Summary
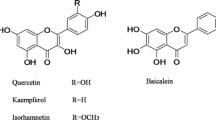
Scutellarin, a flavonoid glycoside, is the primary active ingredient in breviscapine that is a mixture of flavonoid glycosides extracted from a Chinese herbErigeron breviscapus (Vant.) Hand.-Mazz. The pharmacokinetics of scutellarin and its aglycone conjugated metabolites after intraperitoneal injection and oral administration of breviscapine was investigated in rats. The plasma concentration of scutellarin and scutellarein conjugates in serial samples was measured by validated high-performance liquid chromatography methods. The pharmacokinetic results indicated that scutellarin underwent rapid and extensive biotransformationin vivo. After intraperitoneal injection, scutellarin was absorbed rapidly. The profiles of scutellarin and scutellarein conjugates were fitted to a two-compartment open model. Scutellarin and scutellarein conjugates showed a similar time course. No significant difference in tmax, t0.5(α) and t0.5(β) was observed between scutellarin and scutellarein conjugates (p>0.05). After oral administration, fluctuations were observed in the concentration-time profiles of both scutellarin and scutellarein conjugates and the pharmacokinetics could not be explained by classical compartment model. The relative bioavailability of oral administration was very low, 10.67 %±4.78 % for scutellarin and 7.92 %±1.90 % for scutellarein conjugates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu J.M., Huang Z.H. (1991): DengZhan ****n capsules in the treatment of cerebrovascular disorders in 74 patients. Chin. J. New Drugs Clin. Rem., 10, 260–263.
Xu Q.Y., Li X.X. (1995): Influences of DengZhan ****n injection on blood viscosity in patients with high blood viscosity. Chin. J. New Drugs Clin. Rem., 14, 233–235.
Zhang J., Li X.S., Zhang W.D. (2002): The advance in studies on chemical component and pharmacology of Erigeron breviscapus. J. Pharm. Pract., 20, 103–107.
Hong H., Liu G.Q. (2004): Protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by scutellarin. Life Sci., 74, 2959–2973.
Lai M.Y., Hsiu S.L., Tsai S.Y., Hou Y.C., Chao P.D.L. (2003): Comparison of metabolic pharmacokinetics of baicalin and baicalein in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 55, 205–209.
Lai M. Y., Hsiu S.L., Chen C.C., Hou Y.C., Chao P.D.L. (2003): Urinary pharmacokinetics of baicalein, wogonin and their glycosides after oral administration of scutellariae radix in humans. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 26, 79–83.
Hsiu S.L., Huang T.Y., Hou Y.C., Chin D.H., Chao P.D.L. (2002): Comparison of metabolic pharmacokinetics of naringin and naringenin in rabbits. Life Sci., 70, 1481–1489.
Kabaze F.I., Kokkalou E., Georgarakis M., Niopas I. (2004): Validated high-performance liquid chromatographic method utilizing solid-phase extraction for the simultaneous determination of naringenin and hesperetin in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B, 801, 363–367.
Akao T., Kawabata K., Yanagisawa E., Ishihara K., Mizuhara Y., Wakui Y., Sakashita Y., Kobashi K. (2000): Baicalin, the predominant flavone glucuronide of Scutellariae radix, is absorbed from the rat gastrointestinal tract as the aglycone and restored to its original form. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 52, 1563–1568.
Muto R., Motozuka T., Nakano M., Tatsumi Y., Sakamoto F., Kosaka N. (1997): The chemical structure of new substance as the metabolite of baicalin and time profiles for the plasma concentration after oral administration of sho-saiko-to in human. Yakugaku Zasshi, 118, 79–87.
Shimoi K., Okada H., Furugori M., Goda T., Takase S., Suzuki M., Hara Y., Yamamoto H., Kinae N. (1998): Intestinal absorption of luteolin and luteolin 7-O-β-glucoside in rats and humans. FEBS Lett., 438, 220–224.
Murota K., Terao J. (2003): Antioxidative flavonoid quercetin: implication of its intestinal absorption and metabolism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 417, 12–17.
Yang Q., Yang J.Y., Li S.C., Zhang L.M. (2004): The relative bioavailability of breviscapine sustained-release tablets in beagle dogs. West China J. Pharm. Sci., 19, 175–178.
Liu Y.M., Lin A.H., Chen H., Zeng F.D. (2003): Study on pharmacokinetics of scutellarin in rabbits. Acta. Pharm. Sin., 38, 775–778.
Jiang X.H., Li S.H., Lan K., Yang J.Y., Zhou J. (2003): Study on the pharmacokinetics of scutellarin in dogs. Acta. Pharm. Sin., 38, 371–373.
Li S.H., Jiang X.H., Lan K., Yang J.Y., Zhou J. (2003): Pharmacokinetics of scutellarin in dogs. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci., 12, 127–130.
Ge Q.H., Zhou Z., Zhi X.J., Ma L.L., Chen X.H. (2003): Pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability of breviscapine in beagle dogs. Chin. J. Pharm., 34, 618–620.
Li S.H., Jiang X.H., Yang Q., ** C.H. (2003): Pharmacokinetics of scutellarin in rabbits. J. Biomed. Eng., 20, 692–694.
Zhang J.L., Che Q.M., Li S.Z., Zhou T.H. (2003): Study on metabolism of scutellarin in rats by HPLC-MS and HPLC-NMR. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res., 5, 249–256.
Wang H., Chen J.M., Zhang Q.M. (2000): A study on the absorption kinetics of baicalin in rats’ stomachs and small intestines in vitro. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ., 17, 5–7.
Ding J.S., Zhang J.S. (2003): Absorption of breviscapine in small intestine of rat. J. Chin. Pharm. Univ., 34, 65–69.
Murota K., Shimizu S., Chujo H., Moon J.H., Terao J. (2000): Efficiency of absorption and metabolic conversion of quercetin and its glucosides in human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 384, 391–397.
Nemeth K., Plumb G.W., Benin J.G., Juge N., Jacob R., Nairn H.Y., Williamson G., Swallow D.M., Kroon P.A. (2003): Deglycosylation by small intestinal epithelial cell β-glucosidases is a critical step in the absorption and metabolism of dietary flavonoid glycosides in humans. Eur. J. Nutr., 42, 29–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J.M., Weng, W.Y., Huang, X.B. et al. Pharmacokinetics of scutellarin and its aglycone conjugated metabolites in rats. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 30, 165–170 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190615
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190615