Abstract
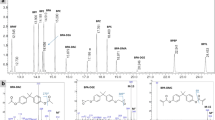
Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry with selected-ion monitoring (GC/MS-SIM) method were used to analyze 23 selected phenols in natural and drinking waters by an in situ acetylation technique. This method was suitable for determining phenol concentrations at the ng/L level because of less background interference and better recoveries. The application range for all these phenols was from 0.01 or 0.04 to 10 μg/L, using a 800 ml water sample. The levels of trace phenols in four Taiwan water treatment plants were in the range of 12–312 ng/L.
The polychlorinated phenols, namely 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol, were evaluated for their ability to induce deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage using a DNA precipitation assay employing mouse embryonic fibroblast cells (C3H10T1/2) with or without a liver microsomal activation system. These agents exhibited a weak positive response when microsomal activation enzymes were present in this assay. When the tetrachlorohydroquinone, a toxic metabolite of pentachlorophenol, was measured by the same method without the activation system, a significant and dose-dependent DNA damage was found. This result indicates that in the evaluation of the carcinogenic potential of these agents, their corresponding metabolites should be taken into consideration. DNA strand breakage caused by these active metabolites may play an important role in the tumorigenetic process of polychlorinated phenols.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfieri A, Crawford G, Ahmad I (1989) One-step sample preparation technique for broad spectrum gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric determination of organic priority pollutants in water. J Assoc Offic Anal Chem 72:760–765
Aruma OI, Halliwell B, Gajewski E, Dizdaroglu M (1991) Copperion-dependent damage to the bases in DNA in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J 273:601–604
Baird RB, Carmona LG, Jenkins RL (1977) The direct-injection GLC analysis of xylenols in industrial wastewaters. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 17:764
Besten CD, Peters MMCG, Bladeren PJV (1989) The metabolism of pentachlorobenzene by rat liver microsomes: The nature of the reactive intermediates formed. Biochem Bioph Res 163:1275–1281
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carstens C-P, Blum JK, Witte I (1990) The role of hydroxyl radicals in tetrachlorohydroquinone induced DNA strand break formation in PM2 DNA and human fibroblasts. Chem-Biol Interact 74:305–314
Chriswell CD, Chang RC, Fritz IS (1975) Chromatographic determination of phenols in water. Anal Chem 47:1325–1329
Cohen G, Cederbaum AI (1979) Chemical evidence for production of hydroxyl radicals during microsomal electron transfer. Science 204:66–68
Coutts RT, Hargesheimer EE, Pasutto FM (1979) Gas chromatographic analysis of trace phenols by direct acetylation in aqueous solution. J Chromatogr 179:291–299
DeMarini DM, Brooks HG, Parkes Ir DG (1990) Induction of prophage Lambda by chlorophenols. Environ Mol Mutagen 15:1–9
Dignam JD, Strobel HW (1977) NADPH-Cytochrome P-450 reductase from rat liver: Purification by affinity chromatography and characterization. Biochem 16:1116–1123
Dunlop WJ, Shew DC, Scalf MR, Cosby RL, Robertson MJ (1976) Identification and analysis of organic pollutants in water. In: Keith LH, Ann Arbor Sci, Ann Arbor, MI. Ch. 27, p 453
Franson MAH (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 18th edition, Part 500, American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Galloway SM, Armstrong MJ, Reuben C, Colman S, Brown B, Cannon C, Bloom AD, Nakamure F, Ahmed M, Dus S, Rimpo J, Marjolin BH, Resnick MA, Anderson B, Zeiger E (1987) Chromosome aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges in Chinese hamster ovary cells: Evaluations of 108 chemicals. Environ Mol Mutagen 10:1–175
Hattemer-Frey HA, Travis CC (1989) Pentachlorophenol: Environmental partitioning and human exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:482–489
Haworth S, Lawlor T, Mortelmans K, Speck W, Zeiger E (1983) Salmonella mutagenicity test results for 250 chemicals. Environ Mutagen 5:3–142
Hileman B (1982) The chlorination question. Environ Sci Technol 16:15A-8A
Jansson K, Jansson V (1986) Inability of chlorophenols to induce 6-thioguanine-resistant mutants in V79 Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res 171:165–168
Juhl U, Blum K, Witte I (1989) The in vitro metabolites of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol and their DNA strand breaking properties. Chem-Biol Interact 69:333–344
Keith LH (1976) Identification and analysis of organic pollutants in water. In: Keith LH, Ann Arbor Sci, Ann Arbor, MI. Ch 36 pp 671
Kohn KW, Erickson LC, Ewig RA, Friedman CA (1976) Fractionation of DNA from mammalian cells by alkaline elution. Biochemistry 15:4629–4636
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Martins EAL, Chubatsu LS, Meneghini R (1991) Role of antioxidants in protecting cellular DNA from damage by oxidative stress. Mutat Res 250:95–101
Meneghini R (1988) Genotoxicity of active oxygen species in mammalian cells. Mutat Res 195:215–230
Olive PL (1988) DNA precipitation assay: A rapid and simple method for detecting DNA damage in mammalian cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 11:487–495
Paasivirta J, Sarkka J, Leskijarvi, Roos A (1980) Transportation and enrichment of chlorinated phenolic compounds in different aquatic food chains. Chemosphere 9:441–456
Roy D, Liehr JG (1988) Temporary decrease in renal quinone reductase activity induced by chronic administration of estradiol to male syrian hamsters. J Biol Chem 263:3646–3651
Rydberg B (1975) The rate of strand separation in alkali of DNA of irradiated mammalian cells. Radiat Res 61:274–287
Shang-Zhi S, Duffield AM (1984) Negative ion chemical ionization gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of some derivatives of tri-, tetra-, and pentachlorophenols. J Chromatogr 284:157–165
Sithole BB, Williams DT (1986) Determination of halogenated phenols in raw and potable water by selected ion gas chromatographymass spectrometry. J Assoc Offic Anal Chem 69:466–473
Sweetman JA, Simmons MS (1980) The production of bromophenols resulting from the chlorination of waters containing bromide ion and phenol. Water Res 14:287–290
Watanabe I, Kashimoto T, Tatsukawa R (1984) Brominated phenol production from the chlorination of wastewater containing bromide ions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 33:395–399
Witte I, Juhl U, Butte W (1985) DNA-damaging properties and cytotoxicity in human fibroblasts of tetrachlorohydroquinone, a pentachlorophenol metabolite. Mutat Res 145:71–75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YJ., Lin, JK. Estimation of selected phenols in drinking water with In situ acetylation and study on the DNA damaging properties of polychlorinated phenols. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 537–542 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00211639
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00211639