Summary
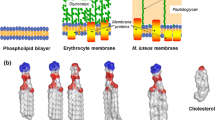
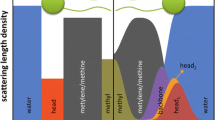
Artificial biomembrane mimetic model systems are used to characterize peptide–membrane interactions using a wide range of methods. Herein, we present the use of selected membrane model systems to investigate peptide–membrane interactions. We describe methods for the preparation of various membrane mimetic media. Our applications will focus on small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs) and large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs) as well as on media more suited for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques, micelles, and fast-tumbling two-component bilayered micelles (bicelles).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gennis, R.B. (1989) Biomembranes: Molecular Structure and Function. Springer, New York.
Magzoub, M., K. Kilk, L.E.G. Erikssom, U. Langel, and A. Gräslund (2001) Interaction and structure induction of cell-penetrating peptides in the presence of phospholipid vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1512, 77–89.
Magzoub, M., L.E.G. Eriksson, and A. Gräslund (2002) Conformational states of the cell-penetrating peptide penetratin when interacting with phospholipid vesicles: effects of surface charge and peptide concentration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1563, 53–63.
Magzoub, M., L.E.G. Eriksson, and A. Gräslund (2003) Comparison of the interaction, positioning, structure induction and membrane perturbation of cell-penetrating peptides and non-translocating variants with phospholipid vesicles. Biophys. Chem. 103, 271–288.
Weinstein J.N., S. Yoshikami, P. Henkart, R. Blumenthal, and W.A. Hagins (1977) Liposome-cell interaction: transfer and intracellular release of a trapped fluorescent marker. Science 195, 489–492.
Andersson, A., J. Danielsson, A. Gräslund, and L. Mäler (2007) Kinetic models for peptide-induced leakage from vesicles and cells. Eur. Biophys. J. 36, 621–635.
Magzoub, M., and A. Gräslund (2004) Cell-penetrating peptides: from inception to application. Q. Rev. Biophys. 37, 147–195.
Terrone, D., S. Leung, W. Sang, L. Roudaia, and J. Silvius (2003) Penetratin and related cell-penetrating cationic peptides can translocate across lipid bilayers in the presence of a transbilayer potential. Biochemistry 42, 13787–13799.
Thorén, P., D. Persson, E. Esbjörner, M. Goksör, B. Lincoln, and B. Nordén (2004) Membrane binding and translocation of cell-penetrating peptides. Biochemistry 43, 3471–3489.
Bárány-Wallje, E., S. Keller, S. Serowy, S. Geibel, P. Pohl, M. Bienert, and M. Dathe (2005) A critical reassessment of penetratin translocation across lipid membranes. Biophys. J. 89, 2513–2521.
Magzoub, M., A. Pramanik, and A. Gräslund (2005) Modeling the endosomal escape of cell-penetrating peptides: transmembrane pH gradient driven translocation across phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry 44, 14890–14897.
Björklund, J., H. Biverståhl, A. Gräslund, L. Mäler, and P. Brzezinski (2006) Real.time transmembrane translocation of penetratin driven by light-generated proton pum**. Biophys. J. Biophys. Lett. 91, L29–L31.
Fischer, A., T. Oberholzer, and P.L. Luisi (2000) Giant vesicles as models to study the interactions between membranes and proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1467, 177–188.
Lindberg, M., J. Jarvet, U. Langel, and A. Gräslund (2001) Secondary structure and position of the cell-penetrating peptide transportan in SDS micelles as determined by NMR. Biochemistry 40, 3141–3149.
Biverståhl, H., A. Andersson, A. Gräslund and L. Mäler (2004) NMR solution structure and membrane interaction of the N-terminal sequence (1–30) of the bovine prion protein. Biochemistry 43, 14940–14947.
Damberg, P., J. Jarvet, and A. Gräslund (2001) Micellar systems as solvents in peptide and protein structure determination. Meth. Enzymol. 339, 271–285.
Chou, J.J., J.D. Kaufman, S.J. Stahl, P.T. Wingfield, and A. Bax (2002) Micelle-induced curvature in a water-insoluble HIV-1 env peptide revealed by NMR dipolar coupling measurement in stretched polyacrylamide gel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 2450–2451.
Andersson A., and L. Mäler (2002) NMR solution structure and dynamics of motilin in isotropic phospholipid bicellar solution. J. Biomol. NMR 24, 103–112.
Ram, P., and J.H. Prestegard (1988) Magnetic field induced ordering of bile salt/phospholipid micelles: new media for NMR structural investigations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 940, 289–294.
Sanders, C.R., and J.H. Prestegard (1990) Magnetically orientable phospholipid bilayers containing small amounts of a bile salt analogue, CHAPSO. Biophys. J. 58, 447–460.
