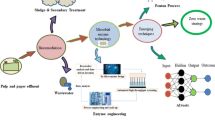
Abstract
Pulp and papermaking industry is a large consumer of fresh water and also an important source of dark-brown-colored wastewater, generated during various stages of pul** and papermaking activities. The colored wastewater discharged from pulp and paper industry even after secondary treatment remains toxic and complex in nature and retains high amount of lignin, lignin residues, resins, acids, chlorinated phenols, and various persistent organic pollutants (POPs) including the adsorbable organic halides (AOXs; halogenated or organochlorine). The existing various conventional methods along with integrated processes (aerated lagoons and activated sludge plants) cannot efficiently treat pulp and paper industry wastewater due to its complex and recalcitrant nature. Hence, the discharged partially treated/or untreated wastewater are contributing to deteriorating water quality due to increasing biological oxygen deman and chemical oxygen demand and decrease of dissolved oxygen.
In a terrestrial ecosystem, the wastewater irrigated soil showed decrease of moisture content and increase of pH and toxic heavy metals content. To tackle this problem associated with hazardous waste disposal, the existing pulp and paper industry wastewater treatment process needs to be improved with better treatment outcomes. Although, several physicochemical methods are available for the treatment of such wastewater, they are more energy intensive and suffer from residual effect. In addition, they are very expensive, inefficient, and produce a huge amount of toxic sludge which is difficult to handle and also produces volatile organic compounds on burning. To combat these challenges, biological treatment using bacteria, fungi, yeasts, and algae has evolved as a preferred means to treat and reduce the toxic organic compounds loaded in generated pulp and paper industry wastewater.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaziz OY, Brink DP, Prothmann J, Ravi K, Sun M, Garcia-Hidalgo J, Sandahl M, Hulteberg CP, Turner C, Liden G, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2016) Biological valorization of low molecular weight lignin. Biotechnol Adv 34(8):1318–1346
Abhishek A, Dwivedi A, Tandan N, Kumar U (2017) Comparative bacterial degradation and detoxification of model and Kraft lignin from pulp paper wastewater and its metabolites. Appl Water Sci 7(2):757–767
Abira MA, van Bruggen JJA, Denny P (2005) Potential of a tropical subsurface constructed wetland to remove phenol from pre-treated pulp and paper mill wastewater. Water Sci Technol 51:173–176
Ahmad M, Taylor CR, Pink D, Burton K, Eastwood D, Bending GD, Bugg TD (2010) Development of novel assays for lignin degradation: comparative analysis of bacterial and fungal lignin degraders. Mol BioSyst 6(5):815–821
Ali M, Sreekrishnan TR (2001) Aquatic toxicity from pulp and paper mill effluents: a review. Adv Environ Res 5:175–196
Alkorta I, Hernandez-Allica J, Becerril J, Amezaga I, Albizu I, Garbiscu C (2004) Recent finding on the phytoremediation of soil contaminated with environmentally toxic heavy metals and metalloids such as zinc, cadmium, lead, and arsenic. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 3:71–90
Apiwattanapiwat W, Siriacha P, Vaithanomsat P (2006) Screening of fungi for decolorization of wastewater from pulp and paper industry. Kasetsart Journal (Nat Sci) 40:215–221
Archana PI, Mahadevan A (2002) Lignin degradation by bacteria. Prog Ind Microbiol 36:311–330
Archibald F, Paice MG, Jurasek L (1990) Decolorization of Kraft bleachery effluent chromophores by Coriolus (Trametes) versicolor. Enzym Microb Technol 12:846–853
Arica MY, Altintas B, Bayramoglu G (2009) Immobilization of laccase onto spacer–arm attached non–porous poly (GMA/EGDMA) beads: application for textile dye degradation. Bioresour Technol 100:665–669
Arivoli A, Mohanraj R, Seenivasan R (2015) Application of vertical flow constructed wetland in treatment of heavy metals from pulp and paper industry wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:13336–13343
Bajpai P, Mehna A, Bajpai PK (1993) Decolorization of Kraft bleach plant effluent with the white rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Process Biochem 28:377–384384
Baker AJM (1981) Accumulator and excluder-strategies in the response of plant to heavy metals. J Plant Nutr 3:643–654
Beauchamp CJ, Simao-Beaunoir A, Beaulieu C, Chalifour F (2006) Confirmation of E. coli among other thermotolerant coliform bacteria in paper mill effluents, wood chips screening rejects and paper sludges. Water Res 40:2452–2462
Becker J, Wittmann C (2019) A field of dreams: lignin valorization into chemicals, materials, fuels, and health-care products. Biotechnol Adv. S0734-9750(19)30035-7
Bérubé PR, Hall ER (2000) Effects of elevated operating temperatures on methanol removal kinetics from synthetic Kraft pulp mill condensate using a membrane bioreactor. Water Res 34(18):4359–4366
Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig AP (2017) Instrumental characterization of organic wastes for evaluation of vermicompost maturity. J Anal Sci Technol 8:2
Bhat SA, Singh S, Singh J, Kumar S, Bhawana VAP (2018) Bioremediation and detoxification of industrial wastes by earthworms: vermicompost as powerful crop nutrient in sustainable agriculture. Bioresour Technol 252:172–179
Birjandi N, Younesi H, Bahramifar N (2016) Treatment of wastewater effluents from paper-recycling plants by coagulation process and optimization of treatment conditions with response surface methodology. Appl Water Sci 6:339–348
Bugg TDH, Ahmad M, Hardiman EM, Rahmanpour R (2011) Pathways for degradation of lignin in bacteria and fungi. Nat Prod Rep 28:1883–1896
Chandra R, Abhishek A (2011) Bacterial decolorization of black liquor in axenic and mixed condition and characterization of metabolites. Biodegradation 22:603–611
