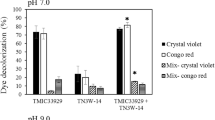
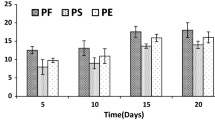
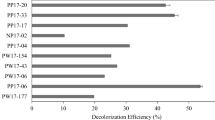
Abstract
Agitation, temperature, inoculum size, initial pH and pH of buffered medium affected the decolorization of Orange II dye byCoriolus versicolor andFunalia trogii. The optimum temperature and initial pH value for decolorization were 30°C and 6.5–7.0, respectively; pH 4.5 was the most efficient in buffered cultures. High decolorization extents were reached at all agitation rates. At an inoculum size of more than 1 mL, the extent of decolorization changed only slightly. High extents were obtained using immobilized fungi at repeated-batch mode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banat I.M., Nigam P., Singh D., Marchant R.: Microbial decolorization of textile dye containing effluents.Bioresource Technol.58, 217–227 (1996).
Bumpus J.A., Brock B.J.: Biodegradation of crystal violet by white-rot fungusPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Appl. Envtron. Microbiol.58, 3598–3604 (1988).
Fahy V., Fitz-Gibbon F.J., Mcmullan G., Singh D., Marchant R.: Decolourization of molasses spent wash byPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Biotechnol. Lett.19, 97–99 (1997).
Kahraman S., Yeşilada O.: Effect of spent cotton stalks on color removal and chemical oxygen demand lowering in olive oil mill wastewater by white-rot fungi.Folia Microbiol.44, 673–676 (1999).
Kahraman S., Yeşilada O.: Industrial and agricultural wastes as substrates for laccase production by white-rot fungi.Folia Microbiol.46, 133–136 (2001).
Kapdan I.K., Kargi F., McMullan G., Marchant R.: Biological decolorization of textile dyestuff byCoriolus versicolor in a packed column reactor.Environ. Technol.21, 231–236 (2000).
Knapp J.S., Zhang F.M., Tapley K.N.: Decolorization of Orange II by a wood rotting fungus.J. Chem. Tech. Biotech.69, 289–296 (1997).
Krčmar P., Ulrich R.: Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyl mixtures by the lignin-degrading fungusPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Folia Microbiol.43, 79–84 (1998).
Martens R., Zadražil F.: Screening of white-rot fungi for their ability to mineralize polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil.Folia Microbiol.43, 97–103 (1998).
Meyer U.: Biodegradation of synthetic organic colorants.FEMS Symp.12, 371–385 (1981).
Novotný Č., Vyas B.R.M., Erbanová P., Kubatová A., Šašek V.: Removal of PCBs by various white-rot fungi in liquid cultures.Folia. Microbiol.42, 136–140 (1997).
Sani R.K., Azmi W., Banerjee U.C.: Comparison of static and shake culture in the decolorization of textile dyes and dye effluents byPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Folia Microbiol.43, 85–88 (1998).
Sirianuntapiboon S., Somchai P., Ohmomo S., Atthasampunna P.: Screening of filamentous fungi having the ability to decolorize molasses pigments.Agric. Biol. Chem.52, 387–392 (1988).
Yang F.-J., Yu J.-T.: Development of bioreactor system using an immobilized white-rot fungus for decolorization.Bioproc. Engin.15, 307–310 (1996).
Yeşilada O.: Decolorization of crystal violet by fungi.World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.11, 601–602 (1995).
Yeşilada O., Fiskin K.: Decolorization of alcoholic wastewater by white-rot fungiCoriolus versicolor, Funalia trogii andPhanerochaete chrysosporium ME446.Turkish J. Biol.19, 191–200 (1995).
Yeşilada O., Ocçan B.: Decolorization of Orange II dye with the crude culture filtrate of white-rot fungus,Coriolus versicolor.Turkish J. Biol.22, 463–476 (1998).
Yeşilada O., Sik S., Sam M.: Biodegradation of olive oil mill wastewater byCoriolus versicolor andFunalia trogii: effects of agitation, initial COD concentration, inoculum size and immobilization.World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.14, 37–42 (1998).
Zhang F., Jeremy S., Tapley K.N.: Development of bioreactor systems for decolorization of Orange II using white-rot fungus.Enzyme Microb. Technol.24, 48–53 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sam, M., Yeşilada, O. Decolorization of orange II dye by white-rot fungi. Folia Microbiol 46, 143–145 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02873593
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02873593