Abstract
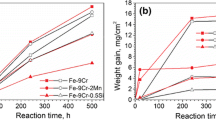
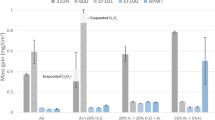
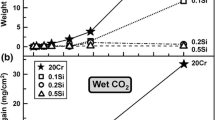
Oxide layers have been grown on Fe-9% Cr, Fe-9% Cr-0.3% Si, and Fe 9% Cr-0.6% Si alloys in carbon dioxide at 853 °K. It is known that such oxides are duplex, the outer layer being magnetite, formed by iron transport. The inner layer is Fe-Cr spinel but little is known about its growth mechanism so this has been investigated using oxygen-18 as a tracer. Oxides were grown first in C16O2 and then in C18O2 and the distribution of oxygen-18 in the scale measured using nuclear techniques. For all the alloys used, significant amounts of oxygen-18 were observed within the inner layer in addition to growth of18O-rich magnetite at the outer surface. The two possibilities of the oxygen-18 being present as a consequence of isotopic exchange or because new oxide had formed within the spinel layer are discussed. Our conclusion is that it is very unlikely that significant isotopic exchange had occurred in any part of the scale, and we deduce that at least a substantial amount of the oxygen-18 in the inner layer was deposited as a result of new oxide formation within that layer. The results also indicate that the location of growth sites within the inner layer differed between the alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. R. Holmes, R. B. Hill, and L. M. Wyatt, eds.,Corrosion of Steels in CO 2(British Nuclear Energy Society, London, 1974).
P. L. Harrison, R. B. Dooley, S. K. Lister, D. B. Meadowcroft, P. J. Nolan, R. E. Pendlebury, P. L. Surman, and M. R. Wootton, inCorrosion of Steels in CO 2,D. R. Holmes, R. B. Hill, and L. M. Wyatt, eds. (British Nuclear Energy Society, London, 1974), p. 220.
J. Hampton, P. C. Rowlands, and P. W. Teare. Corrosion Science Symposium, Nottingham, 1978 and CERL Internal Report RD/L/N49/78, 1978.
M. R. Taylor, Ph.D. thesis, Manchester University, 1976.
A. M. Pritchard and A. E. Truswell, inCorrosion of Steels in CO 2,D. R. Holmes, R. B. Hill, and L. M. Wyatt, eds. (British Nuclear Energy Society, London, 1974), p. 234.
M. G. C. Cox, B. McEnaney, and V. D. Scott,Philos. Mag. 26, 839 (1972).
P. C. Rowlands, J. C. P. Garrett, F. G. Hicks, B. K. Lister, B. Lloyd, and J. A. Twelves, inCorrosion of Steels in CO 2,D. R. Holmes, R. B. Hill, and L. M. Wyatt, eds. (British Nuclear Energy Society, London, 1974), p. 193.
D. G. Barnes, J. M. Calvert, K. A. Hay and D. G. Lees,Philos. Mag. 28, 1303 (1973).
J. M. Calvert, D. J. Derry, and D. G. Lees,J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 7, 940 (1974).
D. J. Neild, P. J. Wise, and D. G. Barnes,J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 5, 2292 (1972).
J. A. Cookson and F. D. Pilling,Thin Solid Films 19, 371 (1973).
P. L. Harrison, Private communication (1976).
P. Kofstad,High Temperature Oxidation of Metals (Wiley, New York, 1966) p. 123.
J. Castle and P. L. Surman,J. Phys. Chem. 73, 632 (1969).
H. Yearian, J. Hortwright, and R. Langenheim,J. Chem. Phys. 22, 1196 (1954).
J. M. Ferguson and P. C. Rowlands, Private communication (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, M.R., Calvert, J.M., Lees, D.G. et al. The mechanism of corrosion of Fe-9%Cr alloys in carbon dioxide. Oxid Met 14, 499 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603476
Received:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603476