Abstract
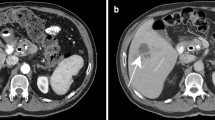
A review of liver sonograms obtained for cancer patients (excluding primary liver cancers) over a 12 year period found 829 benign lesions: non-parasitic cysts (427 cases), hemangiomas (216 cases), solitary calcifications (79 cases), focal fatty infiltration (62 cases), and miscellaneous lesions (45 cases). These benign pathologies represented 41.8% of the focal hepatic lesions observed during this period in this population; hepatic metastases accounted for the remaining 58.2%. Marked female predilection was noted for the nonparasitic cysts, hemangiomas, and focal fatty infiltration; 63–78.7% of these lesions were solitary, and first-line imaging by US was sufficient for diagnosis of 66.1–98.2% of cases. Analysis of lesion evolution over more than 5 years revealed modifications in 17% of hemangiomas, 23.9% of nonparasitic cysts, and 75% of cases of focal fatty infiltration. Systematic pretherapy liver sonography can be proposed owing to the high frequency of benign liver lesions that can create diagnostic problems during follow-up of cancer patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruneton JN, Mourou MY, Dubruque F (1993) Hémangiome. In: Bruneton JN (ed) Imagerie des tumeurs du foie. Masson, Paris, pp 108–128
Bruneton JN, Eresue J, Caramella E et al. (1983) Les kystes congénitaux du foie en échographie. J Radiol 64: 471
Peltokallio V (1970) Nonparasitic cysts of the liver. A clinical study of 117 cases. Ann Clin Gynecol 59 [Suppl 174]: 1
Rampal P, Desmorat H, Bruneton JN et al. (1986) Stéatose hépatique irrégulière. Etude clinique et iconographique de 6 cas. Gastrointest Clin Biol 10: 43
Ishak KG, Rabin L (1975) Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am 59: 995
Barnes PA, Thomas JL, Bernardino ME (1981) Pitfalls in the diagnosis of hepatic cysts by computed tomography. Radiology 141: 129
Acunas B, Rozanes I, Celik L et al. (1992) Purely cystic hydatid disease of the liver: treatment with percutaneous aspiration and injection of hypertonic saline. Radiology 182: 541
Feldmann M (1958) Hemangioma of the liver: special reference to its association with cysts of the liver and pancreas. Am J Clin Pathol 29: 160
Bruneton JN, Drouillard J, Fenart D et al. (1983) Ultrasonography of hepatic cavernous haemangiomas. Br J Radiol 56: 791
Moody AR, Wilson SR (1993) Atypical hepatic hemangioma: a suggestive sonographic morphology. Radiology 188: 413
Wernecke K, Vassallo P, Bick U et al. (1992) The distinction between benign and malignant liver tumors of sonography: value of a hypoechoic halo. AJR 159: 1005
Gaa J, Saini S (1990) Hepatic cavernous hemangioma: diagnosis by means of rapid dynamic nonincremental CT. In: Ferrucci JT, Stark DD (eds) Liver imaging: current trends and new techniques. Andover Medical Publishers, Boston, pp 212–216
Ito K, Honjo K, Matsumoto T et al. (1992) Distinction of hemangiomas from hepatic tumors with delayed enhancement by incremental dynamic CT. JCAT 16: 572
Goldberg MA, Saini S, Hahn PF et al. (1991) Differentiation between hemangiomas and metastases of the liver with ultrafast MR imaging: preliminary results with T2 calculation. AJR 157: 727
L'hermine C, Lescanne D, Bonodeau F et al. (1992) Séméiologie IRM des tumeurs du foie. Rev Im Med 4: 17
Taylor KJW, Ramos I, Morse SS et al. (1987) Focal liver masses: differential diagnosis with pulsed doppler US. Radiology 164: 643
Kudo M, Tomita S, Tochio H et al. (1992) Sonograpyy with intraarterial infusion of carbon dioxide microbubbles (sonographic angiography): value in differential diagnosis of hepatic tumors. AJR 158: 65
Gibney RG, Hendin AP, Cooperberg PL (1987) Sonographically detected hepatic hemangioma: absence of change over time. AJR 149: 953
Alpern MB, Lawson TL, Goley WD et al. (1986) Focal hepatic masses and fatty infiltration by enhanced dynamic CT. Radiology 158: 45
Raptopoulos V, Karellas B, Bernstein J et al. (1991) Value of dual-energy CT in differentiating focal fatty infiltration of the lifer from low-density masses. AJR 157: 721
Yates CK, Streight RA (1986) Focal fatty infiltration of the liver simulating metastatic disease. Radiology 159: 83
Pen JH, Pelermans PA, Van Maercke YM et al. (1986) Clinical significance of focal echogenic liver lesions. Gastrointest Radiol 11: 61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: J. N. Bruneton
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruneton, J.N., Raffaelli, C., Maestro, C. et al. Benign liver lesions: implications of detection in cancer patients. Eur. Radiol. 5, 387–390 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184949
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184949