Abstract
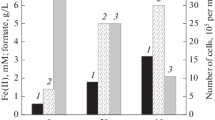
Enrichment cultures that anaerobically degraded oxalate were obtained from lake sediment inocula. From these, 5 pure cultures of anaerobic oxalate-degrading bacteria were isolated and partially characterized. The isolates were Gram-negative, non-sporeforming, non-motile, obligate anaerobes. Oxalate was required for growth and was stoichiometrically converted to formate; 14CO2 was also recovered when 14C-oxalate was added. Maximal growth occurred when the oxalate concentration was 50 mM. Acetate stimulated growth in the presence of oxalate, however, 14C-experiments indicated that acetate was only utilized for cell carbon.
The isolates were either spiral-shaped or rod-shaped organisms. The first morphotype grew much more slowly than the second and exhibited 13-fold lower cell yields. These isolates represent a new strain of oxalate-degrading bacteria. The second morphotype was similar to the anaerobic oxalate-degrading bacteria previously found in rumen. This report extends the known habitats in which anaerobic oxalate-degrading organisms have been found to include aquatic sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison MJ, Cook HM (1981) Oxalate degradation by microbes of the large bowel of herbivores: The effect of dietary oxalate. Science 212:675–676
Allison MJ, Littledike ET, James LF (1977) Changes in ruminal oxalate degradation rates associated with adaptation to oxalate ingestion. J Anim Sci 45:1173–1179
Allison MJ, Dawson KA, Cook HM, Mayberry WR (1985) Oxalobacter formigenes gen. nov., sp. nov: Oxalate-degrading anaerobes that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract. Arch Microbiol 141:1–7
Culbertson CW, Zehnder AJB, Oremland RS (1981) Anaerobic oxidation of acetylene by estuarine sediments and enrichment cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 41:396–403
Daniel SL, Allison MJ, Hartman PA (1983) Enumeration, isolation, and characterization of anaerobic oxalate-degrading bacteria from the rat cecum. Abstracts of the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology p 159
Dawson KA, Allison MJ, Hartman PA (1980a) Isolation and some characteristics of anaerobic axalate-degrading bacteria from the rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:833–839
Dawson KA, Allison MJ, Hartman PA (1980b) Characteristics of anaerobic oxalate-degrading enrichment cultures from the rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:840–846
Ehrlich GG, Goerlitz DF, Bourell JH, Eisen GV, Godsy EM (1981) Liquid chromatographic procedure for fermentation product analysis in the identification of anaerobic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 42:878–885
Hanson RS, Phillips JA (1981) Chemical composition. In: Gerhardt P (ed) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 328–364
James LF, Street JC, Butcher JE (1967) In vitro degradation of oxalate and of cellulose by rumen ingesta from sheep fed Halogeton glomeratus. J Anim Sci 26:1438–1444
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent: J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Pfennig N (1974) Rhodopseudomonas globiformis sp. n., a new species of Rhodospirilleceace. Arch Microbiol 100:197–206
Postgate JR (1963) A strain of Desulfovibrio able to use oxamate. Arch Mikrobiol 46:287–295
Smith RL, Oremland RS (1983) Anaerobic oxalate degradation: Widespread naturel occurrence in aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:106–113
Wolin EA, Wolin MJ, Wolfe RS (1963) Formation of methane by bacterial extracts. J Biol Chem 238:2882–2886
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, R.L., Strohmaier, F.E. & Oremland, R.S. Isolation of anaerobic oxalate-degrading bacteria from freshwater lake sediments. Arch. Microbiol. 141, 8–13 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446732
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446732