Gaemers, S., and A. Bax (2001) Morphology of three lyotropic liquid crystalline biological NMR media studied by translational diffusion anisotropy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 12343–11235.
Arnold, A., T. Labrot, R. Oda, and E.J. Dufourc (2002) Cation modulation of bicelle size and magnetic alignment as revealed by solid-state NMR and electron microscopy. Biophys. J. 83, 2667–2680.
Nieh, M.P., V.A. Raghunathan, C.J. Glinka, T.A. Harroun, G. Pabst, and J. Katsaras (2004) Magnetically alignable phase of phospholipid “bicelle” mixtures is a chiral nematic made up of wormlike micelles. Langmuir 20, 7893–7897.
van Dam, L., G. Karlsson, and K. Edwards (2004) Direct observation and characterization of DMPC/DHPC aggregates under conditions relevant for biological solution NMR. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1664, 241–256.
Triba, M.N., D.E. Warschawski, and P.F. Devaux (2005) Reinvestigation by phosphorus NMR of lipid distribution in bicelles. Biophys. J. 88, 1887–1901.
Triba, M.N., P.F. Devaux, and D.E. Warschawski (2006) Effects of lipid chain length and unsaturation on bicelles stability. A phosphorus NMR study. Biophys. J. 91, 1357–1367.
Vold, R.R., and R.S. Prosser (1996) Magnetically oriented phospholipid bilayer micelles for structural studies of polypeptides. Does the ideal bicelle exist? J. Magnet. Reson. 113, 267–271.
Vold, R.R., S.R. Prosser, and A.J. Deese (1997) Isotropic solutions of phospholipid bicelles: a new membrane mimetic for high-resolution NMR studies of polypeptides. J. Biomol. NMR 9, 329–335.
Glover, K.J., J.A. Whiles, G. Wu, N.-J. Yu, R. Deems, J.O. Struppe, R.E. Stark, E.A. Komives, and R.R. Vold (2001) Structural evaluation of phospholipid bicelles for solution-state studies of membrane-associated biomolecules. Biophys. J. 81, 2163–2171.
Luchette, P.A., T.N. Vetman, R.S. Prosser, R.E.W. Hancock, M.P. Nieh, C.J. Glinka, S. Krueger, and J. Katsaras (2001) Morphology of fast-tumbling bicelles: a small angle neutron scattering and NMR study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1513, 83–94.
Sanders, C.R.I., and G.C. Landis (1995) Reconstitution of membrane proteins into lipid-rich bilayered mixed micelles for NMR studies. Biochemistry 34, 4030–4040.
Faham, S., and J.U. Bowie (2002) Bicelle crystallization: a new method for crystallizing membrane proteins yields a monomeric bacteriorhodopsin structure. J. Mol. Biol. 316, 1–6.
Marcotte, I., and M. Auger (2005) Bicelles as model membranes for solid- and solution-state NMR studies of membrane peptides and proteins. Concepts Magnet. Reson. 24, 17–37.
Prosser, R.S., F. Evanics, J.L. Kitevski, M.S. Al-Abdul-Wahid (2006) Current applications of bicelles in NMR studies of membrane-associated amphiphiles and proteins. Biochemistry 45, 8453–8465.
Andersson A., and L. Mäler (2005) Magnetic resonance investigations of lipid motion in isotropic bicelles. Langmuir 21, 7702–7709.
Bárány-Wallje E., A. Andersson, A. Gräslund, and L. Mäler (2006) Dynamics of transportan in bicelles is surface charge dependent. J. Biomol. NMR 35, 137–147.
Nagle, J.F., and S. Tristram-Nagle (2000) Structure of lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1469, 159–195.
Orädd, G., and G. Lindblom (2004) NMR Studies of lipid lateral diffusion in the DMPC/gramicidin D/water system: peptide aggregation and obstruction effects. Biophys. J. 87, 980–987.
Hinz, H.J., and J.M. Sturtevant (1972) Calorimetric investigation of the influence of cholesterol on the transition properties of bilayers formed from synthetic L-lecithins in aqueous suspension. J. Biol. Chem. 247, 3697–3700.
Mayer, C., G. Gröbner, K. Müller, K. Weisz, and G. Kothe (1990) Orientation-dependent deuteron spin-lattice relaxation times in bilayer membranes: characterization of the overall lipid motion. Chem. Phys. Lett. 165, 155–161.
Ellena, J.F., L.S. Lepore, and D.S. Cafiso (1993) Estimating lipid lateral diffusion in phospholipid vesicles from 13C spin–spin relaxation. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 2952–2957.
Mayer, L.D., M.J. Hope, and P.R. Cullis (1986) Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 858, 161–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Humana Press, a part of Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Mäler, L., Gräslund, A. (2009). Artificial Membrane Models for the Study of Macromolecular Delivery. In: Belting, M. (eds) Macromolecular Drug Delivery. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 480. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-429-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-429-2_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-58829-999-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-59745-429-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols