Abstract
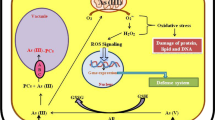
Heavy metal stress is increasing at an alarming rate in agricultural soils through out the world. Heavy metal (Cd, Cu, Zn, Ni, Co, Cr, Pb and As) toxicity have been reported to be responsible for the reduced crop production. Among the heavy metals arsenic (As) is non-essential and toxic to both plants and animals. As can exist in environment in the form of oxidized arsenate (AsV) and reduced arsenite (AsIII). As stress has become a global concern, the uptake of As in the plants through contaminated soil will make its entry into the human food chain. As toxicity can lead to skin, bladder, lung and prostate cancer. Soil contaminated with As is the main source of arsenic in drinking water. Uptake of As by plants is very important in understanding its physiological effects and its metabolism within plants. How plants respond to the arsenic stress in plants is a major concern to biologists. As per the published literature numerous physiological processes are affected by the As toxicity. As is also responsible for oxidative stress in plants through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which attack the biomolecules like, membranes proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids etc. At the same time activity of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants are increased which helped the plant to withstand the toxicity of As. The present chapter throws light on the arsenic toxicity in plants and their tolerance mechanism in plants. The chapter also highlights the generation of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants during As stress.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin MJ, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2002) Uptake kinetics of arsenic species in rice plants. Plant Physiol 128:1120–1128
Adriano DC (2001) Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. Springer, New York,
Adriano DC (1986) Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. Springer, New York,
Ali W, Isayenkov SV, Zhao FJ, Maathuis F (2009) Arsenite transport in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2329–2339
Aniol A, Gustafson JP (1989) Genetics of tolerance in agronomic plants. In: Shaw AJ (ed) Heavy metal tolerance in plants: evolutionary aspects. CRC Press, Florida, pp 255–267
Aten CF, Bourke JB, Martini JH et al (1980) Arsenic and lead in an orchard environment. Environ Toxicol 24:108–115
Axelsen K, Palmgren M (2001). Inventory of the superfamily of P-type ion pumps in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:696–706
Baker AJM (1987) Metal tolerance. New Phytol 106(Suppl):93–111
Baker AJM, Walker PL (1989) Physiological responses of plants to heavy metals and the quantification of tolerance and toxicity. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 1:7–17
Banejad H, Olyaie E (2011) Arsenic toxicity in the irrigation water-soil-plant system: a significant environmental problem. J Am Sci 7(1):125–131
Barlian-Aidid S, Okamoto H (1992) Effects of lead, cadmium and zinc on the electric membrane potential at the xylem/symplast interface and cell elongation of Impatiens balsamina. Environ Exp Bot 32:439–448
Berry WL, Wallace A (1981) Toxicity: the concept and relationship to the dose response curve. J Plant Nutr 3:13–19
Bhattacharya S, Goswami MR, Dhar A, Chattopadhyay D, Mukhopadhyay A, Ghosh UC (2012) Effects of arsenic stress on germination, seedling growth and peroxidase activity in pea seeds and kidney bean seeds. J Universal Pharm Life Sci 2(3):760–770
Bondada B, Ma LQ (2002) Tolerance of heavy metals in vascular plants: arsenic hyperaccumulation by Chinese brake fern (Pteris vittata L.), In: Nayar BK, Chandra S, Srivastava M (eds) Pteridology in New millennium. Kluwer Academy Publishers, 397–420
Bruins MR, Kapil S, Oehme FW (2000) Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 45B:198–207
Chandra S, Srivastava M (2003) Pteridology in the new millennium. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands
Chen M, Ma LQ, Harris WG (1999) Baseline concentrations of 15 trace elements in Florida surface soils. J Environ Qual 28:1173–1181
Chen T, Wei C, Huang Z, Huang Q, Lu Q, Fan Z (2002) Arsenic hyper-accumulator Pteris vittata L. and its arsenic accumulation. Chinese Sci Bull 47:902–905
Clarkson DT (1996) Root structure and sites of ion uptake. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U (eds) Plant roots. The hidden half, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 483–510
Clemens S (2001) Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis. Planta 212:475–486
Clements HF, Munson J (1947) Arsenic toxicity studies in soil and in culture solution. Pacific Sci 1:151–171
Clijsters H, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J (1999) Physiological responses to heavy metals in higher plants; defence against oxidative stress. Z Naturforsch 54c:730–734
