Abstract
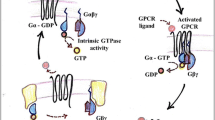
Seven-transmembrane receptors signal through nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) into the cell. G proteins are membrane-associated proteins composed of three subunits termed α, β and γ, of which the Gα subunit classifies the heterotrimer. So far, 23 different mammalian Gα subunits are known, which are grouped in four subfamilies (Gs, Gi, Gq, G12) on the basis of their amino acid similarity. They carry an endogenous GTPase activity allowing reversible functional coupling between ligand-bound receptors and effectors such as enzymes and ion channels. In addition, five Gβ and seven Gγ subunits have been identified which form tightly associated βγ heterodimers. Upon activation by a ligand-bound receptor the G protein dissociates into Gα and Gβγ, which both transmit signal by interacting with effectors. On the G protein level, specificity and selectivity of the incoming signal is accomplished by G protein trimers composed of distinct subunits. On the other hand, many receptors have been shown to activate different G proteins, thereby regulating diverse signal transduction pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT :
-
Cholera toxin
- PT :
-
Pertussis toxin
References
Koesling D, Böhme E, Schultz G (1993) Guanylyl cyclases as effectors of hormone and neurotransmitter receptors. In: Hucho F (ed) Neurotransmitter receptors. Elsevier, pp 325–338
Jan LY, Jan YN (1992) Tracing the roots of ion channels. Cell 69:715–718
Unwin N (1993) Neurotransmitter action: opening of ligandgated ion channels. Neuron [Suppl] 10:31–41
Schlessinger J, Ullrich A (1992) Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinase. Neuron 9:383–391
Egan SE, Weinberg A (1993) The pathway to signal achievement. Nature (London) 365:781–783
Charbonneau H, Tonks NK (1992) 1002 protein phosphatases? Annu Rev Cell Biol 8:463–493
Garbers DL (1992) Guanylyl cyclase receptors and their endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine ligands. Cell 71:1–4
Gudermann T, Nürnberg B, Schultz G (1995) Receptors and G proteins as primary components of transmembrane signal transduction. I. G protein-coupled receptores: structure and function. J Mol Med 73:51–63
Watson S, Arkinstall S (1994) The G protein linked receptor facts book. Academic, New York
Schultz G (1994) G proteins involved in hormonal regulations of the cytoplasmatic calcium concentrations. Ernst Schering Research Foundation, vol 19, Berlin
Sternweis PC, Smrcka AV (1992) Regulation of phospholipase C by G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17:502–506
Iyengar R (1993) Molecular and functional diversity of mammalian Gs-stimulated adenylyl cyclases. FASEB J 7:768–775
Tang WJ, Gilman AG (1992) Adenylyl cyclases. Cell 70:869–972
Dickey BF, Birnbaumer L (eds) (1993) Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 108. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F (1990) The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature (London) 348:125–132
Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F (1991) The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature (London) 349:117–127
Rodbell M, Krans HMJ, Pohl SL, Birnbaumer L (1971) The glucogon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Binding of glucagon: effect of guanyl nucleotides. J Biol Chem 246:1872–1876
Bourne HR, Nicoll R (1993) Molecular machines integrate coincident synaptic signals. Neuron [Suppl] 10:65–75
Clapham DE, Neer EJ (1993) New roles for G protein βγ-dimers in transmembrane signalling. Nature (London) 365:403–406
Leyte A, Barr FA, Kehlenbach RH, Huttner WB (1992) Multiple trimeric G proteins on the trans-golgi network exert stimulatory and inhibitory effects on secretory vescle formation. EMBO J 11:4795–4804
Pimplikar SW, Simons K (1993) Regulation of apical transport in epithelial cells by a Gs class of heterotrimeric G protein. Nature (London) 362:456–458
Bomsel M, Mostov K (1992) Role of heterotrimeric G proteins in membrane traffic. Mol Biol Cell 3:1317–1328
Barr FA, Leyte A, Huttner WB (1992) Trimeric G proteins and vesicle formation. Trends Cell Biol 2:91–94
Birnbaumer L (1992) Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for βγ dimers as well as α subunits. Cell 71:1069–1072
