Abstract
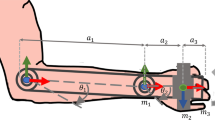
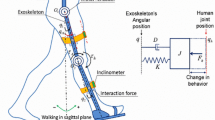
This paper presents a comfort perception analysis of human models interfacing with a novel biped-wheeled-exoskeleton. Usually, many attentions are given to the exoskeleton machine design but, in many cases, without considering the human comfort point of view. This paper merges the conceptual design of the novel biped-wheeled-exoskeleton machine, here proposed in a first time, with the analysis of the comfort perception of human models. The simulation of the human muscular activation is performed using the OpenSim software and the comfort analyses are done thanks to the literature review. Results underline how the comfort perception analysis of a human model with the same constraints of a wearable machine, may optimize the design process of a comfortable wearable hardware by the user. Novel comfortable joints range of motions of a human model, wearing biped-wheeled-exoskeletons, are also the results of this research work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 December 2020
In the original version of the book, the following corrections have been incorporated: Table 1 of Chapter 3 has been removed, and the other tables have been renumbered accordingly. The book and the chapter have been updated with the changes.
References
Zhang, L., Helander, M.G., Drury, C.G.: Identifying factors of comfort and discomfort in sitting. Hum. Factors 38(3), 377–389 (1996)
Corlett, E.N., Bishop, R.P.: A technique for assessing postural discomfort. Ergonomics 19(2), 175–182 (1976)
Drury, C.G., Coury, B.G.: A methodology for chair evaluation. Appl. Ergon. 13(3), 195–202 (1982)
Hignett, S., McAtamney, L.: Rapid entire body assessment (REBA). Appl. Ergon. 31(2), 201–205 (2000)
Borg, G.: Borg’s range model and scales. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 32(2), 110-126 (2001)
Knight, J.F., Baber, C.: A tool to assess the comfort of wearable computers. Hum. Factors 47(1), 77–91 (2005)
Kölsch, M., Beall, A. C., Turk, M.: An objective measure for postural comfort. In: Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, vol. 47, No. 4, pp. 725–728. SAGE Publications, Los Angeles (2003)
Søndergaard, K.H., Olesen, C.G., Søndergaard, E.K., De Zee, M., Madeleine, P.: The variability and complexity of sitting postural control are associated with discomfort. J. Biomech. 43(10), 1997–2001 (2010)
Kee, D., Karwowski, W.: The boundaries for joint angles of isocomfort for sitting and standing males based on perceived comfort of static joint postures. Ergonomics 44(6), 614–648 (2001)
Muscolo, G.G., Recchiuto, C.T., Molfino, R.: Dynamic balance optimization in biped robots: Physical modeling, implementation and tests using an innovative formula. Robotica 33(10), 2083–2099 (2015)
Maiorino, A., Muscolo, G.G.: Biped robots with compliant joints for walking and running performance growing. Front. Mech. Eng. 6, 11 (2020)
Muscolo, G.G., Recchiuto, C.T.: Flexible structure and wheeled feet to simplify biped locomotion of humanoid robots. Int. J. Humanoid Rob. 14(01), 1650030 (2017)
Muscolo, G.G., Caldwell, D., Cannella, F.: Biomechanics of human locomotion with constraints to design flexible-wheeled biped robots. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), pp. 1273–1278. IEEE, 3 July 2017
Muscolo, G.G., Caldwell, D., Cannella, F.: Multibody Dynamics of a flexible legged robot with wheeled feet. In: Proceedings of the ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Multibody Dynamics, pp. 19–22. Czech Republic, Prague, June 2017
Delp, S.L., Anderson, F.C., Arnold, A.S., Loan, P., Habib, A., John, C.T., Thelen, D.G.: OpenSim: Open-source software to create and analyze dynamic simulations of movement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 54(11), 1940–1950 (2007)
Rajagopal, A., Dembia, C.L., DeMers, M.S., Delp, D.D., Hicks, J.L., Delp, S.L.: Full-body musculoskeletal model for muscle-driven simulation of human gait. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(10), 2068–2079 (2016)
Tao, Z., Li, J.K.: Evaluation of human upper limb motion comfort based on motion capture system. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Automation & Computing. Newcastle University, 6-7 Sept 2018
Chester, M.R., Rys, M.J., Konz, S.A.: Leg swelling, comfort and fatigue when sitting, standing, and sit/standing. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 29(5), 289–296 (2002)
Landry, S.C., McKean, K.A., Hubley-Kozey, C.L., Stanish, W.D., Deluzio, K.J.: Knee biomechanics of moderate OA patients measured during gait at a self-selected and fast walking speed. J. Biomech. 40(8), 1754–1761 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zoccali, A., Muscolo, G.G. (2021). Comfort Perception Analysis of Human Models Interfacing with Novel Biped-Wheeled-Exoskeletons. In: Rauter, G., Cattin, P.C., Zam, A., Riener, R., Carbone, G., Pisla, D. (eds) New Trends in Medical and Service Robotics. MESROB 2020. Mechanisms and Machine Science, vol 93. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58104-6_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58104-6_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58103-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58104-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)