang J (1999) Southern corn rust occurred in Hebei Province in 1998. Plant Protect:53
Lubberstedt T, DuBle C, Melchinger A (1998) Application of microsatellites from maize to teosinte and other relatives of maize. Plant Breed 117:447–450
McMullen MD, Simcox K (1995) Genomic organization of disease- and insect-resistance genes in maize. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8:811–815
Melching JS (1975) Corn rust: type, races and destructive potential. In: The American Seed Trade Association, pp 90–115
Rhind D, Waterston JM, Deighton FC (1952) Occurrence of Puccinia polysora Underw in West Africa. Nature 169:631
Rodrigues-Ardon. R, Scott GE, Hennen JF (1980) Maize yield losses caused by southern corn rust. Crop Sci 20:812–814
Scott GE, King SB, Armour JW (1984) Inheritance of resistance to southern corn rust in the maize population. Crop Sci 24:265–267
Ullstrup AJ (1965) Inheritance and linkage of a gene determining resistance in maize to an American race of Puccinia polysora. Phytopathology 55:425–428
Visscher PM, Haley CS, Thompson R (1996) Marker-assisted introgression in backcross breeding programs. Genetics 144:1923-1932
Vos PR, Hogers MB (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang SL (1999) Southern corn rust was epidemic in the Province of Shandong, Henan and Jiangsu. Plant Protect Technol Dissemin 3:40–41
Ye JC (2000) The first inbred line Qi319 immune to maize southern rust bred in china. Sci Agricult Sin 33:110
Zummo N (1988) Components contributing to partial resistance in maize to Puccinia polysora. Plant Dis 72:157–160
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 10th Five-Year Science and Technology Research Program of China (2001BA511B04-01) and the State High-Tech Program of China (2001AA211111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C.X., Wang, Z.L., Yang, D.E. et al. Molecular tagging and genetic map** of the disease resistance gene RppQ to southern corn rust. Theor Appl Genet 108, 945–950 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1506-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1506-7