Hepler JR, Gilman AG (1992) G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17:383–387
Wilkie TM, Gilbert DJ, Olsen AS, Chen XN, Amatruda TT, Korenberg JR, Trask BJ, de Jong P, Reed RR, Simon MI, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG (1992) Evolution of the mammalian G protein α subunit multigene family. Nature Genetics 1:85–91
Gilman AG (1987) G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem 56:615–649
Higashijima T, Ferguson KM, Sternweis PC, Smigel MD, Gilman AG (1987) Effects of Mg2+ and the βγ-subunit complex on the interactions of guanine nucleotides with G proteins. J Biol Chem 262:762–766
Fields TA, Linder ME, Casey PJ (19994) Subtype-specific binding of azidoanilido-GTP by purified G protein α subunits. Biochemistry 33:6877–6883
Laugwitz KL, Spicher K, Schultz G, Offermanns S (1994) Identification of receptor-activated G proteins: selective immunoprecipitation of photolabled G protein α-subunits. Methods Enzymol 237:283–294
Kaldenberg-Stasch S, Baden M, Fessler B, Jakobs KH, Wieland T (1994) Receptor-stimulated guanine nucleoside triphosphate binding to G proteins: nucleotide exchange and β-subunit-mediated phosphotransfer reactions. Eur J Biochem 221:25–33
Sternweis PC (1994) The active role of βγ in signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:198–203
Hille B (1992) G protein-coupled mechanisms and nervous signaling. Neuron 9:187–195 (1992)
Hargrave PA, Hamm HE, Hofmann KP (1993) Interaction of rhodopsin with the G protein, transducin. Bioessays 15:43–50
Nürnberg B (1994) Signaltransduktion durch heterotrimere G Proteine. Pharmazie 49:795–800
Gierschik P, Jakobs KH (1992) ADP-ribosylation of signaltransducing guanine nucleotide binding proteins by cholera and pertussis toxin. In: Herken H, Hucho F (eds) Selective neurotoxicity. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 102. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 807–839
Simon MI, Strathmann MP, Gautam N (1991) Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science 252:802–808
Milligan G (1988) Techniques used in the identification and analysis of function of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Biochem J 255:1–13
Johnson RA, Corbin JD (eds) (1991) Adenylyl cyclase, G proteins and guanylyl cyclase. Methods Enzymol 195
Iyengar R (ed) (1994) Heterotrimeric G proteins. Methods Enzymol 237
Kehlenbach RH, Matthey J, Huttner WB (1995) XLαs is a new type of G protein. Nature (London) 372:804–809
Nürnberg B, Spicher K, Harhammer R, Bosserhoff A, Frank R, Hilz H, Schultz G (1994) Purification of a novel G protein α0-subtype from mammalian brain. Biochem J 300:387–394
Rudolph U, Brabet P, Kaplan J, Hasty P, Bradley A, Birnbaumer L (1993) targeting of the Gi2α gene in IS cells with replacements and insertion vectors. J Recept Res 13:619–629
Mortensen RM, Zubiaur M, Neer EJ, Seidman JG (1991) Embryonic stem cells lacking a functional inhibitory G protein subunit (αi2) produced by gene targeting of both alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7036–7040
Montmayeur JP, Borelli E (1994) Targeting of Gαi2 to the golgi by alternative spliced carboxyl-terminal region. Science 263:95–98
Gollasch M, Kleuss C, Hescheler J, Wittig B, Schultz G (1993) Gi2 and protein kinase C are required for thyrotropinreleasing hormone-induced stimulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in rat pituitary GH3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5587–5591
Kleuss C, Hescheler J, Ewel C, Rosenthal W, Schultz G, Wittig B (1991) Assignment of G protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature (London) 353:43–48
Kleuss C, Scherübl H, Hescheler J, Schultz G, Wittig B (1992) Different β subunits determine G protein interaction with transmembrane receptors. Nature (London) 358:424–426
Kleuss C, Scherübl H, Hescheler J, Schultz G, Wittig B (1993) Selectivity in signal transduction determined by γ subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science 259:832–834
Kalkbrenner F, Degtyar V, Schenker M, Hescheler J, Brendel S, Wittig B, Schultz G (1994) Subunit composition of the G protein coupling galanin receptors to L-type calcium channels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 349:R13
