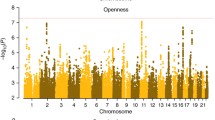
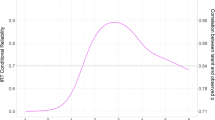
Abstract
Since ancient times, dimensions of personality have been linked with the liability to psychiatric illness. In modern times, several research approaches suggest that personality and the liability to psychiatric illness such as schizophrenia and major depression (MD) are influenced by many of the same genes. If this is true, it could shed light on the genetic architecture of psychiatric illness. It could also validate the use of personality measures in unaffected relatives in linkage and association studies of psychiatric illness. This approach could potentially increase statistical power to detect genetic effects. The personality trait neuroticism (N) may be genetically related to MD, while schizotypal traits may be genetically related to schizophrenia. Twin studies have reported that most of the covariation between N and MD is due to shared additive genetic factors. Adoption studies have demonstrated that the biological offspring of schizophrenic mothers are more likely to have schizotypal personality disorder than are children of control mothers.At the current time, only one genome wide scan of N has been published, which does show some overlap in linkage results with genome scans of MD. However,this should be replicated and more rigorously studied. At the present time, there are no established susceptibility genes for MD. When these are established, it will be necessary to assess their relationship with N. Currently, no genome scans of schizotypy have been published. Furthermore, although several putative susceptibility genes for schizophrenia have been reported and replicated, only one — catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) — has been tested in schizotypy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abkevich V, NJ Camp, CH Hensel, CD Neff, DL Russell, DC Hughes, AM Plenk, MR Lowry, RL Richards, C Carter, GC Frech, S Stone, K Rowe, CA Chau, K Cortado, A Hunt, K Luce, G O’Neil, J Poarch, J Potter, GH Poulsen, H Saxton, M Bernat-Sestak, V Thompson, A Gutin, MH Skolnick, D Shattuck and L Cannon-Albright (2003) Predisposition locus for major depression at chromosome 12q22-12q23.2.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 1271–1281.
Akiskal HS and O Pinto (1999) The evolving bipolar spectrum. Prototypes I, II, III, and I V.Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 22, 517–534, vii.
Akiskal HS, RM Hirschfeld and BI Yerevanian (1983) The relationship of personality to affective disorders.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 40, 801–810.
Arango V, P Ernsberger, PM Marzuk, JS Chen, H Tierney, M Stanley, DJ Reis and JJ Mann (1990) Autoradiographic demonstration of increased serotonin 5-HT2 and beta-adrenergic receptor binding sites in the brain of suicide victims.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 47, 1038–1047.
Arora RC and HY Meltzer (1989) Serotonergic measures in the brains of suicide victims: 5-HT2 binding sites in the frontal cortex of suicide victims and control subjects.Am. J. Psychiatry 146, 730–736.
Avramopoulos D, NC Stefanis, I Hantoumi, N Smyrnis, I Evdokimidis and CN Stefanis (2002) Higher scores of self reported schizotypy in healthy young males carrying the COMT high activity allele.Mol. Psychiatry 7, 706–711.
Baron M and N Risch (1987) The spectrum concept of schizophrenia: evidence for a genetic-environmental continuum.J. Psychiatr. Res. 21, 257–267.
Baron M, R Gruen, L Asnis and S Lord (1985) Familial transmission of schizotypal and borderline personality disorders.Am. J. Psychiatry 142, 927–934.
Boyce P, G Parker, B Barnett, M Cooney and F Smith (1991) Personality as a vulnerability factor to depression.Br. J. Psychiatry 159, 106–114.
Brzustowicz LM, WG Honer, EW Chow, J Hogan, K Hodgkinson and AS Bassett (1997) Use of a quantitative trait to map a locus associated with severity of positive symptoms in familial schizophrenia to chromosome 6p.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 61, 1388–1396.
Cannon TD, TG van Erp and DC Glahn (2002) Elucidating continuities and discontinuities between schizotypy and schizophrenia in the nervous system.Schizophr. Res. 54, 151–156.
Coppen A (1965) Effects of a depressive illness on MPI scores.Br. J. Psychiatry 111, 236–239.
Czerwinski SA, MC Mahaney, JT Williams, L Almasy and J Blangero (1999) Genetic analysis of personality traits and alcoholism using a mixed discrete continuous trait variance component model.Genet. Epidemiol. 17 Suppl 1, S121-S126.
