Abstract
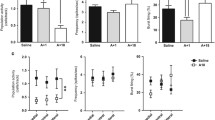
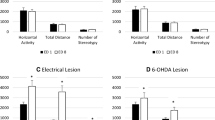
The present study was primarily designed to explore the relationship between phencyclidine(PCP)-induced hyperactivity and the mesolimbic dopamine (DA) system. In addition, the motor-activating and behavioral effects of amphetamine (1.5 mg/kg), SKF-10,047 (25.0 mg/kg), scopolamine (1.0 mg/kg), and caffeine (10.0 mg/kg) were also measured and compared to PCP action. While all compounds produced a moderate to large degree of hyperactivity with varying time courses for effect, gross behavioral observations indicated a greater similarity between PCP and SKF-10,047 than between any of the other drugs. Following bilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nucleus accumbens the robust locomotor-stimulating action of 5 mg/kg PCP was significantly reduced. Such lesions also successfully prevented amphetamine- and SKF-10,047-induced hyperactivity, but not the behavioral activation produced by scopolamine or caffeine. These results suggest that PCP and SKF-10,047, like amphetamine, elicit locomotor activity through presynaptic DA mechanisms within the mesolimbic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brady KT, Balster RL, May EL (1982) Stereoisomers of N-allyl-normetazocine: Phencyclidine-like behavioral effects in squirrel monkeys and rats. Science 215:178–180
Burns RS, Lerner SE (1981) The effects of phencyclidine in man: A review. In: Domino EF (ed) PCP (phencyclidine): Historical and current perspectives. NPP Books, Ann Arbor, MI, pp 449–469
Castellani S, Adams PM (1981a) Acute and chronic phencyclidine effects on locomotor activity, stereotypy and ataxia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 73:143–154
Castellani S, Adams PM (1981b) Effects of dopaminergic drugs or phencyclidine-induced behavior in the rat. Neuropharmacology 20:371–374
Domino EF (1964) Neurobiology of phencyclidine (Sernyl), a drug with an unusual spectrum of pharmacological activity. Int Rev Neurobiol 6:303–347
Domino E (1981) PCP (phencyclidine): Historical and current perspectives. NPP Books, Ann Arbor
Felice IJ, Felice JD, Kissinger PT (1978) Determination of catecholamines in rat brain parts by reverse-phase ion-pair liquid chromatography. J Neurochem 31:1461–1465
Fessler RG, Sturgeon RD, Meltzer HY (1979) Phencyclidine-induced ipsilateral rotation in rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine-induced lesions of the substantia nigra. Life Sci 24:1281–1288
Fink JS, Smith GP (1980) Relationships between selective denervation of dopamine terminal fields in the anterior forebrain and behavioral responses to amphetamine and apomorphine. Brain Res 201:107–127
Finnegan KT, Kanner MI, Meltzer HY (1976) Phencyclidine-induced rotational behavior in rats with nigrostriatal lesions and its modulation by dopaminergic and cholinergic agents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 5:651–660
Fray PJ, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Koob GF, Iversen SD (1980) An observational method for quantifying the behavioral effects of dopamine agonists: Contrasting effects of d-amphetamine and apomorphine. Psychopharmacology 69:253–259
Garey RE, Heath RGH (1976) The effects of phencyclidine on the uptake of 3H-catecholamines by rat striatal and hypothalamic synaptosomes. Life Sci 18:1105–1110
Glick SD, Cox RD, Maayani S, Meibach RC (1979) Anticholinergic behavioral effect of phencyclidine. Eur J Pharmacol 59:103–106
Holtzman SG (1980) Phencyclidine-like discriminative effects of opioids in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 214:614–619
Iwamoto ET (1981) Locomotor activity and antinociception after putative mu, kappa and sigma opioid receptor agonists in the rat: Influence of dopaminergic agonists and antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 217:451–460