Chandra R, Kumar V (2015a) Mechanism of wetland plant rhizosphere bacteria for bioremediation of pollutants in an aquatic ecosystem. In: Chandra R (ed) Advances in Biodegradation and Bioremediation of Industrial Waste. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 329–379
Chandra R, Kumar V (2015b) Biotransformation and biodegradation of organophosphates and organohalides. In: Chandra R (ed) Environmental Waste Management. CRC Press, pp 475–524
Chandra R, Kumar V (2017a) Detection of androgenic-mutagenic compounds and potential autochthonous bacterial communities during in situ bioremediation of post methanated distillery sludge. Front Microbiol 8:887
Chandra R, Kumar V (2017b) Detection of Bacillus and Stenotrophomonas species growing in an organic acid and endocrine-disrupting chemicals rich environment of distillery spent wash and its phytotoxicity. Environ Monit Assess 189:26
Chandra R, Kumar V (2017c) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by potential native plants and their microscopic observation of root growing on stabilized distillery sludge as a prospective tool for in-situ phytoremediation of industrial waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2605–2619
Chandra R, Kumar V (2018) Phytoremediation: a green sustainable technology for industrial waste management. In: Chandra R, Dubey NK, Kumar V (eds) Phytoremediation of environmental pollutants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Chandra R, Singh R (2012) Decolourisation and detoxification of rayon grade pulp paper mill effluent by mixed bacterial culture isolated from pulp paper mill effluent polluted site. Biochem Eng J 61:49–58
Chandra R, Singh S, Raj A (2006) Seasonal bacteriological analysis of gola river water contaminated with pulp paper mill waste in Uttaranchal, India. Environ Monit Assess 118:393–406
Chandra R, Abhishek A, Sankhwar M (2011a) Bacterial decolorization and detoxification of black liquor from rayon grade pulp manufacturing paper industry and detection of their metabolic products. Bioresour Technol 102:6429–6436
Chandra R, Singh R, Yadav S (2011b) Effect of bacterial inoculum ratio in mixed culture for decolourization and detoxification of pulp paper mill effluent. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87:436–444
Chandra R, Saxena G, Kumar V (2015a) Phytoremediation of environmental pollutants: an eco-sustainable green technology to environmental management. In: Chandra R (ed) Advances in biodegradation and bioremediation of industrial waste. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 1–29
Chandra R, Kumar V, Yadav S (2015b) Microbial degradation of lignocellulosic waste and its metabolic products. In: Chandra R (ed) Environmental waste management. CRC Press, pp 249–298
Chandra R, Kumar V, Yadav S (2017a) Extremophilic ligninolytic enzymes. In: Sani R, Krishnaraj R (eds) Extremophilic enzymatic processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks to bioenergy. Springer, Cham
Chandra R, Yadav S, Yadav S (2017b) Phytoextraction potential of heavy metals by native wetland plants growing on chlorolignin containing sludge of pulp and paper industry. Ecol Eng 98:134–145
Chandra R, Kumar V, Tripathi S (2018a) Evaluation of molasses-melanoidin decolourisation by potential bacterial consortium discharged in distillery effluent. 3 Biotech 8:187
Chandra R, Kumar V, Tripathi S, Sharma P (2018b) Heavy metal phytoextraction potential of native weeds and grasses from endocrine-disrupting chemicals rich complex distillery sludge and their histological observations during in situ phytoremediation. Ecol Eng 111:143–156
Chandra R, Dubey NK, Kumar V (2018c) Phytoremediation of environmental pollutants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Chandra R, Kumar V, Singh K (2018d) Hyperaccumulator versus nonhyperaccumulator plants for environmental waste management. In: Chandra R, Dubey NK, Kumar V (eds) Phytoremediation of environmental pollutants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Chandra R, Kumar V, Tripathi S, Sharma P (2018e) Phytoremediation of industrial pollutants and life cycle assessment. In: Chandra R, Dubey NK, Kumar V (eds) Phytoremediation of environmental pollutants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Chauhan N, Thakur IS (2002) Treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent by Pseudomonas fluorescens in fixed film bioreactor. Pollut Res 4(4):429–434
Chedchant J, Petchoy O, Vaithanomsat P, Apiwatanapiwat W, Kreetachat T, Chantranurak S (2009) Decolorization of lignin containing effluent by white–rot fungus Datronia sp. KAPI0039. In: Proceedings of the 47th Kasetsart University Annual Conference, Bangkok
Chen Z, Wan CX (2017) Biological valorization strategies for converting lignin into fuels and chemicals. Renew Sust Energ Rev 73:610–621
Chen YH, Chai LY, Zhu YH, Yang ZH, Zheng Y, Zhang H (2012a) Biodegradation of Kraft lignin by a bacterial strain Comamonas sp. B-9 isolated from eroded bamboo slips. J Appl Microbiol 125:900–906
Chen J, Zhan P, Koopman B, Fang G, Shi Y (2012b) Bioaugmentation with Gordonia strain JW8 in treatment of pulp and paper wastewater. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:899–904
Chen Y, Chai L, Tang C, Yang Z, Zheng Y, Shi Y, Zhang H et al (2012c) Kraft lignin biodegradation by Novosphingobium sp. B-7 and analysis of the degradation process. Bioresour Technol 123:682–685
Choudhary AK, Kumar S, Sharma C (2010) Removal of chlorinated resin and fatty acids from paper mill wastewater through constructed wetland. World Academy of Science. Eng Technol 80:67–71
Chuphal Y, Kumar V, Thakur IS (2005) Biodegradation and decolorization of pulp and paper mill effluent by anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms in a sequential bioreactor. World J Microb Biot 21:1439–1445