D’haenen H, A Bossuyt, J Mertens, C Bossuyt-Piron, M Gijsemans and L Kaufman (1992) SPECT imaging of serotonin2 receptors in depression.Psychiatry Res. 45, 227–237.
Delgado PL, LH Price, HL Miller, RM Salomon, GK Aghajanian, GR Heninger and DS Charney (1994) Serotonin and the neuro-biology of depression. Effects of tryptophan depletion in drug-free depressed patients.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 51, 865–874.
Ellis PM and C Salmond (1994) Is platelet imipramine binding reduced in depression? A meta-analysis.Biol. Psychiatry 36, 292–299.
Erlenmeyer-Kimling L, E Squires-Wheeler, UH Adamo, AS Bassett, BA Cornblatt, CJ Kestenbaum, D Rock, SA Roberts and II Gottesman (1995) The New York High-Risk Project. Psychoses and cluster A personality disorders in offspring of schizophrenic parents at 23 years of follow-up.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 52, 857–865.
Eysenck HJ and MW Eysenck (1985)Personality and Individual Differences. A Natural Science Approach (Plenum Press, New York).
Falconer DS and TFC Mackay (1996)Introduction to Quantitative Genetics (Longman, New York).
Fanous A, C Gardner, D Walsh and KS Kendler (2001) Relationship between positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia and schizotypal symptoms in nonpsychotic relatives.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 58, 669–673.
Fanous A, CO Gardner, CA Prescott, R Cancro and KS Kendler (2002) Neuroticism, major depression and gender: a population-based twin study.Psychol. Med. 32, 719–728.
Farmer A, K Redman, T Harris, A Mahmood, S Sadler, A Pickering and P McGuffin (2002) Neuroticism, extraversion, life events and depression. The Cardiff Depression Study.Br. J. Psychiatry 181, 118–122.
Flory JD, SB Manuck, RE Ferrell, KM Dent, DG Peters and MF Muldoon (1999) Neuroticism is not associated with the serotonin transporter (5-HTTLPR) polymorphism.Mol. Psychiatry 4, 93–96.
Fullerton J, M Cubin, H Tiwari, C Wang, A Bomhra, S Davidson, S Miller, C Fairburn, G Goodwin, MC Neale, S Fiddy, R Mott, DB Allison and J Flint (2003) Linkage analysis of extremely discordant and concordant sibling pairs identifies quantitative-trait loci that influence variation in the human personality trait neuroti-cism.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72, 879–890.
Gelernter J, H Kranzler, EF Coccaro, LJ Siever and AS New (1998) Serotonin transporter protein gene polymorphism and personality measures in African American and European American subjects.Am. J. Psychiatry 155, 1332–1338.
Glatt SJ, SV Faraone and MT Tsuang (2003) Association between a functional catecholO-methyltransferase gene polymorphism and schizophrenia: meta-analysis of case-control and family-based studies.Am. J. Psychiatry 160, 469–476.
Greenberg BD, Q Li, FR Lucas, S Hu, LA Sirota, J Benjamin, KP Lesch, D Hamer and DL Murphy (2000) Association between the serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism and personality traits in a primarily female population sample.Am. J. Med. Genet.96, 202–216.
Gruzelier JH and A Doig (1996) The factorial structure of schizo-typy: Part II. Cognitive asymmetry, arousal, handedness, and sex.Schizophr. Bull. 22, 621–634.
Harrison PJ and MJ Owen (2003) Genes for schizophrenia? Recent findings and their pathophysiological implications.Lancet 361, 417–419.
Hay DA, NG Martin, D Foley, SA Treloar, KM Kirk and AC Heath (2001) Phenotypic and genetic analyses of a short measure of psychosis-proneness in a large-scale Australian twin study.Twin Res. 4, 30–40.
Heninger GR, DS Charney and DE Sternberg (1984) Serotonergic function in depression. Prolactin response to intravenous trypto-phan in depressed patients and healthy subjects.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 41, 398–402.
Hirschfeld RM, GL Klerman, PJ Clayton, MB Keller, P McDonald-Scott and BH Larkin (1983) Assessing personality: effects of the depressive state on trait measurement.Am. J. Psychiatry 140, 695–699.
Jackson SW (1986)Melancholia and Depression: From Hippocratic Times to Modern Times (Yale University Press, New Haven, CT).
Jardine R, NG Martin and AS Henderson (1984) Genetic covariation between neuroticism and the symptoms of anxiety and depression.Genet. Epidemiol. 1, 89–107.
