Summary
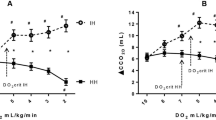
After perfusion stop a\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) decrease has been measured in the carotid body tissue by means of elastically suspended\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) needle electrodes. With the formula\({\text{U}}_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } = \frac{\alpha }{{760}} \cdot \frac{{\Delta P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } }}{{\Delta t}} \cdot 10^5 \) it is possible to calculate the oxygen consumption from this\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) decrease. Our experiments have shown that the oxygen consumption of the non-perfused carotid body of the cat depends linearly on local\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \). The\(\frac{{\Delta P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } }}{{\Delta t}}\) measured in situ (Krebs-Henseleit perfusion) is with 6 Torr/s at a tissue\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) of 100 Torr (37° C) two times higher than the values measured in vitro (Krebs-Henseleit-perfusion). The\(\frac{{\Delta P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } }}{{\Delta t}}\) in vivo corresponds to an oxygen consumption of 1.2 ml O2/100 g min at a\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) of 100 Torr at 37° C. The\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) dependence of the oxygen consumption of the carotid body might be caused by a special oxidase which may be involved in the chemoreceptive process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acker, H., Lübbers, D. W., Purves, M. J.: Local oxygen tension field in the glomus caroticum of the cat and its change at changing arterial\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \). Pflügers Arch.329, 136–155 (1971)
Acker, H., Lübbers, D. W.: Die Veränderung des Gewebesauerstoffdruckes im Glomus caroticum der Katze bei Änderung des arteriellen Sauerstoffdruckes [\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \)(t)-Antwortkurve] und ihre Beeinflussung durch den Blutdruck. Nova Acta Leopoldina38, 277–286 (1973)
Acker, H., Lübbers, D. W., Durst, H.: Autoregulation of flow and oxygen pressure in the isolated hemoglobin-free perfused carotid body of the cat. Arzneimittel-Forsch. (Drug Res.)23, 1611 (1973)
Acker, H., Weigelt, H., Lübbers, D. W., Bingmann, D., Caspers, H.: Effect of changes in Ca2+ and K+ activity upon tissue\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) and chemoreceptor activity of the cat carotid body. XXVI. Int. Congress of Physiol. Sciences.—I. Arterial Chemoreceptors—Srinagar/Indien (1974) (in press)
Acker, H., Lübbers, D. W.: The meaning of the tissue\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) of the carotid body for the chemoreceptive process. In: The peripheral arterial chemoreceptors (M. J. Purves, ed.), pp. 325–343. London: Cambridge University Press 1975
Baumgärtl, H., Lübbers, D. W.: Platinum needle electrode for polarographic measurement of oxygen and hydrogen. In: Oxygen supply (M. Kessler, D. F. Bruley, L. C. Clark, Jr., D. W. Lübbers, I. A. Silver, and J. Strauss, eds.), pp. 130–136. München: Urban & Schwarzenberg 1973
Daly, M. de Burgh, Lambertsen, C. J., Schweitzer, A.: Observations on the volume of blood flow and oxygen utilization of the carotid body in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)125, 67–89 (1964).
Chance, B., Schoener, B., Schindler, F.: The intracellular oxidation-reduction state. In: Oxygen in the animal organism (F. Dickens, and E. Neil, eds.), p. 367. London-New York-Paris-Frankfurt. Pergamon Press 1966
Fay, F. S.: Oxygen consumption of the carotid body. Amer. J. Physiol.218, 518–523 (1970)
Knaust, K.: Sauerstoffversorgung des hämoglobinfrei perfundierten Meerschweinchengehirnes bei Normo- und Hypothermie. Dissertation, Marburg 1969
Kunze, K., Lübbers, D. W.: Die Messung des lokalen O2-Verbrauches von Organen in situ mit der Platinelektrode. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.274, R 74–75 (1961)
Lee, K. D., Mattenheimer, H.: The biochemistry of the carotid body. Enzymol. Biol. Clin.4, 199–216 (1964)
Leitner, L. M., Liaubet, M. J.: Carotid body oxygen consumption of the cat in vitro. Pflügers Arch.323, 315–322 (1971)
Leniger-Follert, E., Lübbers, D. W.: Determination of local myoglobin concentration in the Guinea pig heart. Pflügers Arch.341, 271–280 (1973)
Mills, E., Jöbsis, F. F.: Simultaneous measurement of cytochrome a3 reduction and chemoreceptor afferent activity in the carotid body. Nature (Lond.)225, 1147–1149 (1970)
Purves, M. J.: Changes in oxygen consumption of the carotid body of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)200, 132–133 (1969)
Purves, M. J.: The effect of hypoxia, hypercapnia and hypotension upon carotid body blood flow and oxygen consumption in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)209, 395–416 (1970)
Schäfer, D., Schäfer, S., Lübbers, D. W.: On the population of mitochondria in type I glomus cells of the cat and in cells of other organs. Arzneimittel-Forsch. (Drug Res.)23, 1611 (1973)
Reference deleted
Seidl, E.: On the variability of form and vascularization of the carotid body. Anat. Embryol.149, 79–77 (1976)
Starlinger, H., Lübbers, D. W.: Methodische Untersuchungen zur polarographischen Messung der Atmung und des „kritischen Sauerstoffdrucks” bei Mitochondrien und isolierten Zellen mit der membranbedeckten Platinelektrode. Pflügers Arch.337 19–28 (1972)
Starlinger, H., Lübbers, D. W.: Polarographic measurement of the oxygen pressure performed simultaneously with optical measurements of the redox state of the respiratory chain in suspensions of mitochondria under steady-state conditions and low oxygen tensions. Pflügers Arch.331, 15–22 (1973)
Starlinger, H., Lübbers, D. W.: Oxygen consumption of the isolated carotid body tissue (cat.) Pflügers Arch.366, 61–66 (1976)
Thews, G.: Die Sauerstoffdiffusion im Gehirn. Pflügers Arch.271, 197–226 (1960)
Weigelt, H.: Der lokale Sauerstoffdruck im Glomus caroticum des Kaninchens und seine Bedeutung für die Chemorezeption. Dissertation, Ruhr-Universität Bochum 1975
Whalen, W. J., Nair, P.: Some factors affecting tissue\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) in the carotid body. J. appl. Physiol.39, 562–566 (1975)
Woods, R. I.: Distribution of cytochrome oxidase between all elements of the carotid body. In: peripheral arterial chemoreceptors (M. J. Purves, ed.). London, Cambridge: University Press 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acker, H., Lübbers, D.W. The kinetics of local tissue\(P_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) decrease after perfusion stop within the carotid body of the cat in vivo and in vitro. Pflügers Arch. 369, 135–140 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00591569
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00591569