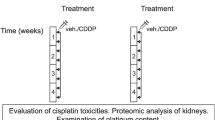
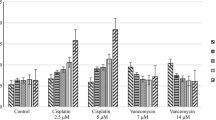
Abstract
The marked morphological, functional and biochemical heterogeneity of the kidney accounts for the site-specific toxicity of several drugs and xenobiotics. Puromycin aminonucleoside, daunomycin and adriamycin exert a direct effect on the glomerular epithelial cells, resulting in foot process fusion, accompanied by increased proteinuria, whereas the proximal tubule, in particular the S2 and S3 segments, is the target site for aminoglycoside, cephalosporin, cisplatin, haiogenated alkene and heavy metal toxicity (Commandeur and Vermuelen 1990).This is assumed to be due to the presence of specifc transport processes and/or enzymes e.g. cysteine conjugate C-S lyase, located in the proximal tubule. Ischaemic damage to the proximal tubule is usually confined to the S3 segment or pars recta in the outer medulla, whereas chemically induced proximal tubular injury is dependent on the physicochemical properties of the toxicant and the localisation of transport systems that result in cell-specific accumulation. For example Cd-metallothionein is specifically reabsorbed by the S1 and S2 segments of the proximal tubule, whereas cephaloridine is toxic to the S2 segment, due to the localisation of the organic anion transporter. The cytotoxicity of cysteine S-conjugates is determined by the activities of several enzymes, including cysteine conjugate C-S lyase, localised in the S1 and S3 segments.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach PH and Bridges JW (1984) The role of metabolic activation of analgesics and non¬steroidal antiinflammatory drugs in the development of renal papillary necrosis and upper urothelial carcinoma. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Med 15:251–274
Chen IC, Stevens JL, Trifillis AL and Jones TW (1990) Renal cysteine conjugate ß-lyase- mediated toxicity studied with pnmary cultures of human proximal tubular cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm 103:463–473
Commandeur JNM and Vermuelen NPE (1990) Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of chemically induced nephrotoxicity: a review. Chem Res Toxicol 3:171–194
Eling TE and Curtis FJ (1992) Xenobiotic metabolism by prostaglandin synthase. Pharmac Ther 53:261–73
Jones TW, Qin C, Schaeffer VH and Stevens JL (1988) Immunohistochemical localization of glutamine transaminase K, a rat kidney cysteine conjugate betalyase, and the relationship to the segment specificity of cysteine conjugate nephrotoxicity. Mol Pharmacol 34:621–627
Jones CL. Buch S, Post M, McCulloch L, Liu E and Eddy AA (1992) Renal extracellular matrix accumulation in acute puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis in rats. Am J Path 141:1381–1396
Green T (1990) Chloroethylenes: a mechanistic approach to human risk evaluation Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 30:73–89
Lash LH and Anders MW (1989) Uptake of nephrotoxic S-conjugates by isolated rat renal proximal tubular cells. J Pharm Exp Ther 248:531–537
Lock EA (1988) Studies on the mechanism of nephrotoxicity and nephrocarcinogenicity of halogenated alkenes. Crit Rev Toxicol 19:23–42
Macfarlane M, Foster JR, Gibson GG, King LJ and Lock EA (1989) Cysteine conjugate beta-lyase of rat kidney cytosol: characterization, immunochemical localization, and correlation with hexachlorobutadiene nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 98:185–197
McCarthy Rl, Lock EA and Hawksworth GM (1994) Cytosolic C-S lyase activity in human kidney samples - relevance for the nephrotoxicity of halogenated alkenes in man. Toxicol Ind Health 10:103–112
Mutti A, Alinovi R, Bergamaschi E et al (1992) Nephropathies and exposure to perchloroethylene in dry-cleaners. Lancet 340:189–193
Naidu KA and Kulkami AP (1994) Lipoxygenase: a non-specific oxidative pathway for xenobiotic metabolism. Prostagl Leukotr and Ess Fatty A 50:155–159
Nakamura T, Ebihara I, Fukui M, Taj)ahashi T. Tomino Y and Koide H (1993) Altered glomerular steady-state levels of tumour necrosis factor-a mRNA during nephrotic and sclerotic phases ofpuromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis in rats Clin Sci 84:349–356
Read NA, Astbury PJ, Evans GO, Goodwin DA and Rowlands A (1995) Nephrotic syndrome associated with N-hydroxyureas, inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase Arch Toxicol 69:480–490
Stewart VC, Tisocki K, Bell JA, Whiting PH and Hawksworth GM (1993) Species differences in prostaglandin synthetase/lipoxygenase mediated cooxidation in the kidney. Br J Clin Pharmac 36 165–165 P
Stewart VC, Tisocki K, Bell JA, Whiting PH and Hawksworth GM (1993) Species differences in prostaglandin synthetase/lipoxygenase mediated cooxidation in the kidney. Br J Clin Pharmac 36 165–165 P
Whiteside CI, Cameron R, Munk S and Levy J (1993) Podocytic cytoskeletal disaggregation and basement-membrane detachment in puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis Am J Pathol 142:1641–1653
Zhang G and Stevens JL (1989) Transport and activation of S-(l,2dichlorovinyl)-L- cysteine and N-acetyl-S-(l,2-dichlorovinyl)-L-cysteine in rat kidney proximal tubules. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 100:51–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hawksworth, G.M., McCarthy, R., McGoldrick, T., Stewart, V., Tisocki, K., Lock, E.A. (1996). Site Specific Drug and Xenobiotic Induced Renal Toxicity. In: Seiler, J.P., Kroftová, O., Eybl, V. (eds) Toxicology - From Cells to Man. Archives of Toxicology, vol 18. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-61105-6_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-61105-6_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-64696-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-61105-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive