Abstract
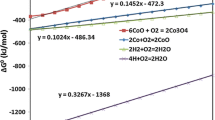
By means of inert markers of radio-platinum, it has been shown that cobalt metal oxidizes by outward diffusion of cobalt atoms through the oxide. Oxidation rates have been measured at various temperatures and oxygen pressures and have been found to agree with the rates calculated from the Wagner equation and the authors’ values for the diffusion coefficient of cobalt in the oxide. The distribution of radio-cobalt in growing oxide layers has been accurately measured and found to be different from that predicted from the Wagner oxidation theory. Attempts have been made to measure the change of lattice parameter of the oxide with composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Valensi: J. Metallurgical Italiana (1950) 3, p. 77; Mettaux et Corrosion (1950) 15, p. 283.
J. Dunn and F. Weikins: Review of the Oxidation and Scaling of Heated Metals. II. The Oxidation of Non-Ferrous Metals. (1936) p. 67. London. H. M. Stationery Office.
E. A. Gulbransen and K. Andrew: Journal Electrochemical Society (1951) 98, p. 241.
R. E. Carter and F. D. Richardson: Trans. AIME (1954) 200, p. 1244; Journal of Metals (November 1954).
M. Davies, M. Simnad, and C. Birchenall: Trans. AIME (1951) 191, p. 889; Journal of Metals (October 1951).
A. Preece and G. Lucus: Journal Institute of Metals (1952) 81, p. 219.
V. Arkharov and K. Graevsksi: Journal of Tech. Phys. Moscow (1944) 14, p. 132.
L. B. Pfeil: Journal Iron and Steel Institute (1929) 119, p. 501.
G. Chauvenet: Thesis, University of Caen (1942).
C. Johns and W. Baldwin: Trans. AIME (1949) 185, p. 720; Journal of Metals (October 1949).
C. Wagner: Diffusion and High Temperature Oxidation of Metals. Atom Movements. (1951) p. 153. Cleveland. ASM. Ztsch. fur Physik. Chem. (1933) B21, p. 25.
E. Shibata and J. Mori: Ztsch. fur Physik. Chem. (1929) A142, p. 151.
N. F. Mott and R. W. Gurney: Electronic Processes in Crystals. (1948) p. 257. Oxford. Clarendon Press.
J. Bardeen, W. N. Brattain, and W. Shockley: Journal of Chemical Physics (1946) 14, p. 714.
W. J. Moore and B. Selikson: Journal of Chemical Physics (1951) 19, p. 1539.
G. W. Castellan and W. J. Moore: Journal of Chemical Physics (1949) 17, p. 41.
G. Cooper: Ph.D. Thesis, Royal College of Science, Imperial College of Science and Technology, Univ. of London (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
R. E. Carter, Junior Member AIME, formerly Graduate Student, Nuffield Research Group in Extraction Metallurgy, Royal School of Mines, London, England
Discussion of this paper, TP 3942E, may be sent, 2 copies, to AIME by Apr. 1, 1955. Manuscript, June 7, 1954. Chicago Meeting, February 1955.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, R.E., Richardson, F.D. & Wagner, C. Oxidation of Cobalt Metal. JOM 7, 336–343 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03377503
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03377503