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182
Cobbett CS (2000) Phytochelatins and their roles in heavy metal detoxification. Plant Physiol 123:825–832
Cumming JR, Taylor GJ (1990) Mechanisms of metal tolerance in plants: physiological adaptations for exclusion of metal ions from the cytoplasm. In: Alscher RG, Cumming JR (eds) Stress responses in plants: adaptation and acclimation mechanisms. Wiley, New York, pp 329–356
Dat J, Vandenabeele S, Vranová E, Van Montagu M, Inzé D, Van Breusegem F (2000) Dual action of the active oxygen species during plant stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:779–795
De Vos CHR, Vonk MJ, Vooijs R, Schat H (1992) Glutathione depletion due to copper-induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol 98:853–858
Ebbs S, Lau I, Ahner B, Kochian L (2002) Phytochelatin synthesis is not responsible for Cd tolerance in the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (J. & C. Presl). Planta 214:635–640
Ernst W (1976) Physiological and biochemical aspects of metal tolerance. In: Mansfield TA (ed) Effects of air pollutants on plants. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 115–133
Ernst WHO (1997a) Population dynamics of plants under exposure and the selection of resistance. In: Schüürmann G, Markert B (eds) Ecotoxicology. Ecological fundamentals, chemical exposure, and biological effects. Wiley, New York, pp 117–132
Ernst WHO (1997b) Effects of heavy metals in plants at the cellular and organismic level. In: Schüürmann G, Markert B (eds) Ecotoxicology. Ecological fundamentals, chemical exposure, and biological effects. Wiley, New York, pp 587–620
Fodor F (2002) Physiological responses of vascular plant to heavy metals. In: Prasad MNV, Strzalka K (eds) Physiology and biochemistry of metal toxicities and tolerance in plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 149–177
Fowler BA (1983) Biological and environmental effects of arsenic. Elsevier Sci. Publ., Amsterdam
Grill E, Gekeler W, Winnacker E-L, Zenk HH (1986) Homo-phytochelatins are heavy metal-binding peptides of homo-glutathione containing Fabales. FEBS Lett 205:47–50
Grill E, Winnacker E-L, Zenk MH (1985) Phytochelatins: the principal heavy-metal complexing peptides of higher plants. Science 230:674–676
Grill E, Winnacker E-L, Zenk MH (1987) Phytochelatins, a class of heavy-metal-binding peptides from plants, are functionally analogous to metallothioneins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:439–443
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53:1–11
Harris WG, Carlisle VW, Chesser SL (1987a) Clay mineralogy as related to morphology of Florida soils with sandy epipedons. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1673–1677
Harris WG, Carlisle VW, van Rees KCJ (1987b) Pedon zonation of hydroxy-interlayered minerals in Ultic Haplaquods. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1367–1372
Hartley-Whitaker J, Ainsworth G, Meharg AA (2001a) Copper and arsenate induced oxidative stress in Holcus lanatus L. clones with differential sensitivity. Plant Cell Environ 24:713–722
Hartley-Whitaker J, Ainsworth G, Vooijs R, Ten Bookum W, Schat H, Meharg AA (2001b) Phytochelatins are involved in differential arsenate tolerance in Holcus lanatus. Plant Physiol 126:299–306
Jacobs LW, Keeney DR (1970) Arsenic-phosphorus interactions in corn. Commu Soil Sci Plant Analy 1:85–93
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 413
Kaur S, Kamli MR, Ali A (2011) Role of arsenic and its resistance in nature. Can J Microbiol 57(10):769–774
Kennedy CD, Gonsalves FAN (1987) The action of divalent zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper and lead on the trans-root potential and H+efflux of excised roots. J Exp Bot 38:800–817
Kenyon DJ, Elfving DC, Pakkala IS, Bache CA, Lisk DJ (1979) Residues of Lead and Arsenic in crops cultured on old orchard soils. Bul Environ Contam Toxicol 22:221–223
Klapheck S, Schlunz S, Bergmann L (1995) Synthesis of phytochelatins and homophytochelatins in Pisum sativum L. Plant Physiol 107:515–521
Kneer R, Zenk MH (1992) Phytochelatins protect plant enzymes from heavy metal poisoning. Phytochemistry 31:2663–2667
Kooijman SALM (1997) Process-oriented descriptions of toxic effects. In: Schüürmann G, Markert B (eds) Ecotoxicology. Ecological fundamentals, chemical exposure, and biological effects. Wiley, New York, pp 483–520
Lui Yl, Xu Y, Ke-Bing D, Tu BK (2012) Absorption and metabolism mechanisms of inorganic arsenic in plants: a review. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 23(3):842–848
Macnair MR (1993) The genetics of metal tolerance in vascular plants. New Phytol 124:541–559
Macnicol RD, Beckett PHT (1985) Critical tissue concentrations of potentially toxic elements. Plant Soil 85:107–129
Maitani T, Kubota H, Sato K, Yamada T (1996) The composition of metals bound to Class III metallothionein (phytochelatin and its desglycyl peptide) induced by various metals in root cultures of Rubia tinctorum. Plant Physiol 110:1145–1150
