Abstract
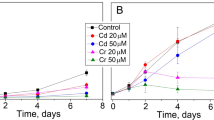
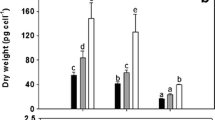
A laboratory investigation was conducted to study the extent and efficiency of cadmium bioaccumulation inScenedesmus obliquus by subjecting this alga to varied sublethal Cd concentrations. The influence of cell population age on Cd bioaccumulation was also studied. Under the experimental conditions employed, growth was not significantly affected by Cd concentrations ranging from 0.01 ppm to 1.00 ppm. At concentrations above 1.00 ppm, however, growth was inhibited markedly. Increases in external Cd concentration caused an increase in total bioaccumulation over the entire range of concentrations, which did not significantly affect growth. Efficiency of Cd bioaccumulation was also concentration dependent, but maximum accumulation efficiency occurred in a medium with a Cd concentration lower than that medium in which maximum total bioaccumulation occurred. Age of the cell population influenced the extent of Cd bioaccumulation. Rapidly growing, young cultures accumulated less Cd than older cultures approaching stationary growth phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, L., F. W. Rabe, and W. H. Funk: Effects of copper, zinc, and cadmium onSelenastrum capricornutum. Water Res.8, 179 (1974).
Cain, J. R., and F. R. Trainor: Regulation of gametogenesis inScenedesmus obliquus (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol.12, 383 (1976).
Coleman, R. D., R. L. Coleman, and E. L. Rice: Zinc and cobalt bioconcentration and toxicity in selected algal species. Bot. Gaz.132, 102 (1971).
Conway, H. L.: Sorption of arsenic and cadmium and their effects on growth, micronutrient utilization, and photosynthetic pigment composition ofAsterionella formosa. J. Fish. Res. Board Can.35; 286 (1978).
Cossa, D.: Sorption du cadmium par une population de la diatoméePhaeodactylum Iricornutum en culture. Mar. Biol.34, 163 (1676).
Durum, W. H., J. D. Hem, and S. G. Heidel: Reconnaissance of selected minor elements in surface waters of the United States, October, 1970. U.S. Geol. Surv. Circ.643, 1 (1971).
Fogg, G. E.: Algal cultures and phytoplankton ecology. 2 ed. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press (1975).
Friberg, L., M. Piscator, G. G. Nordberg, and T. Kjellstrom: Cadmium in the environment. 2 ed. Cleveland: CRC Press (1974).
Gibson, C. E.: The algicidal effect of copper on a green and a blue-green alga and some ecological implications. J. Appl. Ecol.9, 513 (1972).
Klass, E., D. W. Rowe, and E. J. Massaro: The effect of cadmium on population growth of the green algaScenedesmus quadricauda. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.12, 442 (1974).
Melhuus, A., K. L. Seip, and H. M. Seip: A preliminary study of the use of benthic algae as biological indicators of pollution in Sørfjorden, Norway. Environ. Pollut.15, 101 (1978).
Morris, A. W., and A. J. Bale: The accumulation of cadmium, copper, manganese, and zinc byFucus vesiculosus in the British Channel. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci.3, 153 (1974).
Reiniger, P.: Concentration of cadmium in aquatic plants and algal mass in flooded rice culture. Environ. Pollut.14, 297 (1977).
Starr, R. C.: The culture collection of algae at the University of Texas at Austin. J. Phycol14 (Suppl.), 48 (1978).
Sunda, W. G., and J. M. Lewis: Effect of complexation by natural organic ligands on the toxicity of copper to a unicellular alga,Monochrysis lutheri. Limnol. Oceanogr.23, 870 (1978).
Trainor, F. R., J. R. Cain, and L. E. Shubert: Morphology and nutrition of the colonial green algaScenedesmus: 80 years later. Bot. Rev.42, 5 (1976).
Trollope, D. R., and B. Evans: Concentrations of copper, iron, lead, nickel, and zinc in freshwater algal blooms. Environ. Pollut.11, 109 (1976).
Vallee, B. L., and D. D. Ulmer: Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium, and lead. Ann. Rev. Biochem.41, 91 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cain, J.R., Paschal, D.C. & Hayden, C.M. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of cadmium in the colonial green algaScenedesmus obliquus . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 9, 9–16 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055495