Abstract
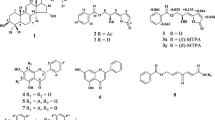
Three diterpenes (1, 8, and9), three triterpenes (3, 4, and7), one saponin (11), four sterols (2, 5, 6, and12), and one cerebroside (10) were isolated from the EtOH extract of the aerial parts ofAralia cordata by repeated silica gel column chromatography. Their chemical structures were identified by comparing their physicochemical and spectral data with those published in literatures. All isolated compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against L 1210, K562, and LLC tumor cell lines using MTT assay. Of which, 3β, 5α-dihydroxy-6β-methoxyergosta-7,22-diene (6) showed a potent cytotoxicity against all cell lines with IC50 values of 11.7, 11.9, and 15.1 μM, respectively, while compounds1, 5, and11 showed a moderate or weak cytotoxicity. These isolates were also examined for their inhibitory activity against COX-1 and COX-2. Although most compounds, except for2, 10, and12, showed a strong inhibitory activity against COX-1, they exhibited a moderate or weak inhibitory activity against COX-2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, X. F., Shen, G., Dat, N. T., Kang, O. H., Lee, Y. M., Lee, J. J., and Kim, Y. H., Inhibitory effect of kaurane type diterpenoids fromAcanthopanax koreanum on TNF-α secretion from trypsin-stimulated HMC-1 cells,Arch. Pharm. Res., 9, 731–734 (2003).
Cambie, R. C., Burfitt, I. E., Goodwin, T. E., and Wenkert, E., The structure of hallol,J. Org. Chem., 40, 3789–3791 (1975).
Dang, N. H., Zhang, X. F., Zheng, M. S., Son, K. H., Chang, H. W., Kim, H. P., Bae, K. H., and Kang, S. S., Inhibitory Constituents against Cyclooxygenases fromAralia cordata Thunb.Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 28–33 (2005).
Han, B. H., Han, Y. N., Han, L. A., Park, M. H., and Lee, E. O., Studies on the anti-inflammatory activity ofAralia continentalis (I).Arch. Pharm. Res., 6, 17–23 (1983).
Hirokazu, K., Ryosuke, K., Toshimi, S., Takashi, M., Toshihiko, H., and Takuji, N., Cytotoxic steroids from the mushroomAgaricus blazei.Phytochemistry, 27, 2777–2779 (1988).
Hung, C. Y. and Yen, G. C., Extraction and identification of antioxidative components of Hsian-tsao (Mesona procumbens Hemsl.).Lebensm.-Wiss. u.-Technol., 34, 306–311 (2001).
Ito, T., Tsukiji, K., and Odagiri, S., Constituents of the Head Space Gas of Udo (Aralia cordata Thunb.).Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi, 52, 223–224 (1978).
Jares, E. A., Tettamanzi, M. C., and Pomilio, A. B., Sitosterol 3-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside fromSenecio bonariensis.Phytochemistry, 29, 340–341 (1990).
Kang, S. S., Kim, J. S., Xu, Y. N., and Kim, Y. H., Isolation of a new cerebroside from the root bark ofAralia elate.J. Nat. Prod., 62, 1059–1060 (1999).
Kwon, H. C. and Lee, K. R., Phytochemical Constituents ofArtemisia japonica ssp.littoricola. Arch. Pharm. Res., 24, 194–197 (2001).
Kwon, H. C., Zee, S. D., Cho, S. Y., Choi, S. U., and Lee, K. R., Cytotoxic ergosterols fromPaecilomyses sp. J300.Arch. Pharm. Res., 25, 851–855 (2002).
Lee, K. R., Peroxide Constituents in the Natural Product Research,Kor. J. Pharmacogn., 22, 145–155 (1991).
Mosmann, T. J., Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays.J. Immunol. Methods, 65, 55–63 (1983).
Okuyama, E., Nishimura, S., and Yamazaki, M., Analgesic principles fromAralia cordata Thunb.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 405–407 (1991).
Park S. H., Oh, S. R., Jung, K. Y., Lee, I. M., Ahn, K. S., Kim, J. G., Lee, J. J., and Lee, H. K., Anticomplement activities of oleanolic acid monodesmosides and bisdesmosides isolated fromTiarella polyphylla.Arch. Pharm. Res., 22, 428–431 (1999).
Park, S. Y. and Kim, J. W., Cytotoxic Polyacetylenes fromAralia cordata.Yakhak Hoeji, 39, 681–688 (1995).
Perry, L. M.,Medicinal Plants of East and Southeast Asia: Attributed Properties and Uses; The MIT Press, Cambridge, p. 41 (1980).
Sakurai, N., Yaguchi, Y., and Inoue, T., Triterpenoids fromMyrica rubra, Phytochemistry, 26, 217–219 (1987).
Sam, N., San-Miguel, B. Arreguy, Taran, M., and Delmond, B., Synthesis and rearrangement of methyl 8,14β-epoxypimarate on the route to cassane diterpene skeleton.Tetrahedron, 47, 9187–9194 (1991).
Sati, O. P., Uniyal, S. K., Bahuguna, S., and Kikuchi, T., Clematoside, S., A triterpenoid saponin from the roots ofClematis grata.Phytochemistry, 29, 3676–3678 (1990).
Sawamura, M., Kim, M. S., Shichiri, K., Tsuji, T., and Machida, K., Volatile constituents of Japanese and Korean Udo (Aralia cordata Thunb.) and Butterbur (Petasites japonicus Miq.).Research Reports of the Kochi University, 38, 49–60 (1989).
Shim, J. S., Park, K. M., Chung, J. Y., and Hwang, J. K., Antibacterial activity of oleanolic acid fromPhysalis angulata against oral pathogens.Nutraceuticals & Food, 7, 215–218 (2002).
Sugiyama, S., Honda, M., Higuchi, R., and Komori, T., Stereochemistry of the Four Diastereomers of Ceramide and Ceramide Lactoside.Liebigs Ann. Chem., 349–356 (1991).
Sy, L. K. and Brown, G. D., Abietane diterpenes fromIllicium angustisepalum.J. Nat. Prod., 61, 907–912 (1998).
Ylva, N., Therese, R., Premila, P., Helena D., and Lars, B., Development of a radiochemical cyclooxygenase-1 and 2in vitro assay for identification of natural products as inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis.J. Nat. Prod., 61, 2–7 (1998).
Yoshihara, K. and Hirose, Y., Terpenes fromAralia Species.Phytochemistry, 12, 468 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, I.S., **, W.Y., Zhang, X. et al. Cytotoxic and COX-2 inhibitory constituents from the aerial parts ofAralia cordata . Arch Pharm Res 29, 548–555 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969263
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969263