Meharg AA, Hartley-Whitaker J (2002) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and non-resistant plant species. New Phytol 154:29–43
Moreno-Jimenez E, Esteban E, Penalosa JM (2012) The fate of arsenic in soil-plant systems. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 215:1–37
Nies DH, Silver S (1995) Ion efflux systems involved in bacterial metal resistances. J Indust Micro biol 14:186–199
Odjegba VJ (2012) Exogenous salicylic acid alleviates arsenic toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Indian J Innovations Dev 1(7):516–522
Ortiz DF, Kreppel L, Speiser DM, Scheel G, McDonald G, Ow DW (1992) Heavy metal tolerance in the fission yeast requires an ATP-binding cassette-type vacuolar membrane transporter. EMBO J 11:3491–3499
Palmgren M (2001) Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase: powerhous for nutrient uptake. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 52:817–845
Pickering IJ, Prince RC, George MJ, Smith RD, George GN, Salt DE (2000) Reduction and coordination of arsenic in Indian mustard. Plant Physiol 122:1171–1178
Piechalak A, Tomaszewska B, Baralkiewicz D, Malecka A (2002) Accumulation and detoxification of lead ions in legumes. Phytochemistry 60:153–162
Pierce ML, Moore CB (1982) Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate on amorphous iron hydroxide. Water Residue 16:1247–1253
Rauser WE (1995) Phytochelatins and related peptides. structure, biosynthesis, and function. Plant Physiol 109:1141–1149
Reddy GN, Prasad NMV (1990) Heavy metal-binding proteins/peptides: occurrence, structure, synthesis and functions. A review. Environ Exp Bot 30:251–264
Rhue RD, Harris WG, Kidder G, Brown RB, Littell RC (1994) A soil based phosphorous retention index for animal waste disposal on sandy soil. Final project report. Florida Depart Environ Protec EPA grant no.9004984910
Rosen BP (1999) Families of arsenic transporters. Trends Microb 7:207–212
Rumberg CB, Engel RE, Meggitt WF (1960) Effect of phosphorus concentration on the absorption of arsenate by oats from nutrient solution. Agronomy J 52:452–453
Salt DE, Rauser WE (1995) MgATP-dependent transport of phytochelatins across the tonoplast of oat roots. Plant Physiol 107:1293–1301
Schat H, Llugany M, Vooijs R, Hartley-Whitaker J, Bleeker PM (2002) The role of phytochelatins in constitutive and adaptive heavy metal tolerances in hyperaccumulator and non-hyperaccumulator metallophytes. J Exp Bot 53:2381–2392
Schat H, Vooijs R, Kuiper E (1996) Identical major gene loci for heavy metal tolerances that have independently evolved in different local populations and subspecies of Silene vulgaris. Evolution 50:1888–1895
Schmoger ME, Oven M, Grill E (2000) Detoxification of arsenic by phytochelatins in plants. Plant Physiol 122:793–801
Sharples JM, Meharg AA, Chambers SM, Cairney JWG (2000) Mechanism of arsenate resistance in the ericoid mycorrhizal fungus Hymenoscyphus ericae. Plant Physiol 124:1327–1334
Steffens JC (1990) The heavy metal-binding peptides of plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 41:553–575
Sturchio E, Boccia P, Meconi C, Zanellato M, Marconi S, Beni C, Aromolo R, Ciampa A, Diana G, Valentini M (2011) Effects of arsenic on soil-plant systems. Chem Ecol 27(1):67–78
Tangahu BV, Sheikh Abdullah SR, Basri H, Idris M, Anuar N, Mukhlisin M (2011) A Review on Heavy metals (As, Pb, and Hg) uptake by plants through phytoremediation. Int J Chem Engineer 2011: doi:10.1155/2011/939161
Tomaszewska B, Tukendorf A, Baralkiewicz D (1996) The synthesis of phytochelatins in lupin roots treated with lead ions. Sci Legume 3:206–217
Ullrich-Eberius CI, Sanz A, Novacky AJ (1989) Evaluation of arsenate and vanadate associated changes of electrical membrane potential and phosphate transport in Lemna gibba G1. J Exp Bot 40:119–128
Woolson EA (1983) Emissions, cycling, and effects of arsenic in soil ecosystems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 52–125
Zhao F, MecGrath SP, Meharg AA (2010) Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: mechanisms of uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Ann Rev Plant Biol 61:535–559
Zhao FJ, Dunham SJ, McGrath SP (2002) Arsenic hyperaccumulation by different fern species. New Phytol 156:27–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Rasool, S., Rehman, M., Mahgoub Azooz, M., Iqbal, M., Siddiqi, T., Ahmad, P. (2013). Arsenic Toxicity and Tolerance Mechanisms in Plants: An Overview. In: Hakeem, K., Ahmad, P., Ozturk, M. (eds) Crop Improvement. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7028-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7028-1_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-7027-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-7028-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)