Abstract
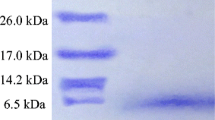
When grown in complex or synthetic media, Lactobacillus casei B 80 synthesizes a mitomycin C-inducible polypeptide with very specific bactericidal activity against the sensitive strain Lactobacillus casei B 109. The amount of secreted bacteriocin in the culture solution was low, about 1 mg/l. The bacteriocin which we called caseicin 80, was also detectable in cell extracts, although only 2% of the total activity was retained intracellularly. Caseicin 80 was concentrated by ultrafiltration and purified by cation exchange chromatography with Cellulose SE-23 and Superose. The molecular weight was in the range of M r=40,000–42,000 and the isoelectric point was pH 4.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barefoot SF, Klaenhammer TR (1984) purification and characterization of the Lactobacillus acidophilus bacteriocin lactacin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 26:328–334
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
De Klerk HC, Smith JA (1967) Properties of a Lactobacillus fermenti bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol 48:309–316
Hosono A, Yastuki K, Tokita F (1977) Isolation and characterization of an inhibitory substance against Escherichia coli produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Milchwissenschaft 32:727–730
Joerger MC, Klaenhammer TR (1986) Characterization and purification of helveticin J and evidence for a chromosomally determined bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 481. J Bacteriol 167:439–446
Mayr-Harting A, Hedges AJ, Berkeley RCW. (1972) Methods for studying bacteriocins. In: Norris JR, Ribbons DW (eds) Methods in microbiology, vol 7A, chap 7. Academic Press, London New York, pp 315–422
McGroarty JA, Reid G (1988) Detection of a lactobacillus substance that inhibits Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol 34:974–978
Mikolajcik EM, Hamdan IY (1975) Lactobacillus acidophilus. 2. Antimicrobial agents. Cultured Dairy Prod J 10:18–20
Muriana PM, Klaenhammer TR (1987) Conjugal transfer of plasmid-encoded determinants for bacteriocin production and immunity in Lactobacillus acidophilus 88. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:553–560
Rammelsberg M, Radler R (1990) Antibacterial polypeptides of Lactobacillus species. J Appl Bacteriol 68 (in press)
Sahl HG, Brandis H (1981) Production, purification and chemical properties of an antistaphylococcal agent produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Gen Microbiol 127:377–384
Shahani KM, Vakil JR, Kilara A (1977) Natural antibiotic acitivity of Lactobacillus acidophilus and bulgaricus. 2. Isolation of acidophilin from L. acidophilus. Cultured Dairy Prod J 12:8–11
Tagg JR, Dajani AS, Wannamaker LW (1976) Bacteriocins of grampositive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 40:722–756
Upreti GC, Hinsdill RD (1975) Production and mode of action of lactocin 27: bacteriocin from a homofermentative Lactobacillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 7:139–145
Vesterberg O (1972) Isoelectric focusing of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta 257:11–19
Warburg O, Christian W (1941) Isolierung und Kristallisation des Gärungsferments Enolase. Biochem Z 310:384–421
Weiller HG, Radler F (1972) Vitamin- und Aminosäurebedarf von Milchsäurebakterien aus Wein und von Rebenblättern. Mitt Klosterneuburg 22:4–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rammelsberg, M., Müller, E. & Radler, F. Caseicin 80: purification and characterization of a new bacteriocin from Lactobacillus casei . Arch. Microbiol. 154, 249–252 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248963
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248963