Clark T, Mitchell C, Donnison A (1992) Bacteriological water quality of pulp and paper mill effluent: the problem of Klebsiella pneumoniae. In Proceedings of the 1992 TAPPI International Environmental Conference, pp 171–180
Costa S, Dedola DG, Pellizzari S, Blo R, Rugiero I, Pedrini P, Tamburini E (2017) Lignin biodegradation in pulp-and-paper mill wastewater by selected white rot fungi water. Water 9(12):935
Costigan SL, Werner J, Ouellet JD, Hill LG, Law RD (2012) Expression profiling and gene ontology analysis in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) liver following exposure to pulp and paper mill effluents. Aquat Toxicol (122–123):44–55
D’Souza DT, Tiwari R, Sah AK, Raghukumar C (2006) Enhanced production of laccase by a marine fungus during treatment of colored effluents and synthetic dyes. Enzym Microb Technol 38:504–511
Da Re V, Papinutti L (2011) Black liquor decolorization by selected white-rot fungi. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165:406–415
Das S, Mazumdar K (2016) Phytoremediation potential of a novel fern, Salvinia cucullata, Roxb. Ex Bory, to pulp and paper mill effluent: physiological and anatomical response. Chemosphere 163:62–72
Denslow ND, Kocerha J, Sepúlveda MS, Gross T, Holm SE (2004) Gene expression fingerprints of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) exposed to pulp and paper mill effluents. Mutat Res 552(1–2):19–34
Devkumari MS, Selvaseelan DA (2008) Impact of paper mill treated effluent irrigation and solid wastes amendment on the productivity of Cumbu napier (CO-3) – a field study. Asian J Exp Sci 22(3):285–293
Dias JCT, Rezende RP, Silva CM, Linardi VR (2005) Biological treatment of Kraft pulp mill foul condensates at high temperatures using a membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem 40(3–4):1125–1129
Dileká FB, Taplamacioglu HM, Tarlan E (1999) Colour and AOX removal from pul** effluents by algae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:585–591
van Driessel B, Christov L (2001) Decolorization of bleach plant effluent by mucoralean and white-rot fungi in a rotating biological contactor reactor. J Biosci Bioeng 92(3):271–276
Duan J, Liang J, Wang Y, W D, Wang D (2016a) Kraft lignin biodegradation by Dysgonomonas sp. WJDL-Y1, a new anaerobic bacterial strain isolated from sludge of a pulp and paper mill. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26(10):1765–1773
Duan J, Huo X, Du WJ, Liang JD, Wang DQ, Yang SC (2016b) Biodegradation of Kraft lignin by a newly isolated anaerobic bacterial strain, Acetoanaerobium sp. WJDL-Y2. Lett Appl Microbiol 62:55–56
Dudášová H, Lukáčová L, Murínová S, Puškárová A, Pangallo D, Dercová K (2014) Bacterial strains isolated from PCB-contaminated sediments and their use for bioaugmentation strategy in microcosms. J Basic Microbiol 54(4):253–260
Emeka CI, Ihediohamma EE, Linus N, Ndubuisi UC, Ebele AG (2011) Physicochemical dynamics of the impact of paper mill effluents on Owerrinta river, eastern Nigeria. J Env Chem Ecotox 3(11):298–303
Erkan HS, Engin GO (2017) The investigation of paper mill industry wastewater treatment and activated sludge properties in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Sci Technol 76(7–8):1715–1725
Esposito E, Canhos VP, Nelson D (1991) Screening of lignin-degrading fungi for removal of color from Kraft mill wastewater with no additional extra carbon-source. Biotechnol Lett 13:571–576
Ferrer I, Dezotti M, Durdn N, de Qufmica F (1991) Decolorization of Kraft effluent by free and immobilized lignin peroxidases and horseradish peroxidase. Biotechnol Lett 13(3):577–532
Fulthorpe RR, Allen DG (1995) A comparison of organochlorine removal from bleached kraft pulp and paper-mill effluents by dehalogenating Pseudomonas, Ancylobacter and Methylobacterium strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:782–789
Galil NI, Sheindorf C, Stahl N, Tenenbaum A, Levinsky A (2003) Membrane bioreactors for final treatment of wastewater. Water Sci Technol 48(8):103–110
Garbisu C, Alkorta I (2001) Phytoextraction: a cost-effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresour Technol 77(3):229–236
Garg SK, Modi DR (1999) Decolorization of pulp-paper mill effluents by white-rot fungi. Crit Rev Biotechnol 19(2):85–112
Gauthier F, Archibald F (2001) The ecology of “fecal indicator” bacteria commonly found in pulp and paper mill water systems. Water Resour 35(9):2207–2218
Gaur N, Narasimhulu K, Pydi Setty Y (2018) Extraction of ligninolytic enzymes from novel Klebsiella pneumoniae strains and its application in wastewater treatment. Appl Water Sci 8:111
van Ginkel CG, Kester H, Stroo CA, van Haperen AM (1999) Biodegradation of EDTA in pulp and paper mill effluent by activated sludge. Water Sci Technol 40(11–12):259–265
Glenn JK, Gold MH (1985) Purification and characterization of an extracellular Mn(II)-dependent peroxidase from the lignin-degrading basidiomycete, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys 242(2):329–341
Gommers K, De Wever H, Brauns E, Peys K (2007) Recalcitrant COD degradation by an integrated system of ozonation and membrane bioreactor. Water Sci Technol 55(12):245–251
Gonder ZB, Arayici S, Barlas H (2012) Treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater using ultrafiltration process: optimization of the fouling and rejections. Indian Eng Chem Res 51:6184–6195
Guan W, Yin M, He T, **e S (2015) Influence of substrate type on microbial community structure in vertical-flow constructed wetland treating polluted river water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:16202–16209
Gupta R, Garg VK (2009) Vermiremediation and nutrient recovery of non-recyclable paper waste employing Eisenia fetida. J Hazard Mater 162(1):430–439
Gupta V, Minocha AK, Jain N (2001) Batch and continuous studies on treatment of pulp mill wastewater by Aeromonas formicans. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 76(6):547–552