Joyce EM, Koob GF (1981) Amphetamine-, scopolamine- and caffeine-induced locomotor activity following 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the mesolimbic dopamine system. Psychopharmacology 73:311–313
Kanner M, Finnegan K, Meltzer HY (1975) Dopaminergic effects of phencyclidine in rats with nigrostriatal lesions. Psychopharmacol Commun 114:393–401
Keats AS, Telford J (1964) Narcotic antagonists as analgesics: Clinical aspects. Adv Chem Ser 45:170–176
Kelly PH, Seviour PW, Iversen SD (1975) Amphetamine and apomorphine responses in the rat following 6-OHDA lesions of the nucleus accumbens septi and corpus striatum. Brain Res 94:507–522
Kelly PH, Iversen SD (1976) Selective 6-OHDA-induced destruction of mesolimbic dopamine neurons: Abolition of psychostimulant-induced locomotor activity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 40:45–56
Koob GF, Riley SJ, Smith SC, Robbins TW (1978) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nucleus accumbens septi and olfactory tubercle on feeding, locomotor activity and amphetamine anorexia in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 92:917–927
Koob GF, Stinus L, LeMoal M (1981) Hyperactivity and hypoactivity produced by lesions to the mesolimbic dopamine system. Behav Brain Res 3:341–359
Martin WR (1967) Opioid antagonists. Pharmacol Rev 19:463–521
Martin WR, Eades CG, Thompson JA, Huppler RE, Gilbert PE (1976) The effects of morphine- and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:517–532
Meltzer HY, Sturgeon RD, Simonovic M, Fessler RG (1981) Phencyclidine as an indirect dopamine agonist. In: Domino EF (ed) PCP (phencyclidine): Historical and current perspectives. NPP Books, Ann Arbor, pp 207–242
Murray TF, Horita A (1979) Phencyclidine-induced stereotyped behavior in rats: Dose-response effects and antagonism by neuroleptics. Life Sci 24:2217–2226
Pijnenburg AJJ, Honig WMM, Van Rossum JM (1975) Inhibition of d-amphetamine-induced locomotor activity by injection of haloperidol into the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Psychopharmacologia 41:87–95
Quirion R, Hammer Jr RP, Herkenham M, Pert CB (1981) Phencyclidine (angel dust)/gs opiate receptor: Visualization by tritium-sensitive film. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 78:5881–5885
Schlemmer RF, Jackson JA, Preston KL, Bederka JP, Garver DL, Davis JM (1978) Phencyclidine-induced stereotyped behavior in monkeys: Antagonism by pimozide. Eur J Pharmacol 52:379–384
Shannon HE (1981) Evaluation of phencyclidine analogs on the basis of their discriminative stimulus properties in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 216:543–551
Snyder SH, Banerjee SP, Yamamura HI, Greenberg D (1974) Drugs, neurotransmitters, and schizophrenia. Science 184:1243–1253
Stevens JR (1973) An anatomy of schizophrenia? Arch Gen Psychiatry 29:177–189
Sturgeon RD, Fessler RG, London SF, Meltzer HY (1981) A comparison of the effects of neuroleptics on phencyclidine-induced behaviors in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 76:37–53
Vaupel DB, Jasinski DR (1979) Acute single-dose effects of phencyclidine (PCP) in the dog. Fed Proc 38:435
Wang RY (1981) Dopaminergic neurons in the rat ventral tegmental area. III. Effects of D- and L-amphetamine. Brain Res Rev 3:153–165
Woodruff GN, McCarthy PS, Walker RJ (1976) Studies on the pharmacology of neurones in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Brain Res 115:233–242
Zukin RS, Zukin SR (1981) Multiple opiate receptors: Emerging concepts. Life Sci 29:2681–2690
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
French, E.D., Vantini, G. Phencyclidine-induced locomotor activity in the rat is blocked by 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the nucleus accumbens: Comparisons to other psychomotor stimulants. Psychopharmacology 82, 83–88 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426386
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426386