Abstract
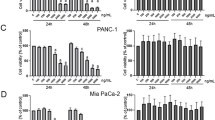
Pancreatic cancer is not only common, but also extremely difficult to treat, for which it has been called "the challenge of the twenty-first century". In this study, we find that prodigiosin could effectively inhibit the proliferation of human pancreatic cancer cells H8898 in a dose-and-time-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 75μmol according to the results of MTT and cell proliferation assays. This inhibitive effect may relate to two factors: mitotic arrest and cell death. Results of clone formation and Flow cytometry analysis (FCAS) suggested that prodigiosin has the capability of restraining mitosis by regulating the cell cycle. Prodigiosin also could induce apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells at low concentration and results in the fragmentation pattern of DNA. Prodigiosin may effectively enter cells and promote the level of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROSin) in a dose-dependent manner. The generation of ROS may play an important role in the cytotoxic effect. All these results demonstrate that prodigiosin can obviously inhibit the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells H8898 by arresting the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis. Increased ROS lead this cytotoxic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Liu, J., Shen, Y. et al. Inhibitive Effect of Prodigiosin on the Proliferation of Human Malignant Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Med Chem Res 14, 181–197 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-005-0133-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-005-0133-z