Hall TJ, Fisher RP, Rodgers JH, Minshall GW, Landis WG, Kovacs TG, Firth BK, Dube MG, Deardorff TL, Borton DL (2009) A long-term, multitrophic level study to assess pulp and paper mill effluent effects on aquatic communities in four us receiving waters: background and status. Integr Environ Assess Manag 5(2):189–198
Hammer DA, Pullin BP, McMurry DK, Lee JW (1993) Testing color removal from pulp mill wastewaters with constructed wetlands. In: Moshiri AG (ed) Constructed wetlands for water pollution improvement. CRC Press/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 449–452
Haq I, Kumar S, Kumari V, Singh SK, Raj A (2016) Evaluation of bioremediation potentiality of ligninolytic Serratia liquefaciens for detoxification of pulp and paper mill effluent. J Hazard Mater 305:190–199
Haq I, Kumar S, Raj A, Lohani M, Satyanarayana GNV (2017) Genotoxicity assessment of pulp and paper mill effluent before and after bacterial degradation using Allium cepa test. Chemosphere 169:642–650
Hatakka A (2001) Biodegradation of lignin. In: Hofrichter M, Steinbuchel A (eds) Lignin, humic substances and coal. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 129–180
Hatano K, Frederick DJ, Moore JA (1994) Microbial ecology of constructed wetland used for treating pulp mill wastewater. Water Sci Technol 29(4):233–239
Hermosilla D, Merayo N, Gasco A, Blanco A (2015) The application of advanced oxidation technologies to the treatment of effluents from pulp and paper industry: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:168–191
Hewitt LM, Kovacs TG, Dube MG, MacLatchy DL, Martel PH, McMaster ME, Paice MG, Parrott JL, van Den Heuvel MR, van Der Kraak GJ (2008) Altered reproduction in fish exposed to pulp and paper mill effluents: roles of individual compounds and mill operating conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(3):682–697
Hofrichter M (2002) A review: lignin conversion by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Enzyme Microb Tech 30:454–466
Hooda R, Bhardwaj NK, Singh P (2015) Screening and identification of ligninolytic bacteria for the treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent. Water Air Soil Poll 226:305
Hou LP, Yang Y, Shu H, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Fang GZ, **n L, Shi WJ, Yao L, Cheng XM (2018) Masculinization and reproductive effects in western mosquito fish (Gambusia affinis) after long-term exposure to androstenedione. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:509–515
Huang XF, Santhanam N, Badri DV, Hunter WJ, Manter DK, Decker SR, Vivanco JM, Reardon KF (2013) Isolation and characterization of lignin-degrading bacteria from rainforest soils. Biotechnol Bioeng 110(6):1616–1626
Huntley BE, Jones AC, Cabelli VJ (1766) Klebsiella densities in waters receiving wood pulp effluents. J Water Pollut Control Fed 48(7):1766–1771
Idise OE, Okoko FJ, Ogar O, Egbah A (2012) The effects of solid wood waste discharge on the physico-chemical and microbial characteristics of the Warri river. Afr J Microbiol Res 6(20):4302–4314
Jenkins RL, Wilson EM, Angus RA, Howell WM, Kirk M (2003) Androstenedione and progesterone in the sediment of a river receiving paper mill effluent. Toxicol Sci 73:53–59
Johansson T (2012) Application of membrane bioreactors in the pulp and paper industry. Master’s Thesis, Uppsala University, Environmental and Aquatic Civil Engineering Program.
Kadlec RH, Wallace SD (2009) Treatment wetlands, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Kang K, Sung J, Kim D (2007) Evaluation of white-rot fungi for biopul** of wood. Mycobiology 35(4):205–209
Kannan K, Oblisami G (1990) Decolorization of pulp and paper mill effluent by growth of Aspergillus niger. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 6:114–116
Karrascha B, Parra O, Cid H, Mehrens M, Pacheco P, Urrutia R, Valdovinos C, Zaror C (2006) Effects of pulp and paper mill effluents on the microplankton and microbial self-purification capabilities of the Biobıo River, Chile. Sci Total Environ 359:194–208
Kaur A, Singh J, Vig AP, Dhaliwal SS, Rup PJ (2010) Cocomposting with and without Eisenia fetida for conversion of toxic paper mill sludge to a soil conditioner. Bioresour Technol 101(21):8192–8198
Keharia H, Madamwar D (2003) Bioremediation concepts for treatment of dye containing wastewater: a review. Indian J Exp Biol 41:1068–1075
Kirk TK, Tien M, Faison BD (1984) Biochemistry of the oxidation of lignin by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biotechnol Adv 2(2):183–199
Kirk TK, Burgess RR, Koning JW (1992) Use of fungi in pul** wood: an overview of biopul** research. In: Leatham GF (ed) Frontiers in industrial mycology. Springer, Boston, pp 99–111
Knight RL, Hilleke J, Grayson S (1994) Design and performance of the champion pilot-constructed wetland treatment system. TAPPI J 77:240–245
Kreetachat T, Chaisan O, Vaithanomsat P (2016) Decolorization of pulp and paper mill effluents using wood rotting fungus Fibrodontia sp. RCK783S. Int J Environ Sci Dev 7(5). https://doi.org/10.7763/IJESD.2016.V7.792
Kumar V, Chandra R (2018a) Characterisation of manganese peroxidase and laccase producing bacteria capable for degradation of sucrose glutamic acid-maillard products at different nutritional and environmental conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:32
Kumar V, Chandra R (2018b) Bacterial assisted phytoremediation of industrial waste pollutants and eco-restoration. In: Chandra R, Dubey NK, Kumar V (eds) Phytoremediation of environmental pollutants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Kumar V, Chandra R (2020a) Bacterial-assisted phytoextraction mechanism of heavy metals by native hyperaccumulator plants from distillery waste contaminated site for eco-restoration. In: Microbes for sustainable development and bioremediation. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Kumar V, Chandra R (2020b) Bioremediation of melanoidins containing distillery waste for environmental safety. In: Saxena G, Bharagava RN (eds) Bioremediation of industrial waste for environmental safety, Microbes and methods for industrial waste management, vol II. Springer, Singapore