Nürnberg B, Degtiar VE, Harhammer R, Uhde M, Hescheler J, Schultz G (1994) Hormone-induced G0-subtype-specific inhibition of calcium currents. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 349:R13
Kaupp UB, Koch KW (1992) Role of cGMP and Ca2+ in vertebrate photoreceptor excitation and adaptation. Annu Rev Physiol 54:153–175
Noel JP, Hamm HE, Sigler PB (1993) The 2. 2 Å crystal structure of transducin-α complexed with GTPγS. Nature (London) 366:654–663
Lambbright DG, Noel JP, Hamm HE, Sigler PB (1994) Structural determinants for actvation of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature (London) 369:621–628
Coleman DE, Berghuis AM, Lee E, Linder ME, Gilman AG, Sprang SR (1994) Structures of active conformations of Giαl and the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. Science 265:1405–1412
Goody RS (1994) How G proteins turn off. Nature (London) 372:220–221
Kleuss C, Raw AS, Lee E, Sprang SR, Gilman AG (1994) Mechanism of GTP hydrolysis by G protein α subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9828–9831
Sondek J, Lambbright DG, Noel JP, Hamm HE, Sigler PB (1994) GTPase mechanism of G protein from the 1. 7 Å crystal structure of transducin α·GDP·AlF −4 . Nature (London) 372:276–279
McLaughlin SK, Mckinnon PJ, Margolskee RF (1992) Gustducin as a taste-cell specific G protein closely related to the transducins. Nature (London) 357:563–569
Casey PJ, Fong HKW, Simon MI, Gilman AG (1990) Gz, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein with unique biochemical properties. J Biol Chem 265:2383–2390
Kozasa T, Hepler JR, Smrcka AV, Simon MI, Rhee SG, Sternweis PC, Gilman AG (1993) Purification and characterization of recombinant G16α from Sf9 cells: activation of purified phospholipase C isoenzymes by G protein α subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9176–9180
Dennis EA, Rhee SG, Billah MM, Hannun YA (1991) Role of phospholipases in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J 5:2068–2077
Wange RL, Smrcka AV, Sternweis PC, Exton JH (1991) Photoaffinity labeling of two rat liver plasma membrane proteins with [32P]y-azidoanilido GTP in response to vasopressin. J Biol Chem 266:11409–11412
Offermanns S, Laugwitz KL, Spicher K, Schultz G (1994) G proteins of the G12 family are activated via thromboxane A2 and thrombin receptors in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:504–508
Wilkie TM, Scherle PA, Strathmann MP, Slepak VZ, Simon MI (1991) Characterzation of G protein α subunits in the Gq class: expression in murine tissues and in stromal and hematopoietic cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10049–10053
Amatruda TT, Steele DA, Slepak VZ, Simon MI (1991) Gα16, a G protein α subunit specifically expressed in hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5587–5591
Milligan G, Mullaney I, McCallum JF (1993) Distribution and relative levels of expression of the phosphoinositidase-Clinked G proteins Gqα and G11α:abscence of G11α in human platelets and haematopoietically derived cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta 1179:208–212
Amatruda TT, Gerard NP, Gerard C, Simon MI (1993) Specific interactions of chemoattractant factor receptors with G proteins. J Biol Chem 268:10139–10144
Wu D, LaRosa GJ, Simon MI (1993) G protein-coupled signal transduction pathways for interleukin-8. Science 261:101–103
Strathmann MP, Simon MI (1991) Goα12 and Gα13 subunits define a fourth class of G protein α subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5582–5586
Spicher K, Kalkbrenner F, Zobel A, Harhammer R, Nürnberg B, Söling A, Schultz G (1994) G12 and G13 α-subunits are immunochemically detectable in membranes of most tissues of various mammalian species. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 198:906–914
Harhammer R, Nürnberg B, Spicher K, Schultz G (1994): Purification G protein Gα13 from rat brain membranes. Biochem J 303:135–140
Singer WD, Miller RT, Sternweis PC (1994) Purification and characterization of the α subunit of G13. J Biol Chem 269:19769–19802
Harhammer R, Nürnberg B, Spicher K, Schultz G (1994) Rapid purification of Gα13 from bovine brain membranes: supportive effect of ethylene glycol. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 204:835–840
