Abstract
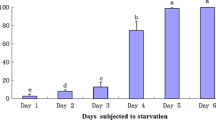
The effects of starvation on the metabolic rate and the glucose, glycogen and total lipid contents in the freshwater prosobranch snailBellamya bengalensis (Lamarck) have been investigated. Starvation influenced the metabolic rate ofB. bengalensis. Although there was an initial increase, the metabolic rate of both the sexes decreased in the later stages of starvation. There was a marked difference in the utilization of nutrient stores between male and female snails starved for 55 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayne B L 1973 The responses of 3 species of bivalve molluscs to declining oxygen tension at reduced salinity;Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 45 793–806
Bayne B L, Thompson R J and Widdows J 1976 Physiology I. InMarine mussels: their ecology and physiology (ed.) B L Bayne (Cambridge: Univ. Press) pp. 121–206
Berg K and Ockelmann K W 1959 The respiration of freshwater snails;J. Exp. Biol. 36 690–708
Calow P 1975 The respiratory strategies of two species of freshwater gastropod (Ancylus fluviatilis Mull, andPlanorbis contortus (Linn) ) in relation to temperature, oxygen concentration and body size and season;Physiol. Zool. 48 114–129
Davies P S 1966 Physiological ecology ofPatella. 1. The effect of body size and temperature on metabolic rate;J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 46 647–658
Duerr F 1965 Some aspects of diet on the respiration rate of the freshwater pulmonate snailLymnaea palustris;Proc. Dak. Acad. Sci. 44 245
Emerson D 1967 Carbohydrate oriented metabolism ofPlanorbis corneus (Mollusca: Planorbidae) during starvation;Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 22 571–579
Emerson D and Duerr F 1967 Some physiological effects of starvation in the intertidal prosobranchLittorina planaxis (Philippi, 1847);Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 20 45–53
Ganapati P N and Prasada Rao D G V 1960 Studies on the respiration of barnacles: Oxygen uptake and the metabolic rate in relation to body size inBalanus amphitrite communis (darwin).J. Anim. Morphol. Physiol. 7 27–31
Giese A 1966 Lipids in the ecology of marine invertebrates;Physiol. Rev. 46 244–298
Golterman H L 1970Methods for chemical analysis of freshwaters (Oxford: Black well Scientific Publ.), I.B.P. Hand Book No. 8, p. 166
Heeg J 1977 Oxygen consumption and the use of metabolic resources during starvation and aestivation inBulinus (Physopsis) africanus (Pulmonata: Planorbidae);Malacologia 16 549–560
Kemp A, Adrenne J M and Kitts van Hejningen 1954 A colorimetric micro method for determination of glycogen in tissues;Biochem. J. 56 646–648
Lomte V S and Nagabhushanam R 1971 Studies on the respiration of freshwater musselPerreysia corrugata;Hydrobiologia 38 239–246
Mane U H 1975 Oxygen consumption of the clamKatelysia opima in relation to environmental conditions;Broteria 44 33–38
Mane U H and Talikhedker P M 1976 Respiration of the wedge clamDonax cuneatus;Indian J. Mar. Sci. 5 243–246
Martin A 1961 The carbohydrate metabolism of mollusca. InComp. Physiol, carbohydrate metabolism in heterothermic animals (ed.) A Martin (Seattle: University of Washington Press) 35–64
Martin A and Goddard C 1966 Carbohydrate metabolism. InPhysiology of mollusca (eds) K M Wilbur and C M Yonge (New York: Academic Press)2 275–308
Newell R C 1970Biology of intertidal animals (London: Logos Press Ltd.) pp 539
Pande S V, Parvin Khan R and Venkatasubrahmanyan T A 1963 Microdetermination of lipids and serum total fatty acids;Anal. Biochem. 6 415–423
Snedcor G W and Cochran W G 1967Statistical methods (Calcutta: Oxford and IBH Publishing Co.) pp. 593
Stickle W B and Duerr F G 1970 The effects of starvation on the respiration and major nutrient stores ofThais lamellosa;Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 33 689–695
von Brand T 1931 Der Jahreszyklus im Stoffbestand der weinbergchnecke(Helix pomatia);Z. Vergl. Physiol. 14 200–264 Not referred to in the original
Not referred to in the original von Brand T, Noland M and Mann E 1948 Observations on the respiration ofAustralorbis glabratus and some other aquatic snails;Biol. Bull. 95 199–213
von Brand T, McMahon P and Noland M 1957 Physiological observations on starvation and desiccation of the snailAustralorbis glabratus;Biol. Bull. 113 89–102
Widdows J 1973 Effect of temperature and food on the heart beat, ventilation rate and oxygen uptake ofMytilus edulis;Mar. Biol. 20 269–276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satya Reddy, D., Balaparameswara Rao, M. Effects of starvation on respiration and major nutrient stores of the prosobranch snailBellamya bengalensis (Lamarck). Proc Ani Sci 94, 99–110 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03186333
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03186333