Kumar V, Chopra AK (2011) Alterations in physico-chemical characteristics of soil after irrigation with paper mill effluent. J Chem Pharm Res 3(6):7–22
Kumar V, Chopra AK (2016) Reduction of pollution load of paper mill effluent by phytoremediation technique using water caltrop (Trapa natans L.). Cogent Environ Sci 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311843.2016.1153216
Kumar V, Dhall P, Kumar R, Singh YP, Kumar A (2012) Bioremediation of agro-based pulp mill effluent by microbial consortium comprising autochthonous bacteria. Sci World J:7, 127014
Kumar V, Shahi SK, Singh S (2018) Bioremediation: an eco-sustainable approach for restoration of contaminated sites. In: Singh J, Sharma D, Kumar G, Sharma NR (eds) Microbial bioprospecting for sustainable development. Springer
Kumar V, Singh J, Kumar P (2019) Heavy metal uptake by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes L.) from paper mill effluent (PME): experimental and prediction modeling studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14400–14413
Kumari M, Yadav RS, Yadav KD (2002) Secretion of lignin peroxidase by Penicillium citrinum, Fusarium oxysporum and Aspergillus terreus. Indian J Exp Biol 40(7):802–880
Lacorte S, Latorre A, Barcelo D, Rigol A, Malmqvist A, Welander T (2003) Organic compounds in paper mill process waters and effluents. Trends Anal Chem 22(10):725–737
Lafond RA, Ferguson JF (1991) Anaerobic and aerobic biological treatment processes for removal of chlorinated organics from Kraft bleaching wastes. In: Tappi proceeding of the environmental conference. Tappi Press, Atlanta, pp 797–812
Lankinen VP, Inkeröinen MM, Pellinen J, Hatakka AI (1991) The onset of lignin-modifying enzymes, decrease of AOX and color removal by white-rot fungi grown on bleach plant effluents. Water Sci Technol 24(3–4):189–198
Larsson L, Andersson T, Forlin L, Hardig J (1988) Physiological disturbances in fish exposed to bleached Kraft mill effluents. Water Sci Technol 20:67–76
Latorre A, Malmqvist A, Lacorte S, Welander T, Barcelo D (2007) Evaluation of the treatment efficiencies of paper mill white waters in terms of organic composition and toxicity. Environ Pollut 147:648–655
Leadbitter D (2009) Some effects of bleached Kraft pulp mill effluents on aquatic organisms – a review. Wetlands 8(3):28–35
Lee J, Koh D, Andijani M, Saw SM, Munoz C, Chia SE, Wong ML, Hong CY, Ong CN (2012) Effluents from a pulp and paper mill: a skin and health surveys of children living in upstream and downstream villages. Occup Environ Med 59:373–379
Lerner M, Stahl N, Galil NI (2007) Comparative study of MBR and activated sludge in the treatment of paper mill wastewater. Water Sci Technol 55:23–29
Lin H, Gao W, Meng F, Liao BQ, Leung KT, Zhao L, Chen J, Hong H (2012) Membrane bioreactors for industrial wastewater treatment: a critical review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:677–740
Liss SN, Allen DG (1992) Microbiological study of a bleached Kraft pulp mill aerated lagoon. J Pulp Paper Sci 18(6):216–220
Long SC, Stietz JR, Olstadt J, Hedman CJ, Plummer JD (2012) Characterizing paper mill effluent using indicators and source tracking methods. J Am Water Works Assoc 104(3):E150–E161
Mahesh S, Prasad B, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2006) Electrochemical degradation of pulp and paper mill wastewater. Part 1. COD and color removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:2830–2839
Mahesh S, Garg KK, Srivastava VC, Mishra IM, Prasad B, Mall ID (2016) Continuous electrocoagulation treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater: operating cost and sludge study. RSC Adv 6:16223–16233
Maheshwari R, Rani B, Saxena A, Prasad M, Singh U (2012) Analysis of effluents released from recycled paper industry. Science Sage 3(1):82–85
Malaviya P, Rathore VS (2007) Bioremediation of pulp and paper mill effluent by a novel fungal consortium isolated from polluted soil. Bioresour Technol 98:3647–3651
Manzanares P, Fajardo S, Martin C (1995) Production of ligninolytic activities when treating paper pulp effluents by Trametes versicolor. J Biotechnol 43:125–132
Martel PH, O'Connor B, Kovacs TG, van den Heuvel MR, Parrott JL, McMaster ME, MacLatchy DL, van Der Kraak GJ, Hewitt LM (2017) The relationship between organic loading and effects on fish reproduction for pulp mill effluents across Canada. Environ Sci Technol 51(6):3499–3507
Martin C, Manzanares P (1994) A study of the decolorization of straw soda pul** effluents by Trametes versicolor. Bioresour Technol 47:209–214
Mazumdar K, Das S (2015) Phytoremediation of Pb, Zn, Fe, and Mg with 25 wetland plant species from a paper mill contaminated site in North East India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:701–710
Medhi UJ, Talukdar AK, Deka S (2008) Effect of pulp and paper mill effluent on seed germination and seedling growth of mustard (Brassica campestris), pea (Pisum sativum) and rice (Oryza sativa) seeds. Pollut Res 27(3):437–442
Medhi UJ, Talukdar AK, Deka S (2011) Impact of paper mill effluent on growth and development of certain agricultural crops. J Environ Biol 32:185–188
Megraw SR, Farkas MO (1993) E. Coli: a potential source of native fecal coliforms in pulp paper mill effluent. Pulp Paper Canada 94(6):39–41
Mehna A, Bajpai P, Bajpai PK (1995) Studies on decolorization of effluent from a small pulp mill utilizing agriresidues with Trametes versicolor. Enzym Microb Technol 17:18–22
Michel FC Jr, Balachandra Dass S, Grulke EA, Adinarayana Reddy C (1991) Role of manganese peroxidases and lignin peroxidases of Phanerochaete chrysosporium in the decolorization of Kraft bleach plant effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(8):2368–2375
