Abstract
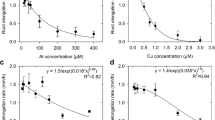
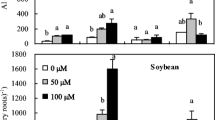
Aluminium (Al) binding in the apoplasm of the cells of plant roots has been implicated in Al toxicity, but little is known of the reactions between Al and components of the apoplasm. Because of its role in determining root cation-exchange capacity, calcium (Ca) pectate in the root cell wall has been considered especially important in binding Al. Synthetic Ca pectate was prepared at pH 5.4 and 4.0 (separate experiments), and reacted with solutions containing Ca (0.05 to 15 mM) and Al (0 to 200 µM). A sorption reaction was proposed to explain the preferential binding of Al over Ca by Ca pectate at both pH 5.4 and 4.0. An increase in Al bound by Ca pectate reduced Ca sorption and vice versa, the Ca present in the supernatant increasing by 1.65±0.15 nmol for each 1 nmol Al sorbed. Further, the volume of solution entrained by the Ca pectate gel decreased with increased Ca and Al concentrations in solution. The reduced pore size suggested by this finding may have important implications for nutrient uptake and cell elongation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alva A K, Asher C J and Edwards D G 1986 The role of calcium in alleviating aluminium toxicity. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 37, 375–382.
Blamey F P C, Edmeades D C and Wheeler D M 1990 Role of root cation-exchange capacity in differential aluminum tolerance of Lotus species. J. Plant Nutr. 13, 729–744.
Blamey F P C, Asher C J, Edwards D G and Kerven G L 1993a In vitro evidence of aluminum effects on solution movement through root cell walls. J. Plant Nutr. 16, 555–562.
Blamey F P C, Asher C J, Kerven G L and Edwards D G 1993b Factors affecting aluminium sorption by calcium pectate. Plant and Soil 149, 87–94.
Brady D J, Edwards D G, Asher C J and Blamey F P C 1993 Calcium amelioration of aluminium toxicity effects on root hair development in soybean (Glycine max L.) Merr.. New Phytol. 123, 531–538.
Carpita N C and Gibeaut D M 1993 Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants: consistency of molecular structure with the physical properties of the walls during growth. Plant J. 3, 1–30.
Clarkson D T 1967 Interactions between aluminium and phosphorus on root surfaces and cell wall material. Plant and Soil 27, 347–356.
Haynes R J 1980 Ion exchange properties of roots and ionic interactions within the root apoplasm: Their role in ion accumulation by plants. Bot. Rev. 46, 75–99.
Horst W J, Wagner A and Marschner H 1982 Mucilage protects root meristems from aluminium injury. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 105, 435–444.
Klimashevskii E L and Dedov V M 1980 Characteristics of an elastic cell wall of the root in relation to genotypic variance of plant resistance to aluminum ions. Isv. Sib. Atb. Akad. Nauk. SSSR Ser. Biol. Nauk. 1, 108–12 (Chem. Abstr. 93, 142–143).
Knight A H, Crooke W M and Inkson R H E 1961 Cation-exchange capacities of tissues of higher and lower plants and their related uronic acid contents. Nature (London) 192, 142–143.
Ostatek-Boczynski Z A, Kerven G L and Blamey F P C 1995 Aluminium reactions with polygalacturonate and related organic ligands. Plant and Soil 171, 41–45.
Rengel Z 1992 Role of calcium in aluminium toxicity. New Phytol. 121, 499–513.
Taylor G J 1991 Current views of the aluminum stress response; the physiological basis of tolerance. Curr. Top. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 10, 57–93.
Zhang G and Taylor G J 1989 Kinetics of aluminum uptake by excised roots of aluminum-tolerant and aluminum-sensitive cultivars of Triticum aestivum L. Plant Physiol. 91, 1094–1099.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blamey, F.P.C., Dowling, A.J. Antagonism between aluminium and calcium for sorption by calcium pectate. Plant Soil 171, 137–140 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009576
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009576