Abstract
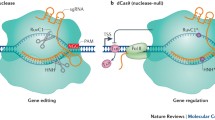
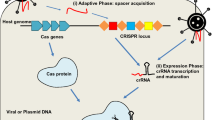
In recent years, Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) system has become the most popular one for genome editing. When the nuclease domains of Cas9 protein are mutated into deactivated form (dCas9), CRISPR/dCas9 still retains the ability to bind the targeted DNA sequence, but loses the endonuclease cleavage activity. Taking advantage of the characteristics of this engineered nuclease inactive Cas9, the CRISPR/dCas system has been repurposed into versatile RNA-guided, DNA-targeting platforms, such as genome imaging, gene regulation, and epigenetic modification. Specifically, fusion of dCas9 with activation domains allows specific and efficient transcriptional activation on a genome-wide scale among diverse organisms. The purpose of this chapter is to review most important the recently published literature on CRISPR/dCas9-based transcriptional activation systems. Compared with the conventional approaches for enhancement of the expression of specific genes of interest, CRISPR/Cas9-based system has emerged as a promising technology for genome regulation, allowing specificity, convenience, robustness, and scalability for endogenous gene activation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balboa D, Weltner J, Eurola S et al (2015) Conditionally stabilized dCas9 activator for controlling gene expression in human cell reprogramming and differentiation. Stem Cell Rep 5:448–459. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.08.001
Bikard D, Jiang W, Samai P et al (2013) Programmable repression and activation of bacterial gene expression using an engineered CRISPR-Cas system. Nucleic Acids Res 41:7429–7437. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt520
Black JB, Adler AF, Wang H-G et al (2016) Targeted epigenetic remodeling of endogenous loci by CRISPR/Cas9-based transcriptional activators directly converts fibroblasts to neuronal cells. Cell Stem Cell 19:406–414. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2016.07.001
Chakraborty S, Ji H, Kabadi AM et al (2014) A CRISPR/Cas9-based system for reprogramming cell lineage specification. Stem Cell Rep 3:940–947. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.09.013
Chavez A, Scheiman J, Vora S et al (2015) Highly efficient Cas9-mediated transcriptional programming. Nat Methods 12:326–328. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3312
Chavez A, Tuttle M, Pruitt BW et al (2016) Comparison of Cas9 activators in multiple species. Nat Methods 13:563–567. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3871
Chen B, Gilbert LA, Cimini BA et al (2013) Dynamic imaging of genomic loci in living human cells by an optimized CRISPR/Cas system. Cell 155:1479–1493. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.001
Cheng AW, Wang H, Yang H et al (2013) Multiplexed activation of endogenous genes by CRISPR-on, an RNA-guided transcriptional activator system. Cell Res 23:1163–1171. doi:10.1038/cr.2013.122
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D et al (2013) Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339:819–823. doi:10.1126/science.1231143
Dominguez AA, Lim WA, Qi LS (2016) Beyond editing: repurposing CRISPR-Cas9 for precision genome regulation and interrogation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:5–15. doi:10.1038/nrm.2015.2
Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2014) Genome editing. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 346:1258096. doi:10.1126/science.1258096
Gasiunas G, Barrangou R, Horvath P, Siksnys V (2012) Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E2579–E2586. doi:10.1073/pnas.1208507109
Gilbert LA, Larson MH, Morsut L et al (2013) CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. Cell 154:442–451. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.044
Gilbert LA, Horlbeck MA, Adamson B et al (2014) Genome-scale CRISPR-mediated control of gene repression and activation. Cell 159:647–661. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.029
Hilton IB, D’Ippolito AM, Vockley CM et al (2015) Epigenome editing by a CRISPR-Cas9-based acetyltransferase activates genes from promoters and enhancers. Nat Biotechnol 33:510–517. doi:10.1038/nbt.3199
Jiang F, Doudna JA (2015) The structural biology of CRISPR-Cas systems. Curr Opin Struct Biol 30:100–111. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2015.02.002
**ek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I et al (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337:816–821. doi:10.1126/science.1225829
Kearns NA, Genga RMJ, Enuameh MS et al (2014) Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription and differentiation in human pluripotent stem cells. Development 141:219–223. doi:10.1242/dev.103341
Kearns NA, Pham H, Tabak B et al (2015) Functional annotation of native enhancers with a Cas9-histone demethylase fusion. Nat Methods 12:401–403. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3325
Konermann S, Brigham MD, Trevino AE et al (2015) Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex. Nature 517:583–588. doi:10.1038/nature14136
Maeder ML, Linder SJ, Cascio VM et al (2013) CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes. Nat Methods 10:977–979. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2598
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM et al (2013) RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 339:823–826. doi:10.1126/science.1232033
Perez-Pinera P, Kocak DD, Vockley CM et al (2013) RNA-guided gene activation by CRISPR–Cas9-based transcription factors. Nat Methods 10:973–976. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2600
Qi LS, Larson MH, Gilbert LA et al (2013) Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Cell 152:1173–1183. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.022
Sternberg SH, Redding S, **ek M et al (2014) DNA interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9. Nature 507:62–67. doi:10.1038/nature13011
Tanenbaum ME, Gilbert LA, Qi LS et al (2014) A protein-tagging system for signal amplification in gene expression and fluorescence imaging. Cell 159:635–646. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.039
Waddington CH (1957) The strategy ofthe genes. Allen, London
**ong X, Chen M, Lim WA et al (2016) CRISPR/Cas9 for human genome engineering and disease research. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 17:131–154. doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-083115-022258
Zalatan JG, Lee ME, Almeida R et al (2015) Engineering complex synthetic transcriptional programs with CRISPR RNA scaffolds. Cell 160:339–350. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.052
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Chen, M., Qi, L.S. (2017). Repurposing CRISPR System for Transcriptional Activation. In: Li, LC. (eds) RNA Activation. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 983. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4310-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4310-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-4309-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-4310-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)