Mishra M, Thakur IS (2010) Isolation and characterization of alkalotolerant bacteria and optimization of process parameters for decolorization and detoxification of pulp and paper mill effluent by Taguchi approach. Biodegradation 21:967
Mishra S, Mohanty M, Pradhan C, Patra HK, Das R, Sahoo S (2013) Physicochemical assessment of paper mill effluent and its heavy metal remediation sing aquatic macrophytes – a case study at JK paper mill, Rayagada, India. Environ Monit Assess 185(5):4347–4359
Mishra M, Das MT, Thakur IS (2014) Mammalian cell-line based toxicological evaluation of paper mill black liquor treated in a soil microcosm by indigenous alkalo-tolerant Bacillus sp. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:2966–2976
Mishra T, Ramola S, Shankhwar AK, Rabha AK, Srivastava RK (2016) Pulp and paper mill effluent treatment by hybrid anaerobic upflow fixed-bed bioreactor combined with slow sand filter. Desalin Water Treat 57:10528–10536
Mittar D, Khanna PK, Marwaha SS, Kennedy JF (1992) Biobleaching of pulp and paper mill effluents by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 53:81–92
Modi DR, Chandra H, Garg SK (1998) Decolorization of bagasse based paper mill effluent by white-rot fungus, Trametes versicolor. Bioresource Technol 66:79–81
Moore JA, Skarda SM, Sherwood R (1994) Wetland treatment of pulp mill wastewater effluent. Water Sci Technol 29(4):241–247
Morii H, Nakamiya K, Kinoshita S (1995) Isolation of a lignin-decolorizing bacterium. J Ferment Bioeng 80:296–299
Muttray AF, Yu Z, Mohn WW (2001) Population dynamics and metabolic activity of Pseudomonas abietaniphila BKME-9 within pulp mill wastewater microbial communities assayed by competitive PCR and RT-PCR. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38(1):21–31
Nagarathnamma R, Bajpai P (1999) Decolorization and detoxification of extraction-stage effluent from chlorine bleaching of Kraft pulp by Rhizopus oryzae. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(3):1078–1082
Nagarathnamma R, Bajpai P, Bajpai PK (1999) Studies on decolourization, degradation and detoxification of chlorinated lignin compounds in Kraft bleaching effluents by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. Process Biochem 34:939–948
Nestmanna ER, Lee EG-H (1985) Genetic activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of compounds found in effluents of pulp and paper mills. Mutat Res/Genet Toxicol 155(1–2):53–60
Oakes KD, Tremblay LA, van der Kraak GJ (2005) Short-term lab exposures of immature rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to sulfite and Kraft pulp-mill effluents: effects on oxidative stress and circulating sex steroids. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(6):1451–1461
Ojha AK, Markandeya (2016) Lignin decolorization and degradation of pulp and paper mill effluent by ligninolytic bacteria. Iranica J Energ Environ 7(3):282–293
Ojunga S, Masese FO, Manyala JO, Etiegni L, Onkware AO, Senelwa K, Raburu PO, Balozi BK, Omutange ES (2010) Impact of a Kraft pulp and paper mill effluent on phytoplankton & macroinvertebrates in river Nzoia, Kenya. Water Qual Res J Canada 45(2):235–250
Oke N, Singh S, Garg A (2017) A comparative treatment of bleaching wastewater by physicochemical processes. Water Sci Technol 76(9–10):2367–2379
Orlando EF, Davis WP, Guillette LJ Jr (2002) Aromatase activity in the ovary and brain of the eastern mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) exposed to paper mill effluent. Environ Health Perspect 110:429–433
Orrego R, Pandelides Z, Guchardi J, Holdway D (2011) Effects of pulp and paper mill effluent extracts on liver anaerobic and aerobic metabolic enzymes in rainbow trout. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74(4):761–768
Pandey A, Panwar S, Mishra S, Siddiqui NA (2012) Comparison of fish toxicity & microtox toxicity of luminescent bacteria due to bleach plant effluent released from agro & wood based pulp and paper mills. Environ Anal Toxicol 2(1):1–4
Parks LG, Lambright CS, Orlando EF, Guillette LJ Jr, Ankley GT, Gray LE Jr (2001) Masculinization of female mosquitofish in Kraft mill effluent-contaminated Fenholloway River water is associated with androgen receptor agonist activity. Toxicol Sci 62(2):257–267
Patel A, Arora N, Pruthi V, Pruthi PA (2017) Biological treatment of pulp and paper industry effluent by oleaginous yeast integrated with production of biodiesel as sustainable transportation fuel. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.184
Pathan TS, Sonawane DL, Khillare YK (2009) Toxicity and behavioural changes in freshwater fish Rasbora daniconius exposed to paper mill effluent. Bot Res Int 2(4):263–266
Peralta-Zamora P, Gomes De Morases S, Esposito E, Antunes R, Reyes J, Duran N (1998) Decolourisation of pulp mill effluents with immobilised lignin and manganese peroxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Int Technol 19:521–528
Perestelo F, Falcon MA, Perez ML, Roig EC, de la Fuente Martin G (1989) Bioalteration of Kraft pine lignin by Bacillus megaterium isolated from compost piles. J Ferment Bioeng 68:151–153
Pihlajamäki A, Nyström M (2002) Comparison of nanofiltration and tight ultrafiltration membranes in the filtration of paper mill process water. J Desal 149:131–136
Pokhrel D, Viraraghavan T (2004) Treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater – a review. Sci Total Environ 333:37–58
Poole NJ, Wildish DJ, Kristmanson DD, Waldichuk M (1977) The effects of the pulp and paper industry on the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 8(1–4):153–195
Pradhan SC, Behera P (2011) Changes in some physical properties of soil amended with effluent of emami paper mills located at Balgopalpur, Balasore, Orissa. The Bioscan 6(1):153–155
Qadir I, Chhipa RC (2015) Critical evaluation of some available treatment techniques for textile and paper industry effluents: a review. Am Chem Sci J 6(2):77–90
