Summary
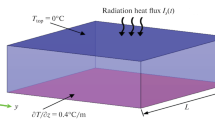
Problems of turbulent dissipation of a cold air lake (CAL) and the inversion layer bordering CAL on the upper boundary are presented and studied with the compound model. In wintertime such cold air lakes can persist for days even if rather strong winds are blowing above them. The required conditions for CAL dissipation are removed processes of its formation or maintenance, as well as a sufficiently strong invasion of turbulence in the inversion layer from above down-wards. By this, the inversion layer at first becomes stronger and dissipation is stopped, until the increase of turbulent kinetic energy of the upper flow enables further dissipation. Such turbulent dissipation process is shown by the model for typical conditions and for different initial values of the relevent variables.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya, S. P., 1988:Introduction to Micrometeorology. New York: Academic Press, 307 pp.
Businger, J. A., 1982. Equation and concepts. In: Nieuwstadt, F. T. M., van Dop, H., (eds.),Atmosph. Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling. Dordrecht: D. Reidel Pub. Comp., 1–36.
Davies, H. C., Phillips, P. D., 1985: Mountain drag along the Gotthard section during ALPEX.J. Atoms. Sci.,42, 2093–2109.
Emeis, S., 1987: Pressure drag and effective roughness length with neutral stratification.Bound.-Layer Meteor.,39, 379–401.
Furger, M., 1990:Die Radiosondierungen von Payerne. Opfikon: Lenticularis, 191 pp.
Furger, M., Wanner, H., Engel, J., Troxler, F. X., Valsangiacomo, A., 1989: Zur Durchluftung der Täler und Vorlandsenken der Schweiz.Geographica Bernesia,F20, 162 pp.
Galperin, B., Hassid, S., 1986: A modified turbulent energy model for geophysical flows: Influence of the ground proximity.Bound.-Layer Meteor.,35, 155–165.
Johnson, R. C., Simpson, T. K. M., 1991: The automatic weather station network in the balquihidder catchments, Scotland.Weather 46, 47–50.
Lazar, R., 1989: Ergebnisse einer Immisionsklimatischen Untersuchung im Raum Bruck-Leoben-Kapfenberg.Arb. Geogr. Inst. Graz. 29, 153–189.
Nieuwstadt, F. T. M., van Dop, H., 1988:Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling, Dordrecht: D. Reidel Pub. Comp., 358 pp.
Pasquill, F., 1974:Atmospheric Diffusion. 2nd Ed., Chichester: Ellis Horwood, 442 pp.
Petkovšek, Z., 1974. Dissipation of the upper layer of all-day radiation fog in basins.Zbornik met. radova,5, 71–74.
Petkovšek, Z., 1978a: Zones of convergence in local air flow in valleys and basins.Veröff. Schweiz. Met. Zentralan.,40, 92–96.
Petkovšek, Z., 1978b: Relief meteorologically relevant characteristics of basins.Z. Meteorol.,28, 327–334.
Petkovšek, Z., 1985: Die Beendigung von Luftverunreini-gungsperioden in TalbeckenZ. Meteorol.,35, 370–372.
Pichler, H., 1984:Dynamik der Atmosphäre. Zürich: Bibliographisches Institut AG, 456 pp.
Stilke, G., Essig, M. U., 1988: On special structures of noctural boundary layer in pre-Alpine regions.Proc. 20th Int. conf. Alpine Met. V-II, 4.8, 1–14.
Tennekes, H., 1982: Similarity relarity relations, scaling laws and spectral dynamics. In: Nieuwstadt, F. T. M., van Dop, H. (eds.)Atmosph. Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling, Dordrecht: D. Reidel Publ. Comp., 37–68.
Vinnichenko, N. K., 1970: The kinetic energy spectrum in the free atmosphere—one second to five years,Tellus,22, 158–166.
Vrhovec, T., 1991: A cold air lake formation in a basin—a simulation with a mesoscale numerical model.Meterol. Atmos. Phys.,46, 91–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 6 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petkovšek, Z. Turbulent dissipation of cold air lake in a basin. Meteorl. Atmos. Phys. 47, 237–245 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01025620
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01025620