Abstract
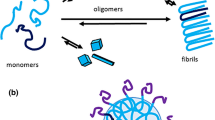
Template-assisted propagation of Tau fibrils is essential for the spreading of Tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. In this process, small seeds of fibrils recruit Tau monomers onto their ends. The physical properties of the fibrils play an important role in their propagation. Here, we describe two different electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) techniques that have provided crucial insights into the structure of Tau fibrils. Both techniques rely on the site-directed introduction of one or two spin labels into the protein monomer. Continuous-wave (CW) EPR provides information on which amino acid residues are contained in the fibril core and how they are stacked along the long fibril axis. Double electron–electron resonance (DEER) determines distances between two spin labels within a single protein and hence provides insights into their spatial arrangement in the fibril cross section. Because of the long distance range accessible to DEER (~2–5 nm) populations of distinct fibril conformers can be differentiated.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:663–672
Spillantini MG, Goedert M (2013) Tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12:609–622
Wu JW, Herman M, Liu L et al (2013) Small misfolded Tau species are internalized via bulk endocytosis and anterogradely and retrogradely transported in neurons. J Biol Chem 288:1856–1870
Kfoury N, Holmes BB, Jiang H et al (2012) Trans-cellular propagation of tau aggregation by fibrillar species. J Biol Chem 287:19440–19451
de Calignon A, Polydoro M, Suarez-Calvet M et al (2012) Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 73:685–697
Liu L, Drouet V, Wu JW et al (2012) Trans-synaptic spread of tau pathology in vivo. PLoS One 7:e31302
Soto C (2012) Transmissible proteins: expanding the prion heresy. Cell 149:968–977
Hubbell WL, Lopez CJ, Altenbach C et al (2013) Technological advances in site-directed spin labeling of proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 23:725–733
Berliner LJ, Grunwald J, Hankovszky HO et al (1982) A novel reversible thiol-specific spin label: papain active site labeling and inhibition. Anal Biochem 119:450–455
Torok M, Milton S, Kayed R et al (2002) Structural and dynamic features of Alzheimer’s Abeta peptide in amyloid fibrils studied by site-directed spin labeling. J Biol Chem 277:40810–40815
Margittai M, Langen R (2004) Template-assisted filament growth by parallel stacking of tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10278–10283
Chen M, Margittai M, Chen J et al (2007) Investigation of alpha-synuclein fibril structure by site-directed spin labeling. J Biol Chem 282:24970–24979
Jayasinghe SA, Langen R (2004) Identifying structural features of fibrillar islet amyloid polypeptide using site-directed spin labeling. J Biol Chem 279:48420–48425
Tanaka M, Chien P, Yonekura K et al (2005) Mechanism of cross-species prion transmission: an infectious conformation compatible with two highly divergent yeast prion proteins. Cell 121:49–62
Ngo S, Gu L, Guo Z (2011) Hierarchical organization in the amyloid core of yeast prion protein Ure2. J Biol Chem 286:29691–29699
Ladner CL, Chen M, Smith DP et al (2010) Stacked sets of parallel, in-register beta-strands of beta2-microglobulin in amyloid fibrils revealed by site-directed spin labeling and chemical labeling. J Biol Chem 285:17137–17147
Cobb NJ, Sonnichsen FD, McHaourab H et al (2007) Molecular architecture of human prion protein amyloid: a parallel, in-register beta-structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18946–18951
Margittai M, Langen R (2008) Fibrils with parallel in-register structure constitute a major class of amyloid fibrils: molecular insights from electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys 41:265–297
Bedrood S, Li Y, Isas JM et al (2012) Fibril structure of human islet amyloid polypeptide. J Biol Chem 287:5235–5241
Karyagina I, Becker S, Giller K et al (2011) Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy measures the distance between the external beta-strands of folded alpha-synuclein in amyloid fibrils. Biophys J 101:L1–L3
Pornsuwan S, Giller K, Riedel D et al (2013) Long-range distances in amyloid fibrils of alpha-Synuclein from PELDOR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52:10290–10294
Siddiqua A, Luo Y, Meyer V et al (2012) Conformational basis for asymmetric seeding barrier in filaments of three- and four-repeat tau. J Am Chem Soc 134:10271–10278
Meyer V, Dinkel PD, Luo Y et al (2014) Single mutations in tau modulate the populations of fibril conformers through seed selection. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:1590–1593
Eaton GR, Eaton SS, Barr DP, Weber RT (2010) Quantitative EPR. Springer, Wien
Margittai M, Langen R (2006) Spin labeling analysis of amyloids and other protein aggregates. Methods Enzymol 413:122–139
Friedhoff P, von Bergen M, Mandelkow EM et al (1998) A nucleated assembly mechanism of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:15712–15717
Jeschke G (2012) DEER distance measurements on proteins. Annu Rev Phys Chem 63:419–446
Jeschke G, Chechik V, Ionita P et al (2006) DeerAnalysis2006: a comprehensive software package for analyzing pulsed ELDOR data. Appl Magn Reson 30:473–498
Sen KI, Logan TM, Fajer PG (2007) Protein dynamics and monomer-monomer interactions in AntR activation by electron paramagnetic resonance and double electron-electron resonance. Biochemistry 46:11639–11649
Brandon S, Beth AH, Hustedt EJ (2012) The global analysis of DEER data. J Magn Reson 218:93–104
Huber M, Lindgren M, Hammarstrom P et al (2001) Phase memory relaxation times of spin labels in human carbonic anhydrase II: pulsed EPR to determine spin label location. Biophys Chem 94:245–256
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Grant R01NS076619.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Meyer, V., Margittai, M. (2016). Spin Labeling and Characterization of Tau Fibrils Using Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR). In: Eliezer, D. (eds) Protein Amyloid Aggregation. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1345. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2978-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2978-8_12
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2977-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2978-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols