Summary
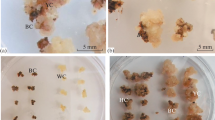
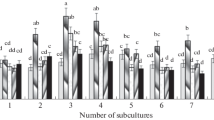
Tracheary element differentiation in cultured explants of pith parenchyma isolated from heads of romaine lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. Romana) was strongly inhibited by concentrations of gentamicin sulfate recommended for tissue culture media (50 to 100 μg/ml). Similar results were obtained with cultured explants of Jerusalem artichoke tuber (Helianthus tuberosus L.). Callus formation was suppressed in the presence of increasing levels of gentamicin sulfate in both tissue systems. Plant tissue culture media employed in studies on cell division and xylem differentiation should be supplemented with this antibiotic in concentrations of 10 μg/ml or less according to these results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudin, A.; Healey, A.; Phillips, C. A.; Gump, D. W.; Forsyth, B. R. Antibacterial activity of gentamicin sulfate in tissue culture. Appl. Microbiol. 20: 989–990; 1970.
Kassanis, B.; White, R. F. A simplified method of obtaining tobacco protoplasts for infection with tobacco mosaic virus. J. Gen. Virol. 24: 447–452; 1974.
Raveh, D.; Huberman, E.; Galun, E.In vitro culture of tobacco protoplasts: use of feeder techniques to support division of cells plated at low densities. In Vitro 9: 216–222; 1973.
Zhuravlev, Y. N.; Yudakova, Z. S.; Pisetskaya, N. F. Effects of viral protein, viral RNA, and some other polyelectrolytes on infection of tobacco protoplasts. Virology 73: 454–460; 1976.
Kassanis, B.; White, R. F.; Woods, R. D. Inhibition of multiplication of tobacco mosaic virus in protoplasts by antibiotics and its prevention by divalent metals. J. Gen. Virol. 28: 185–191; 1975.
Dalessandro, G.; Roberts, L. W. Induction of xylogenesis in pith parenchyma explants ofLactura. Am. J. Bot. 58: 378–385; 1971.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plantarum 15: 473–497; 1962.
Dalessandro, G. Interaction of auxin, cytokinin, and gibberellin on cell division and xylem differentiation in cultured explants of Jerusalem artichoke. Plant Cell Physiol. 14: 1167–1176; 1973.
Brown, R.; Rickless, P. A new method for the study of cell division and cell extension with some preliminary observations on the effect of temperature and nutrients. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (Biol.) 136: 110–125; 1949.
Banko, T. J.; Roberts, L. W.; Boe, A. A. The detection of cytokinins in xylem exudate ofColeus blumei Benth. by the induction of xylogenesis in pith parenchyma explants ofLactuca sativa L.. Ann. Bot. 40: 651–654; 1976.
Milanesi, G.; Ciferri, O. Studies on the mechanism of action of gentamicin. Effect on protein synthesis in cell-free extracts ofEscherichia coli. Biochemistry 5: 3926–3935; 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dodds, J.H., Roberts, L.W. Some inhibitory effects of gentamicin on plant tissue cultures. In Vitro 17, 467–470 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633507
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633507