Jorm AF, AS Henderson, PA Jacomb, H Christensen, AE Korten, B Rodgers, X Tan and S Easteal (1998) An association study of a functional polymorphism of the serotonin transporter gene with personality and psychiatric symptoms.Mol. Psychiatry 3, 449–451.
Kendler KS (1985) Diagnostic approaches to schizotypal personality disorder: a historical perspective.Schizophr. Bull. 11, 538–553.
Kendler KS, M McGuire, AM Gruenberg, A O’Hare, M Spellman and D Walsh (1993a) The Roscommon family study. III. Schizophrenia-related personality disorders in relatives.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 50, 781–788.
Kendler KS, MC Neale, RC Kessler, AC Heath and LJ Eaves (1993b) A longitudinal twin study of personality and major depression in women.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 50, 853–862.
Kendler KS, M McGuire, AM Gruenberg and D Walsh (1995a) Schizotypal symptoms and signs in the Roscommon family study. Their factor structure and familial relationship with psychotic and affective disorders.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 52, 296–303.
Kendler KS, MC Neale and D Walsh (1995b) Evaluating the spectrum concept of schizophrenia in the Roscommon family study.Am. J. Psychiatry 152, 749–754.
Kerr TA, K Schapira, M Roth and RF Garside (1970) The relationship between the Maudsley Personality Inventory and the course of affective disorders.Br. J. Psychiatry 116, 11–19.
Kety SS, D Rosenthal, PH Wender, F Schulsinger and B Jacobsen (1975) Mental illness in the biological and adoptive families of adopted individuals who have become schizophrenic: a preliminary report based on psychiatric interviews, In: Finch JF, D Rosenthal and H Brill (Eds.),Genetic Research in Psychiatry (Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD) 147–165.
Kraepelin E (1921)Manic-Depressive Illiness and Paranoia (E & S Livingstone, Edinburgh, Scotland).
Kretschmer E (1936)Physique and Character (Kegan Paul Trench Trubner & Co., London, England).
Krieg JC, CJ Lauer, L Hermle, U von Bardeleben, T Pollmacher and F Holsboer (1990) Psychometric, polysomnographic, and neu-roendocrine measures in subjects at high risk for psychiatric disorders: preliminary results.Neuropsychobiology 23, 57–67.
Lander E and L Kruglyak (1995) Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results.Nat. Genet. 11, 241–247.
Lauer CJ, T Bronisch, M Kainz, W Schreiber, F Holsboer and JC Krieg (1997) Pre-morbid psychometric profile of subjects at high familial risk for affective disorder.Psychol. Med. 27, 355–362.
Levinson DF and BJ Mowry (1991) Defining the schizophrenia spectrum: issues for genetic linkage studies.Schizophr. Bull. 17, 491–514.
Linney YM, RM Murray, ER Peters, AM MacDonald, F Rijsdijk and PC Sham (2003) A quantitative genetic analysis of schizo-typal personality traits.Psychol. Med. 33, 803–816.
MacDonald AW, III, MF Pogue-Geile, TT Debski and S Manuck (2001) Genetic and environmental influences on schizotypy: a community-based twin study.Schizophr. Bull. 27, 47–58.
Maier W, D Lichtermann, J Minges and R Heun (1992) Personality traits in subjects at risk for unipolar major depression: a family study perspective.J. Affect. Disord. 24, 153–163.
Melke J, M Landen, F Baghei, R Rosmond, G Holm, P Bjorntorp, L Westberg, M Hellstrand and E Eriksson (2001) Serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms are associated with anxiety-related personality traits in women.Am. J. Med. Genet. 105, 458–463.
Mendlewicz J, I Massat, D Souery, J Del Favero, L Oruc, MM Nothen, D Blackwood, W Muir, S Battersby, B Lerer, RH Segman, R Kaneva, A Serretti, R Lilli, C Lorenzi, M Jakovljevic, S Ivezic, M Rietschel, V Milanova and C Van Broeckhoven (2004) Serotonin transporter 5HTTLPR polymorphism and affective disorders: no evidence of association in a large European multicenter study.Eur. J. Hum. Genet. In press
Murakami F, T Shimomura, K Kotani, S Ikawa, E Nanba and K Adachi (1999) Anxiety traits associated with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region in the Japanese.J. Hum. Genet. 44, 15–17.
