Abstract
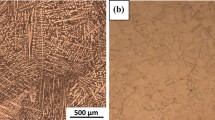
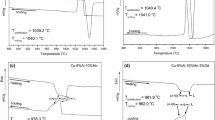
The microstructure of as-cast Cu-AI-Ni alloys, based on copper containing 9 to 10 wt pct Al and up to 5 wt pct Ni, has been examined. The development of the microstructure on continuous cooling has also been investigated. For alloys with 9.2 to 9.3 wt pct Al, and less than 1 wt pct Ni, the as-cast microstructure consists of proeutectoid α solid solution, α + γ2 eutectoid, and martensitic β. If the nickel content is more than 2.5 wt pct, the α + γ2 eutectoid is replaced by α + β ′2 eutectoid, and no martensitic β is observed in the as-cast alloys. The morphologies of the β ′2 and γ2 eutectoid phases are similar; both have the Kurdjumov-Sachs (K-S) orientation relationship with the a phase. Two eutectoid reactions, involving β to α + γ2 and β to α + β′2, have been observed in an alloy containing 9.7 wt pct Al and 2.7 wt pct Ni. When both eutectoid reactions occur, the Nishiyama-Wassermann (N-W) orientation relationship exists between γ2 or β ′2 and the α phase. During continuous cooling, proeutectoid α solid solution is the first phase to precipitate from the high-temperature β phase. The β to α + β ′2 eutectoid reaction starts at higher temperatures than the β to α + γ2 reaction. Tempering of the as-cast alloys results in the elimination of the martensitic β.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Hasan, A. Jahanafrooz, G.W. Lorimer, and N. Ridley:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1337–45.
A. Jahanafrooz, F. Hasan, G.W. Lorimer, and N. Ridley:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1951–56. ,
F. Hasan, J. Iqbal, and N. Ridley:Mater. Sci. Technol., 1985, vol. 1, pp. 312–15.
W.O. Alexander : J. Inst. Met., 1938, pp. 163–89.
A.J. Bradley and H.J. Goldschmit:J. Inst. Met., 1939, vol. 65, pp. 389–401.
W. Köster, U. Zwicker, and K.Z. Moeller:Z. Metallkd., 1948, vol. 39, pp. 225–31.
R. Thomson and J.O. Edwards: Report MRP/PMRL/76-27(J), Part 1, CANMET, Ottawa, ON, Canada.
P. Brezina:Int. Met. Rev., 1982, vol. 27, pp. 77–120.
G. Cliff and G.W. Lorimer:J. Microsc, 1975, vol. 103, pp. 203–07.
P. Weill-Couly and D. Arnaud :Fonderie, 1973, no. 322, pp. 123-35.
J.C. Rowlands and T.R.H.M. Brown:Proc. 4th Int. Congr. on Marine Corrosion and Fouling, Entibes, Juan-les-Pins, June 1976, Centre de Recherches et d’Etudes Ocannograthique, Boulogne, France.
R. Paton and P.J. Le Thomas:Fonderie, 1963, no. 214, pp. 462–66.
D. Arnaud, R. Paton, S. Wigg, and C. Mascre:Fonderie, 1964, no. 226, pp. 403–30.
JCPDS X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data File, 4-836, 5-607, JCPDS 24-3.
P.R. Swann and H. Warlimont:Acta Metall., 1963, vol. 11, pp. 511–27.
H. Warlimont and L. Delaey:Prog. Mater. Sci., 1974, vol. 18, pp. 25-32 and 41–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Y.S. SUN formerly Research Associate with the Manchester Materials Science Centre.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y.S., Lorimer, G.W. & Ridley, N. Microstructure and its development in Cu-Al-Ni alloys. Metall Trans A 21, 575–588 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02671930
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02671930