Summary
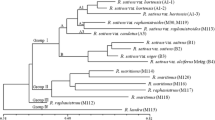
The genetic similarities of eight closely related rye cultivars were estimated using two molecular marking techniques: restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Cultivars were evaluated for variation by 11 random cDNA and genomic clones used in combination with four restriction enzymes and 40 decamer primers. A total of 53 polymorphic RFLP fragments and 94 polymorphic RAPD fragments were observed. Based on the presence/absence of fragments, two genetic similarity matrices were calculated which were then used in cluster analysis. Differences between pair of cultivars were observed in RFLP and RAPD dendrograms. RFLP analysis produced estimates of genetic relationships more in accordance with the partially known pedigree of the cultivars than did RAPD analysis. The use of bulk samples of DNA in these analyses affected the sensitivity of RAPD assays more strongly. Dendrograms which took into account all fragments produced, either by RFLP or RAPD, reflected better the relationships between cultivars than did dendrograms based on only one type of marker. This reflects the importance of the number of markers used in determining the genetic relationships between genotypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, D., V., Simonsen & V., Loeschcke, 1987. Allozyme variation in rye, Secale cereale L. 2. Commercial varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 74: 560–565.
Dawson, I.K., K.J., Chalmers, R., Waugh & W., Powell, 1993. Detection and analysis of genetic variation in Hordeum spontaneum populations from Israel using RAPD markers. Mol. Ecol. 2: 151–159.
Devos, K.M. & M.D., Gale, 1992. The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 567–572.
Ellsworth, D.L., K.D., Rittenhouse & R.L., Honeycutt, 1993. Artifactual variation in randomly amplified polymorphic DNA banding patterns. Biotechniques 14: 214–217.
González, J.M. & E., Ferrer, 1993. Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis in Hordeum species. Genome 36: 1029–1031.
Graner, A., H., Siedler, A., Jahoor, R.G., Herrmann & G., Wenzel, 1990. Assessment of the degree and the type of restriction fragment length polymorphism in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Theor. Appl. Genet. 80: 826–832.
He, S., H., Ohm & S., Mackenzie, 1992. Detection of DNA sequence polymorphisms among wheat varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 573–578.
Helentjaris, T., G., King, M., Slocum, C., Siedenstrang & S., Wegman, 1985. Restriction fragment polymorphisms as probes for plant diversity and their development as tools for applied plant breeding. Plant Mol. Biol. 5: 109–118.
Heun, M., J.M., Murphy & T.D., Phillips, 1994. A comparison of RAPD and isozyme analyses for determining the genetic relationships among Avena sterilis L. accessions. Theor. Appl. Genet. 87: 689–696.
Hoisington, D., M., Khairallah & D., González-de-Léon, 1994. Laboratory Protocols: CIMMYT Applied Molecular Genetics Laboratory. Second Edition, Mexico, DF: CIMMYT.
Joshi, C.P. & T., Nguyen, 1993. RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) analysis based intervarietal genetic relationships among hexaploid wheats. Plant Sci. 93: 95–103.
Loarce, Y., G. Hueros & E. Ferrer, 1995. A genetic linkage map of rye based on molecular markers. (submitted)
Lubbers, E.L., K.S., Gill, T.S., Cox & B.S., Gill, 1991. Variation of molecular markers among geographically diverse accessions of Triticum tauschii. Genome 34: 354–361.
Mantel, N., 1967. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res. 27: 209–220.
Micheli, M.R., R., Bova, P., Calissano & E., D'Ambrosio, 1993. Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting using combinations of oligonucleotide primers. Biotechniques 15: 388–389.
Michelmore, R.W., I., Paran & R.V., Kesseli, 1991. Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions using segregating populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 9828–9832.
Monte, J.V., C.L., McIntyre & J.P., Gustafson, 1993. Analysis of phylogenetic relationships in the Triticeae tribe using RFLPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 649–655.
Moser, H. & M., Lee, 1994. RFLP variation and genealogical distance, multivariate distance, heterosis and genetic variance in oats. Theor. Appl. Genet. 87: 947–956.
Nei, M., 1972. Genetic distance between populations. Amer. Nat. 106: 283–292.
Nei, M. & W., Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studing genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 5269–5273.
Phillip, U., P., Wheling & G., Wricke, 1994. A linkage map of rye. Theor. Appl. Genet. 88: 243–248.
Riedy, M.F., W.J., Hamilton, III & C.F., Aquadro, 1992. Excess of non-parental bands in offspring from known primate pedigrees assayed using RAPD PCR. Nucl. Acids Res. 20: 918.
Rohlf, F.J., 1989. NTSYS.PC. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 1.5. Applied Biostatistic Inc., New York.
Dos Santos, J.B., J., Nienhuis, P., Skroch, J., Tivang & M.K., Slocum, 1994. Comparison of RAPD and RFLP genetic markers in determining genetic similarity among Brassica oleracea L. genotypes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 87: 909–915.
Sharp, P.J., M., Kreiss, P.R., Shewry & M.D., Gale, 1988. Location of β-amylase sequences in wheat and its relatives. Theor. Appl. Genet. 75: 286–290.
Siedler, H., M.M., Messmer, G.M., Schachermayr, H., Winzeler, M., Winzeler & B., Keller, 1994. Genetic diversity in European wheat and spelt breeding material based on RFLP data. Theor. Appl. Genet. 88: 994–1003.
Song, K., T.C., Osborne & P.H., Williams, 1990. Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). 3. Genome relationships in Brassica and related genear and the origin of B. oleracea and B. rapa (syn. campestris). Theor. Appl. Genet. 79: 497–506.
Thormann, C.E., M.E., Ferreira, L.E.A., Camargo, J.G., Tivang & T.C., Osborne, 1994. Comparison of RFLP and RAPD markers to estimating genetic relationships within and among cruciferous species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 88: 973–980.
Tinker, N.A., M.G., Fortin & D.E., Miller, 1993. Random amplified polymorphic DNA and pedigree relationships in spring barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 85: 976–984.
Van der, Ven, W.T.G., N., Duncan, G., Ramsay, M., Phillips, W., Powell & R., Waugh, 1993. Taxonomic relationships between V. faba and its relatives based on nuclear and mitochondrial RFLPs and PCR analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 71–80.
Vierling, R.A. & H.T., Nguyen, 1992. Use of RAPD markers to determine the genetic diversity of diploid wheat genotypes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 835–838.
Wang, Z.Y. & S.D., Tanksley, 1989. Restriction fragment length polymorphism in Oriza sativa L. Genome 32: 1113–1118.
Whitkus, R., J., Doebley & J.F., Wendel, 1994. Nuclear DNA markers in systematics and evolution. In: R.L., Phillips & I.K., Vasil (Eds). DNA Based Markers in Plants. Kluwer Acad. Publ., The Netherlands.
Williams, J.G.K., A.R., Kubelik, K.J., Livak, J.A., Rafalski & S.V., Tingey, 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers and useful as genetic markers. Nucl. Acids Res. 18: 6531–6535.
Zhang, Q., M.A., Shagai-Maroof & A., Kleinhofs, 1993. Comparative diversity analysis of RFLPs and isozymes within and among populations of Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum. Genetics 134: 909–916.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loarce, Y., Gallego, R. & Ferrer, E. A comparative analysis of the genetic relationships between rye cultivars using RFLP and RAPD markers. Euphytica 88, 107–115 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032441
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032441