Abstract
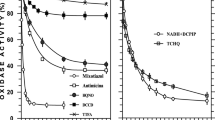
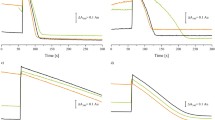
Membranes of Klebsiella pneumoniae, grown anaerobically on citrate, contain a NADH oxidase activity that is activated specifically by Na+ or Li+ ions and effectively inhibited by 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline-N-oxide (HQNO). Cytochromes b and d were present in the membranes, and the steady state reduction level of cytochrome b increased on NaCl addition. Inverted bacterial membrane vesicles accumulated Na+ ions upon NADH oxidation. Na+ uptake was completely inhibited by monensin and by HQNO and slightly stimulated by carbonylcyanide-p-trifluoromethoxy phenylhydrazone (FCCP), thus indicating the operation of a primary Na+ pump. A Triton extract of the bacterial membranes did not catalyze NADH oxidation by O2, but by ferricyanide or menadione in a Na+-independent manner. The Na+-dependent NADH oxidation by O2 was restored by adding ubiquinone-1 in micromolar concentrations. After inhibition of the terminal oxidase with KCN, ubiquinol was formed from ubiquinone-1 and NADH. The reaction was stimulated about 6-fold by 10 mM NaCl and was severely inhibited by low amounts of HQNO. Superoxide radicals were formed during electron transfer from NADH to ubiquinone-1. These radicals disappeared by adding NaCl, but not with NaCl and HQNO. It is suggested that the superoxide radicals arise from semiquinone radicals which are formed by one electron reduction of quinone in a Na+-independent reaction sequence and then dismutate in a Na+ and HQNO sensitive reaction to quinone and quinol. The mechanism of the respiratory Na+ pump of K. pneumoniae appears to be quite similar to that of Vibrio alginolyticus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FCCP:
-
carbonylcyanide-p-trifluoromethoxy phenylhydrazone
- HQNO:
-
2-n-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline-N-oxide
- luminol:
-
5-amino-2,3-dihydro-1,4-phthalazinedione
- Q-1:
-
ubiquinone-1
- QH2 :
-
ubiquinol-1
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
References
Buckel W, Semmler R (1983) Purification, characterization and reconstitution of glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase, a biotin dependent sodium pump from anaerobic bacteria. Eur J Biochem 136:427–434
Dimroth P (1982) The generation of an electrochemical gradient of sodium ions upon decarboxylation of oxaloacetate by the membrane-bound and Na+-activated oxaloacetate decarboxylase from Klebsiella aerogenes. Eur J Biochem 121:443–449
Dimroth P (1986) Preparation, characterization and reconstitution of oxaloacetate decarboxylase from Klebsiella aerogenes, a sodium pump. Meth Enzymol 125:530–540
Dimroth P (1987) Sodium ion transport decarboxylases and other aspects of sodium ion cycling in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 51:320–340
Dimroth P, Thomer A (1983) Subunit composition of oxaloacetate decarboxylase and characterization of the α-chain as carboxyltransferase. Eur J Biochem 137:107–112
Hayashi M, Unemoto T (1987) Subunit composition and their roles in the sodium-transport NADH: quinone reductase of a marine bacterium, Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochim Biophys Acta 890: 47–54
Hilpert W, Dimroth P (1983) Purification and characterization of a new sodium transport decarboxylase. Methylmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase from Veillonella alcalescens. Eur J Biochem 138:579–583
Ken-Dror S, Lanyi JK, Schobert B, Silver B, Avi-Dor Y (1986a) An NADH: quinone oxidoreductase of the halotolerant bacterium Ba1 is specifically dependent on sodium ions. Arch Biochem Biophys 244:766–772
Ken-Dror S, Preger R, Avi-Dor Y (1986b) Functional characterization of the uncoupler-insensitive Na+ pump of the halotolerant bacterium, Ba1. Arch Biochem Biophys 244:122–127
Laubinger W, Dimroth P (1987) Characterization of the Na+-stimulated ATPase of Propionigenium modestum as an enzyme of the F1F0 type. Eur J Biochem 168:475–480
Laubinger W, Dimroth P (1988) Characterization of the ATP synthase of Propionigenium modestum as a primary sodium pump. Biochemistry 27:7531–7537
Michelson AM (1978) Purification and properties of Pholas dactylus luciferin and luciferase. Meth Enzymol 57:385–406
Tokuda H, Unemoto T (1982) Characterization of the respiration-dependent Na+ pump in the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biol Chem 257:10007–10014
Tokuda H, Unemoto T (1984) Na+ is translocated at NADH: quinone oxidoreductase segment in the respiratory chain of Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biol Chem 259:7785–7790
Tsuchiya T, Shinoda S (1985) Respiration-driven Na+ pump and Na+ circulation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol 162: 794–798
Udagawa T, Unemoto T, Tokuda H (1986) Generation of Na+ electrochemical potential by the Na+-motive NADH oxidase and Na+/H+ antiport system of a moderately halophilic Vibrio costicola. J Biol Chem 261:2616–2622
Unemoto T, Hayashi M (1979) NADH: quinone oxidoreductase as a site of Na+-dependent activation of the respiratory chain of a marine Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biochem 85:1461–1467
Unemoto T, Hayashi M, Hayashi M (1977) Na+-dependent activation of NADH oxidase in membrane fractions from halophilic Vibrio alginolyticus and V. costicolus. J Biochem 82:1389–1395
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dimroth, P., Thomer, A. A primary respiratory Na+ pump of an anaerobic bacterium: the Na+-dependent NADH:quinone oxidoreductase of Klebsiella pneumoniae . Arch. Microbiol. 151, 439–444 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00416604
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00416604