Neale MC and L Cardon (1992)Methodology for Genetic Studies of Twins and Families (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands).
Nuechterlein KH, RF Asarnow, KL Subotnik, DL Fogelson, DL Payne, KS Kendler, MC Neale, KC Jacobson and J Mintz (2002) The structure of schizotypy: relationships between neurocogni-tive and personality disorder features in relatives of schizophrenic patients in the UCLA Family Study.Schizophr. Res. 54, 121–130.
Nurnberger JI Jr, T Foroud, L Flury, J Su, ET Meyer, K Hu, R Crowe, H Edenberg, A Goate, L Bierut, T Reich, M Schuckit and W Reich (2001) Evidence for a locus on chromosome 1 that influences vulnerability to alcoholism and affective disorder.Am. J. Psychiatry 158, 718–724.
Nystrom S and B Lindegard (1975) Predisposition for mental syndromes: a study comparing predisposition for depression, neurasthenia and anxiety state.Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 51, 69–76.
Parnas J, TD Cannon, B Jacobsen, H Schulsinger, F Schulsinger and SA Mednick (1993) Lifetime DSM-III-R diagnostic outcomes in the offspring of schizophrenic mothers. Results from the Copenhagen High-Risk Study.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 50, 707–714.
Rado S (1953) Dynamics and classification of disordered behavior.Am. J. Psychiatry 110, 406–416.
Reich T, JW James and CA Morris (1972) The use of multiple thresholds in determining the mode of transmission of semi-continuous traits.Ann. Hum. Genet. 36, 163–184.
Riley BP and P McGuffin (2000) Linkage and associated studies of schizophrenia.Am. J. Med. Genet. 97, 23–44.
Roberts SB, CJ MacLean, MC Neale, LJ Eaves and KS Kendler (1999) Replication of linkage studies of complex traits: an examination of variation in location estimates.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65, 876–884.
Schneider K (1958)Psychopathic Personalities (Cassell & Co Ltd, London, England).
Sen S, S Villafuerte, R Nesse, SF Stoltenberg, J Hopcian, L Gleiberman, A Weder and M Burmeister (2004) Serotonin transporter and GABA(A) alpha 6 receptor variants are associated with neuroticism.Biol. Psychiatry 55, 244–249.
Shifman S, M Bronstein, M Sternfeld, A Pisante-Shalom, E Lev-Lehman, A Weizman, I Reznik, B Spivak, N Grisaru, L Karp, R Schiffer, M Kotler, RD Strous, M Swartz-Vanetik, HY Knobler, E Shinar, JS Beckmann, B Yakir, N Risch, NB Zak and A Darvasi (2002) A highly significant association between a COMT haplo-type and schizophrenia.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 1296–1302.
Siever LJ, DL Murphy, S Slater, E de la Vega and S Lipper (1984) Plasma prolactin changes following fenfluramine in depressed patients compared to controls: an evaluation of central serotoner-gic responsivity in depression.Life Sci. 34, 1029–1039.
Spitzer RL, J Endicott and M Gibbon (1979) Crossing the border into borderline personality and borderline schizophrenia. The development of criteria.Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 36, 17–24.
Straub RE, Y Jiang, CJ MacLean, Y Ma, BT Webb, MV Myakishev, C Harris-Kerr, B Wormley, H Sadek, B Kadambi, AJ Cesare, A Gibberman, X Wang, FA O’Neill, D Walsh and KS Kendler (2002) Genetic variation in the 6p22.3 gene DTNBP1, the human ortholog of the mouse dysbindin gene, is associated with schizophrenia.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 337–348.
Tienari P, LC Wynne, K Laksy, J Moring, P Nieminen, A Sorri, I Lahti and KE Wahlberg (2003) Genetic boundaries of the schizophrenia spectrum: evidence from the Finnish Adoptive Family Study of Schizophrenia.Am. J. Psychiatry 160, 1587–1594.
Wetzel RD, CR Cloninger, B Hong and T Reich (1980) Personality as a subclinical expression of the affective disorders.Compr. Psychiatry 21, 197–205.
Wonodi I, OC Stine, BD Mitchell, RW Buchanan and GK Thaker (2003) Association between Val108/158 Met polymorphism of the COMT gene and schizophrenia.Am. J. Med. Genet. 120B, 47–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fanous, A.H., Kendler, K.S. The genetic relationship of personality to major depression and schizophrenia. neurotox res 6, 43–50 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033295
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033295