Harhammer R, Nürnberg B, Spicher K, Schultz G (1995) Differential properties of the purified members of the G protein G12-subfamily. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol (in press)
Voyno-Yasenetskaya T, Conklin BR, Gilbert RL, Hooley R, Bourne HR, Barber DL (1994) Gα13 stimulates Na-H exchange. J Biol Chem 269:4721–4724
Dhanasekaran N, Vara Prasad MVVS, Wadsworth SJ, Dermott JM, van Rossum G (1994) protein kinase C-dependent and -independent activation of Na+/H+ exchanger by Gα12 class of G proteins. J Biol Chem 269:11802–11806
Wilk-Blaszczak MA, Singer WD, Gutowski S, Sternweis PC, Berladetti F (1994) The G protein G13 mediates bradykinin inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current. Neuron 13:1215–1224
Xu N, Bradley L, Ambdukar I, Gutkind JS (1993) A mutant α subunit of G12 potentiates the eicosanoid pathway and is highly oncogenic in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6741–6745
Jiang H, Wu D, Simon MI (1993) The transforming activity of activated Ga12. FEBS Lett 330:319–322
Xu N, Voyno-Yasenetskaya T, Gutkind JS (1994) Potent transforming activity of the G13 α subunit defines a novel family of oncogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 201:603–609
Chan AML, Fleming TP, McGovern ES, Chedid M, Miki T, Aaronson SA (1993) Expression cDNA cloning of a transforming gene encoding the wild-type Gα12 gene product. Mol Cell Biol 13:762–768
Yamane HK, Fung BKK (1993) Covalent modifications of G proteins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 32:201–241
Casey PJ (1994) Lipid modifications of G proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:219–225
Casey P (1992) Visual differences. Nature (London) 359:671–672
Degtyarev MY, Spiegel AM, Jones TL (1993) Increased palmitoylation of the Gs protein α subunit after activation by the β-adrenergic receptor or cholera toxin. J Biol Chem 268:23769–23772
Linder ME, Middleton P, Hepler JR, Taussig R, Gilman AG, Mumby SM (1993) Lipid modifications of G proteins: α subunits are palmitoylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:3675–3679
Parenti M, Vigano MA, Newman CMH, Milligan G, Magee AI (1993) A novel N-terminal motif for palmitoylation of G protein α subunits. Biochem J 291:349–353
Veit M, Nürnberg B, Spicher K, Harteneck C, Ponimaskin E, Schultz G, Schmidt MFG (1994) The α-subunits of G12 and G13 are palmitoylated, but not amidically myristoylated. FEBS Lett 339:160–164
Mumby SM, Kleuss C, Gilman AG (1994) Receptor regulation of G protein palmtoylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2800–2804
Wedegaertner PB, Chu DH, Wilson PT, Levis MJ, Bourne HR (1993) Palmitoylation is required for signaling functions and membrane attachment of Gqα and Gsα. J Biol Chem 268:25001–25008
Hallak H, Muszbek L, Laposata M, Belmonte E, Brass LF, Manning DR (1994) Covalent binding of arachidonate to G protein α subunits of human platelets. J Biol Chem 269:4713–4716
Lounsbury KM, Casey PJ, Brass LF, Manning DR (1991) Phosphorylation of Gz in human platelets, selectivity and site of modification. J Biol Chem 266:22051–22056
Lounsbury KM, Schlegel B, Poncz M, Brass LF, Manning DR (1993) Analysis of Gzα by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 268:3494–3498
Strassheim D, Malbon CC (1994) Phosphorylation of Gαi2 attenuates inhibitory adenylyl cyclase in neuroblastoma/glioma hybrid (NG-108–15) cells. J Biol Chem 269:14307–14313
Pfeifer A, Nürnberg B, Kamm S, Uhde U, Schultz G, Ruth P, Hofmann F (1995) Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase blocks pertussis toxin-sensitive hormone receptor signaling pathways in CHO-cells. J Biol Chem (in press)
Iñiguez-Lluhi J, Kleuss C, Gilman AG (1993) The importance of G protein βγ subunits. Trends Cell Biol 3:230–236
Watson AJ, Katz A, Simon MI (1994) A fifth member of the mammalian G protein β-subunit family. J Biol Chem 269:22150–22156
Spring DJ, Neer EJ (1994) A 14-amino acid region of the G protein γ subunit is sufficient to confer selectivity of γ binding to the β subunit. J Biol Chem 269:22882–22886
Kisselev OG, Ermolaeva MV, Gautam N (1994) A farnesylated domain in the G protein γ subunit is a specific determinant of receptor coupling. J Biol Chem 269:21399–21402
