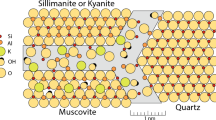
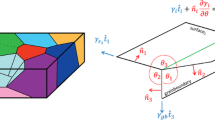
Abstract
Geologists have long held the belief that diffusion along grain boundaries in rocks would provide the means for mass transport over distances in the range of centimetres to metres needed to explain various metasomatic phenomena. Indeed, measured grain-boundary diffusion coefficients support this belief, as the ratio D GB i /D VOL i is commonly greater than 104 at metamorphic temperatures. To assess the role of grain-boundary diffusion in metamorphic processes this contribution:
-
(1)
reviews the current understanding of the nature of grain boundaries in oxides and silicates;
-
(2)
reviews the mathematical description of grain-boundary diffusion;
-
(3)
summarizes available grain-boundary diffusion data for oxides and silicates;
-
(4)
uses these results to explore the scale of mass transport by grain-boundary diffusion in metamorphic systems at geologic time scales.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aines, R.D., and Rossman, G.R. (1984) Water in minerals? A peak in the infrared. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 4059–4071.
Atkinson, A. (1985) Grain boundary diffusion—Structural effects and mechanisms. J. de Phys. 46, C4-379–C4-391.
Atkinson, A., Hughes, A.E., and Hammou, A. (1981) The self-diffusion of Ni in undoped and Al-doped NiO single crystals. Philos. Mag. A 43,1071–1091.
Atkinson, A., Pummery, F.C.W., and Monty, C. (1985) Diffusion of O18 tracer in NiO grain boundaries, in Transport in Nonstoichiometric Compounds, edited by G. Sinkovich and V.S. Stubican. NATO ASI Ser. B, Physics 129, 359–370.
Atkinson, A., and Taylor, R.I. (1981) The diffusion of 63Ni along grain boundaries in nickel oxide. Philos. Mag. A 43, 979–998.
Atkinson, A., and Taylor, R.I. (1982) Diffusion of 57Co along grain boundaries in NiO. Philos. Mag. A 45, 583–592.
Atkinson, A., and Taylor, R.I. (1984) Diffusion of 51Cr tracer in Cr203 and the growth of Cr2O3 films, in Transport in Nonstoichiometric Compounds, edited by G. Sinkovich and V.S. Stubican, NATO ASI Ser. B, Physics 129, 285–295.
Atkinson, A., and Taylor, R.I. (1986) Impurity diffusion in NiO grain boundaries. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 41, 315–323.
Atkinson, A., Taylor, R.I., and Hughes, A.E. (1982) A quantitative demonstration of the grain boundary diffusion mechanism for the oxidation of metals. Philos. Mag. 45, 823–833.
Atkinson, H.V., and Duffy, D.M. (1986) Calculation of activation energies for defect movement during coincidence boundary migration in nickel oxide using computer simulation techniques. Acta Metall. 34, 2371–2380.
Azaroff, L.V. (1961) Role of crystal structure in diffusion. I. Diffusion paths in closest-packed crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 1658–1662.
Balluffi, R.W. (editor) (1979) Grain-Boundary Structure and Kinetics. American Society of Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 470 pp.
Balluffi, R.W. (1984) Grain boundary diffusion mechanisms in metals, in Diffusion in Crystalline Solids, edited by G.E. Murch and A.S. Nowick, pp. 319–377. Academic Press, Orlando.
Balluffi, R.W., Bristowe, P.D., and Brokman, A. (1983) Structure of large-angle grain boundaries in metals and ceramic oxides, in Character of Grain Boundaries, edited by M.F. Yan and A.H. Heuer. Adv. Ceram., vol. 6, pp. 15–35. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Balluffi, R.W., Brokman, A., and King, A.H. (1982) CSL/DSC lattice model for general crystal-crystal boundaries and their line defects. Acta Metall. 30, 1453–1470.
Bannister, M.J. (1967) Interdependence of pore removal and grain growth during the later stages of sintering in beryllium oxide, in Sintering and Related Phenomena, Materials Science Research, vol. 6, edited by G.C. Kuczynski, N.A. Hooten, and N.F. Gibbon, pp. 581–605. Gordon and Breach, New York.
Bollmann, W. (1970) Crystal Defects and Crystalline Interfaces. Springer-Verlag, New York, 255 pp.
Bourret, A., d’Anterroches, C., and Penisson, J.M. (1982) Structure des joints en microscopie electronique haute resolution (MHER). J. de Phys. 43, C6-83–C6-90.
Bradhurst, D.H., and De Bruin, H.J. (1969) Measurement of self-diffusion of oxygen in beryllium oxide by proton activation of oxygen-18. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 5, 21–27.
Brady, J.B. (1983) Intergranular diffusion in metamorphic rocks. Amer. J. Sci. 283A (Orville Volume), 181–200.
Brokman, A., and Balluffi, R.W. (1981) Coincidence lattice model for the structure and energy of grain boundaries. Acta Metall. 29, 1703–1719.[10]
Cannon, R.M., Rhodes, W.H., and Heuer, A.H. (1980) Plastic deformation of fine grained alumina (A1203): I. Interface-controlled diffusional creep. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 63, 46–53.
Carter, C.B. (1984) The structure of grain boundaries and phase boundaries in ceramics, in Electron Microscopy of Materials, edited by W. Krakow, D.A. Smith, and L.W. Hobbs, pp. 267–278. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 31. North-Holland, New York.
