Abstract
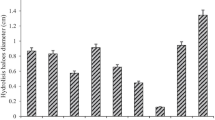
Xylanase is a well-known enzyme for the conversion of agricultural biomass into xylose using enzymatic hydrolysis process. Agricultural residues are the rich source of lignocellulosic biomass. Recently there has been increasing interest in the use of agricultural residues for the production of industrially important enzymes along with other value-added by-products. Large-scale purification of the desired enzyme from fermentation broth and purification of enzymes via economically feasible methods are the main obstacle in biotechnological industries. In the present study, aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) was utilized for the purification of extracellular crude xylanase obtained from the submerged culture of Aspergillus oryzae LC1 (ITCC-8571/NAIMCC-F-03390). Various sulphate salts were tested for xylanase purification, among them MgSO4 showed best results with PEG and was selected for further studies. Response surface methodology based on Box-Behnken design was used for optimizing the ATPS parameters, such as the molecular weight of PEG, MgSO4 and PEG concentration. The purification factor of xylanase was found maximum in the presence of high-molecular-weight PEG (8000), PEG intermediate concentration (11.3% w/w) and high MgSO4 salt concentration (22.5% w/w). A 13-fold increase in purification factor was obtained under optimized conditions, with partition coefficient 8.8% and enzyme yield 86.8% at the top phase. The partially purified xylanase obtained using ATPS was further used for the enzymatic hydrolysis of different agricultural residues, followed by the analysis of the hydrolysis products by TLC.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taneja K, Gupta S, Kuhad RC (2002) Properties and application of a partially purified alkaline xylanase from an alkalophilic fungus Aspergillus nidulans KK-99. Bioresour Technol 85(1):39–42
Tabka M, Herpoel-Gimbert I, Monod F, Asther M, Sigoillot JC (2006) Enzymatic saccharification of wheat straw for bioethanol production by a combined cellulase xylanase and feruloyl esterase treatment. Enzym Microb Technol 39(4):897–902
Patil G, Raghavarao K (2007) Aqueous two phase extraction for purification of C-phycocyanin. Biochem Eng J 34(2):156–164
Garai D, Kumar V (2013) Aqueous two phase extraction of alkaline fungal xylanase in PEG/phosphate system: optimization by Box-Behnken design approach. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2(2):125–131
Naganagouda K, Mulimani V (2008) Aqueous two-phase extraction (ATPE): an attractive and economically viable technology for downstream processing of Aspergillus oryzae α-galactosidase. Process Biochem 43(11):1293–1299
Cardoen D, Joshi P, Diels L, Sarma PM, Pant D (2015) Agriculture biomass in India: part 1. Estimation and characterization. Resour Conserv Recycl 102:39–48
ElMekawy A, Diels L, De Wever H, Pant D (2013) Valorization of cereal based biorefinery byproducts: reality and expectations. Environ Sci Technol 47(16):9014–9027
ElMekawy A, Diels L, Bertin L, De Wever H, Pant D (2014) Potential biovalorization techniques for olive mill biorefinery wastewater. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 8(2):283–293
Bhardwaj N, Chanda K, Kumar B, Prasad HK, Sharma GD, Verma P (2017) Statistical optimization of nutritional and physical parameters for Xylanase production from newly isolated Aspergillus oryzae LC1 and its application in the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic agro-residues. Bioresources 12(4):8519–8538
Ghose T, Bisaria VS (1987) Measurement of hemicellulase activities: part I xylanases. Pure Appl Chem 59(12):1739–1751
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Lowry CC, Kraeft NH, Hughes FA Jr (1951) Blastomycosis of the lung. Am J Surg 81(6):676–679
Haaland PD (1989) Experimental design in biotechnology, vol 105. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Babu BR, Rastogi N, Raghavarao K (2008) Liquid–liquid extraction of bromelain and polyphenol oxidase using aqueous two-phase system. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 47(1):83–89
Vaidya BK, Suthar HK, Kasture S, Nene S (2006) Purification of potato polyphenol oxidase (PPO) by partitioning in aqueous two-phase system. Biochem Eng J 28(2):161–166
Antov MG, Pericin DM, Dasic MG (2006) Aqueous two-phase partitioning of xylanase produced by solid-state cultivation of Polyporus squamosus. Process Biochem 41(1):232–235
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to DBT for providing the financial support (Grant No. BT/304/NE/TBP/2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bhardwaj, N., Verma, P. (2020). Extraction of Fungal Xylanase Using ATPS-PEG/Sulphate and Its Application in Hydrolysis of Agricultural Residues. In: Sadhukhan, P., Premi, S. (eds) Biotechnological Applications in Human Health. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3453-9_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3453-9_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3452-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3453-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)