Abstract
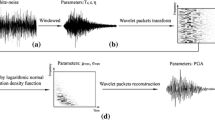
— The technique of Midorikawa (1993) has been modified to obtain a resultant envelope function at the observation point by placing the rupture causing an earthquake in a layered earth model. The method and its dependency on various modelling parameters are studied in detail. The complete study shows that the generated resultant envelope follows important strong motion characteristics such as directivity and attenuation effects. The simulated resultant envelope is further used for generating synthetic accelerograms by multiplying filtered white noise with the envelope of accelerogram at a particular observation point. Filters through which white noise passes include the effects of geometrical spreading, anelastic attenuation and near-site attenuation at high frequencies.¶Uttarkashi earthquake is among few Indian earthquakes for which strong motion data are available at thirteen different stations. Using the technique presented in this work, envelope function as well as complete acceleration time history during Uttarkashi earthquake has been simulated at these observation points. Comparison of peak acceleration, duration and acceleration response spectra confirms the utility and efficacy of the approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
(Received July 13, 1999, accepted 8 August, 2000)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, A., Singh, S. & Giroti, K. The Simulation of Ground Motions Using Envelope Summations. Pure appl. geophys. 158, 877–901 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00001211
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00001211