Ragunathan R, Swaminathan K (2004) Biological treatment of a pulp and paper industry effluent by Pleurotus spp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:389–393
Raj A, Chandra R (2004) Comparative analysis of physico-chemical and bacteriological parameters of Kraft and pulp paper mill effluents. Indian J Environ Protect 24(7):481–489
Raj A, Chandra R, Patel DK (2005) Physico-chemical characterization of pulp and paper mill effluent and toxicity assessment by a tubificid worm, Tubifex tubifex. Toxicol Int 12(2):109–118
Raj A, Chandra R, Reddy MMK, Purohit HJ, Kapley A (2007a) Biodegradation of Kraft lignin by a newly isolated bacterial strain, Aneurinibacillus aneurinilyticus from the sludge of a pulp paper mill. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(6):793–799
Raj A, Reddy MMK, Chandra R (2007b) Decolorisation and treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent by lignin-degrading Bacillus sp. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1683
Raj A, Kumara S, Haq I, Singh SK (2014a) Bioremediation and toxicity reduction in pulp and paper mill effluent by newly isolated ligninolytic Paenibacillus sp. Ecol Eng 71:355–362
Raj A, Kumar S, Haq I, Singh SK (2014b) Bioremediation and toxicity reduction in pulp and paper mill effluent by newly isolated ligninolytic Paenibacillus sp. Ecol Eng 71:355–362
Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2008) Influence of metal resistant-plant growth-promoting bacteria on the growth of Ricinus communis in soil contaminated with heavy metals. Chemosphere 71:834–842
Rajwar D, Paliwal R, Rai JPN (2017) Biodegradation of pulp and paper mill effluent by co-culturing ascomycetous fungi in repeated batch process. Environ Monit Assess 189:482
Rani N, Maheshwari RC, Kumar V, Vijay VK (2011) Purification of pulp and paper mill effluent through Typha and Canna using constructed wetlands technology. J Water Reuse Desalin 1(4):237–242
Rocha-Santos T, Ferreira F, Silva L, Freitas AC, Pereira R, Diniz M, Castro L, Peres I, Duarte AC (2010) Effects of tertiary treatment by fungi on organic compounds in a Kraft pulp mill effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:866–874
Rodrigues AC, Boroski M, Shimada NS, Garcia JC, Nozaki J, Hioka N (2008) Treatment of paper pulp and paper mill wastewater by coagulation–flocculation followed by heterogeneous photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 194(1):1–10
Roy RP, Prasad J, Joshi AP (2008) Changes in soil properties due to irrigation with paper industry wastewater. J Environ Sci Eng 50(4):277–282
Saikia MK, Kalita S, Sarma GC (2010) Algal indices to predict pulp and paper mill pollution load of Elenga Beel (Wetland) Assam, India. Soc Appl Sci 1(4):815–821
Saikia MK, Kalita S, Sarma GC (2011) An experimental investigation on growth stimulation (+) and inhibition (−) of algae (Oscillatoria chlorina and Scenedesmus quadricauda) treated with pulp and paper mill effluents. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Technol 2(4):87–94
Sandstrom O, Neuman E, Karas P (1988) Effects of bleached pulp mill effluent on growth and gonad function in Baltic coastal fish. Water Sci Technol 20:107–118
Savant DV, Abdul-Rahman R, Ranade DR (2006) Anaerobic degradation of adsorbable organic halides (AOX) from pulp and paper industry wastewater. Bioresour Technol 97:1092–1104
Schutyser W, Renders T, Van den Bosch S, Koelewijn S-F, Beckham GT, Sels BF (2018) Chemicals from lignin: an interplay of lignocellulose fractionation, depolymerisation, and upgrading. Chem Soc Rev 47:852–908
Sharma S, Agarwal L, Kumar R (2008) Purification, immobilization and characterization of tannase from Penicillium variable. Bioresour Technol 99:2544–2551
Shi Y, Chai L, Tang C, Yang Z, Zheng Y, Chen Y, **g Q (2013) Biochemical investigation of Kraft lignin degradation by Pandoraea sp. B-6 isolated from bamboo slips. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:1957–1965
Singh AK, Chandra R (2019) Pollutants released from the pulp paper industry: aquatic toxicity and their health hazards. Aquat Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.04.007
Singh P, Thakur IS (2006) Colour removal of anaerobically treated pulp and paper mill effluent by microorganisms in two steps bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 97:218–223
Singh YP, Dhall P, Mathur RM, Jain RK, Thakur V, Kumar V, Kumar R, Kumar A (2011) Bioremediation of pulp and paper mill effluent by tannic acid degrading Enterobacter sp. Water Air Soil Pollut 218:693–701
Singhal A, Thakur IS (2009a) Decolourisation and detoxification of pulp and paper mill effluent by Emericella nidulans var. nidulans. J Hazard Mat 171:619–625
Singhal A, Thakur IS (2009b) Decolourisation and detoxification of pulp and paper mill effluent by Cryptococcus sp. Biochem Eng J 46:21–27
Singhal A, Thakur IS (2012) Two step sequential treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent by Cryptococcus albidus and Emericella nidulans var. nidulans in 2 L bioreactor. Can J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.20547
Sonowal PJ, Dhamodharan K, Khwairkpam M, Kalamdhad AS (2013) Feasibility of vermicomposting dewatered sludge from paper mills using Perionyx excavatus. Eur J Environ Sci 3:6–23
Srivastava R, Kumar D, Gupta SK (2005) Bioremediation of municipal sludge by vermitechnology and toxicity assessment by Allium cepa. Bioresour Technol 96:1867–1871
Stephenson R, Duff S (1996) Coagulation and precipitation of a mechanical pul** effluent—II. Toxicity removal and metal salt recovery. J Water Res 30:793–798
Stottmeister U, Wiessner A, Kuschk P, Kappelmeyer MK, Bederski RA, Muller H, Moormann H (2003) Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Adv 22:93–117
Subramonian W, Wu TY, Chai S (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of industrial pulp and paper mill effluent using synthesized magnetic Fe2O3-TiO2: treatment efficiency and characterizations of reused photocatalyst. J Environ Manag 187:298–310