Neer EJ, Schmidt CJ, Nambudripad R, Smith TF (1994) The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature (London) 371:297–300
Lupas A, van Dyke M, Stock J (1991) Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science 252:1162–1164
Lupas AN, Lupas JM, Stock JB (1992) Do G protein subunits associate via a three-stranded coiled coil? FEBS Lett 314:105–108
Garritsen A, van Galen PJM, Simonds WF (1993) The Nterminal coiled-coil domain of β is essential for γ association: a model for G protein βγ subunit interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7706–7710
Simonds WF, Manji HK, Garritsen A (1993) G proteins and βARK: a new twist for the coiled coil. Trends. J Biochem Sci 18:315–317
Bubis J, Khorana HG (1990) Sites of interaction in the complex between β- and γ-subunits of transducin. J Biol Chem 265:12995–12999
Pronin AN, Gautam N (1992) Interaction between G protein β and γ subunit types is selective. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6220–6224
Higgins JB, Casey PJ (1994) In vitro processing of recombinant G protein γ subunits. J Biol Chem 269:9067–9073
Fukada Y, Matsuda T, Kokame K, Takao T, Shimonishi Y, Akino T, Yoshizawa T (1994) Effects of carboxyl methylation of photoreceptor G protein γ-subunit in visual transduction. J Biol Chem 269:5163–5170
Dietrich A, Meister M, Brazil D, Camps M, Gierschik P (1994) Stimulation of phospholipase C-β2 by recombinant guanine-nucleotide-binding protein βγ-dimers produced in a baculovirus/insect cell expression system. Requirement of γsubunit isoprenylation for stimulation of phospholipase C. Eur J Biochem 219:171–178
Yamada M, Jahangir A, Hosoya Y, Inanobe A, Katada T, Kurachi Y (1994) GK * and brain Gβγ activate muscarinic K+ channel through the same mechanism. J Biol Chem 268:24551–24554
Thomason PA, James SR, Casey PJ, Downes CP (1994) A G protein βγ-subunit-responsive phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in human platelet cytosol. J Biol Chem 269:16525–16528
Lefkowitz RJ (1993) G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Cell 74:409–412
Crespo P, Xu N, Simonds WF, Gutkind JS (1994) Ras-dependent activation of MAP kinase pathway mediated by G protein βγ subunits. Nature (London) 369:418–420
Faure M, Voyno-Yasenetskaya TA, Bourne HR (1994) cAMP and βγ subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins stimulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in COS-7 cells. J Biol Chem 269:7851–7854
Musacchio A, Gibson T, Rice P, Thompson J, Saraste M (1993) The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 18:343–348
Gibson T, Hyvönen M, Musacchio A, Saraste M, Birney E (1994) PH domain: the first anniversary. Trends Biochem Sci 19:349–353
Parker PJ, Hemmings BA, Gierschik P (1994) PH domains and phospholipases — a meaningful relationship? Trends Biochem Sci 18:343–348
Touhara K, Inglese J, Pitcher JA, Shaw G, Lefkowitz RJ (1994) Binding of G protein βγ-subunits to pleckstrin homology domains. J Biol Chem 269:10217–10220
Ismailov II, McDuffie JH, Benos DJ (1994) Protein kinase A phosphorylation and G protein regulation of purified renal Na+ channels in planar bilayer membranes. J Biol Chem 269:10235–10241
Bubien JK, Jope RS, Warnock DG (1994) G proteins modulate amiloride-sensitive sodium channels. J Biol Chem 269:17780–17783
Bokoch GM, Gilman AG (1984) Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachdonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell 39:301–308
Okajima F, Ui M (1984) ADP-ribosylation of the specific membrane proteins by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, associated with inhibition of a chemotactic peptide-induced arachidonate release in neutrophils. J Biol Chem 259:13863–13871
Exton JH (1990) Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem 265:1–4
Fasolato C, Innocenti B, Pozzan T (1994) Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx: how many mechanisms for how many channels? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 15:77–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nürnberg, B., Gudermann, T. & Schultz, G. Receptors and G proteins as primary components of transmembrane signal transduction. J Mol Med 73, 123–132 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198240
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198240