Sutharn S, Sajwan P, Kumar K (2014) Vermiremediation of heavy metals in wastewater sludge from paper and pulp industry using earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 109:177–184
Swamy NK, Singh P, Sarathy IP (2011) Precipitation of phenols from paper industry waste paper using ferric chloride. RASÁYAN J Chem 4:452–456
Talat Mahmood PE, Asce M, Elliott A (2006) Activated sludge process modification for sludge yield reduction using pulp and paper wastewater. J Environ Eng 132:1019–1027
Tarlan E, Dilek FB, Yetis U (2002a) Effectiveness of algae in the treatment of a wood-based pulp and paper industry wastewater. Bioresour Technol 84(1):1–5
Tarlan E, Yetis Ü, Dilek FB (2002b) Algal treatment of pulp and paper industry wastewaters in SBR systems. Water Sci Technol 45(12):151–158
Tettleton RP, Howell FG, Reaves RP (1993) Performance of a constructed marsh in the tertiary treatment of bleach Kraft pulp mill effluent: results of a 2-year pilot project. In: Moshiri AG (ed) Constructed wetlands for water quality improvement. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, pp 437–440
Thakur IS (2004) Screening and identification of microbial strains for removal of colour and adsorbable organic halogens in pulp and paper mill effluent. Process Biochem 39(11):1693–1699
Thompson G, Swai J, Kay M, Forster C (2001) The treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent: a review. Bioresour Technol 77:275–286
Thut RN (1990) Treatment of pulp mill effluent by an artificial marsh. Large-scale pilot study. Proceeding of the TAPPI Environmental Conference, TAPPI, TAPPI, Washington, DC, pp. 121–127
Thut RN (1993) Feasibility of treating pulp mill effluent with a constructed wetland. In: Moshiri AG (ed) Constructed wetlands for water quality improvement. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, pp 441–447
Tien M, Kirk TK (1984) Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H2O2-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81(8):2280–2284
Tiku DK, Kumar A, Chaturvedi R, Makhijani SD, Manoharan A, Kumar R (2010) Holistic bioremediation of pulp mill effluents using autochthonous bacteria. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 64:173–183
Tyor AK, Fulia A, Sharma RK (2012) Impact of paper mill effluent on the survival and hatchability of Cyprinus carpio. Res J Environ Toxicol 6(2):33–41
Usha MT, Sarat Chandra T, Sarada R, Chauhan VS (2016) Removal of nutrients and organic pollution load from pulp and paper mill effluent by microalgae in outdoor open pond. Bioresour Technol 214:856–860
Van den Bosch S, Koelewijn SF, Renders T, Van den Bossche G, Vangeel T, Schutyser W, Sels BF (2018) Catalytic strategies towards lignin-derived chemicals. Top Curr Chem (Cham) 376(5):36
Verma Y (2008) Toxicity assessment of pulp- paper mill effluents employing Daphnia bioassay. Jpn J Environ Toxicol 11(2):151–156
Vymazal J (2014) Constructed wetlands for treatment of industrial wastewaters: a review. Ecol Eng 73:724–751
Wartman CA, Hogana NS, Hewitt LM, McMaster ME, Landman MJ, Taylor S, Kovacs TG, van den Heuvel MR (2009) Androgenic effects of a Canadian bleached kraft pulp and paper effluent as assessed using three spine stickle back (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Aquat Toxicol 92(3):131–139
Watson SB, Ridal J, Zaitlin B, Lo A (2003) Odours from pulp mill effluent treatment ponds: the origin of significant levels of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol (MIB). Chemosphere 51(8):765–773
Wong DW (2009) Structure and action mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157(2):174–209
Wu J, **ao Y, Yu H (2005) Degradation of lignin in pulp mill wastewaters by white-rot fungi on biofilm. Bioresour Technol 96:1357–1363
Xu Z, Qin L, Cai M, Hua W, ** M (2018) Biodegradation of Kraft lignin by newly isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas putida, and Ochrobactrum tritici strains. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(14):14171–14181
Yadav RD, Chaudhry S, Dhiman SS (2010) Biopul** and its potential to reduce effluent loads from bleaching of hardwood Kraft pulp. Bioresources 5:159–171
Yadav D, Pruthi V, Kumar P (2016) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal in aerated stirred tank reactor using aerobic bacterial consortium. J Water Process Eng 13:61–69
Yang C, Cao G, Li Y, Zhang X, Ren H et al (2008) Correction: a constructed alkaline consortium and its dynamics in treating alkaline black liquor with very high pollution load. PLOS ONE 3(12). https://doi.org/10.1371/annotation/2cc5374b-b2cf-4f78-9952-0343272bfe2f
Yeber MC, Rodrlguez J, Freer J, Baeza J, Durdn N, Mansilla HD (1999) Advanced oxidation of a pulp mill bleaching wastewater. Chemosphere 39(10):1679–1688
Yu Z, Mohn WW (2002) Bioaugmentation with the resin acid-degrading bacterium Zoogloea resiniphila DhA-35 to counteract pH stress in an aerated lagoon treating pulp and paper mill effluent. Water Res 36:2793–2801
Zhang Y, Ma C, Ye F, Kong Y, Li H (2009) The treatment of wastewater of paper mill with integrated membrane process. Desalination 236(1–3):349–356
Zouari H, Labat M, Sayadi S (2002) Degradation of 4-chlorophenol by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium in free and immobilized cultures. Bioresour Technol 84:145–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kumar, V., Thakur, I.S., Shah, M.P. (2020). Bioremediation Approaches for Treatment of Pulp and Paper Industry Wastewater: Recent Advances and Challenges. In: Shah, M. (eds) Microbial Bioremediation & Biodegradation. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1812-6_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1812-6_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-1811-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-1812-6
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)