Carter, C.B., and Elgat, Z. (1983) Migration of grain boundaries in Si and Ge, in Character of Grain Boundaries, edited by M.F. Yan and A.H. Heuer, Adv. Ceram., vol. 6, pp. 192–201. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Carter, C.B., Kohlstedt, D.L., and Sass, S.L., (1980). Electron diffraction and micros¬copy studies of the structure of grain boundaries in A1203. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 63, 623–627.
Carter, C.B., and Sass, S.L. (1981) Electron diffraction and microscopy techniques for studying grain-boundary structure. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 64, 335–345.
Chen, W.K., and Peterson, N.L. (1972) Correlation effects and effects of cobalt additions on cobalt and nickel diffusion in NiO. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 33, 881–892.
Chen, W.K., and Peterson, N.L. (1980) Grain-boundary diffusion of 60Co and 51Cr in NiO. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 63, 566–570.
Chen, W.K., Peterson, N.L., and Robinson, L.C. (1973) Chromium tracer diffusion in NiO crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 34, 705–709.
Chokshi, A.H. (1988) Critical appraisal of diffusivity determinations from experimental creep data. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 71, C241–C243.
Christensen, J.N., Rosenfeld, J.L., and DePaolo, D.J. (1989) Rates of tectonometa- morphic processes from rubidium and strontium isotopes in garnet. Science 244, 1465–1469.
Coble, R.L. (1963) Model for boundary diffusion controlled creep in polycrystalline materials. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1679–1682.
Condit, R.H. (1974) Diffusion path networks in the wurtzite lattice, in Defects and Transport in Oxides, edited by M.S. Selzer and R.I. Jaffee, pp. 303–313. Plenum Press, New York.
Condit, R.H. (1985) An approach to analyzing diffusion in olivine, in Point Defects in Minerals, edited by R.N. Schrock, pp. 106–115. Amer. Geophys. Union, Geo-physical Mon. 31.
Condit, R.H., Weed, H.C., and Piwinskii, A.J. (1985) A technique for observing oxygen diffusion along grain boundary regions in synthetic forsterite, in Point Defects in Minerals, edited by R.N. Schrock, pp. 97–105. Amer. Geophys. Union, Geophysical Mon. 31.
Crank, J. (1975) The Mathematics of Diffusion ( 2nd ed. ). Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 414 pp.
Daniels, A.U. Jr., Lowrie, R.C. Jr., Gibby, R.L., and Cutler, I.B. (1962) Observations on normal grain growth in magnesia and calcia. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 45, 282–285.
Dhaline, G., Dechamps, M., and Revcolevschi, A. (1983) Energy of tilt boundaries and mass transport mechanisms in nickel oxide, in Character of Grain Boundaries, edited by M.F. Yan and A.H. Heuer. Adv. Ceram., vol. 6, pp. 139–150. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Dhaline, G., Dechamps, M., and Revcolevschi, A. (1982) Relative energies of <011> tilt boundaries in NiO. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc 65, 611–612.
Dennis, P.F. (1984a) Oxygen self-diffusion in quartz under hydrothermal conditions.J. Geophys. Res. 89, 4047–4057.
Dennis, P.F. (1984b) Oxygen self diffusion in quartz. Progress in Experimental Petrology. 6th Rpt., Nat. Env. Res. Council, Pub. Ser. D, N. 25, pp. 260–265.
Dubois, D., Monty, C., and Philibert, J. (1982) Oxygen self-diffusion in NiO single crystals. Philos. Mag. A 46, 419–433.
Duffy, D.M., and Tasker, P.W. (1983) Computer simulation of <011> tilt grain boundaries in nickel oxide. Philos. Mag. A 48, 155–162.
Duffy, D.M., and Tasker, P.W. (1985) The calculated properties of grain boundaries in nickel oxide. J. de Phys. 46, C4, 185–194.
Duffy, D.M., and Tasker, P.W. (1986) Theoretical studies of diffusion processes down coincident tilt boundaries in NiO. Philos. Mag. A 54, 759–771.
Elphick, S.C., Dennis, P.F., and Graham, C.M. (1986) An experimental study of the diffusion of oxygen in quartz and albite using an overgrowth technique. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 92, 322–330.
Fisher, J.C. (1951) Calculation of diffusion penetration curves for surface and grain boundary diffusion. J. Appl. Phys. 22, 74–77.
Florjancic, M., Mader, W., Ruehle, M., and Turwitt, M. (1985) HREM and diffraction studies if an Al203/Nb interface. J. de Phys. 46, C4-129–C4-140.
Freer, R. (1980) Self-diffusion and impurity diffusion in oxides (Bibliography). J. Mater. Sci. 15, 803–824.
Freer, R. (1981) Diffusion in silicate minerals and glasses: A data digest and guide to the literature. Contrib. Mineral Petrol. 76, 440–454.
Giletti, B.J., and Yund, R.A. (1984) Oxygen diffusion in quartz. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 4039–4046.
Giletti, B.J., Yund, R.A., and Semet, M. (1976) Silicon diffusion in quartz (Abs.). Geol Soc. Amer. Abs. Prog. 8, 883–884.
Giletti, B.B., Hickey, J.H., and Tullis, T.E. (1979) Oxygen diffusion in olivine under hydrous conditions (Abs.). EOS Amer. Geophys. Union Trans. 60, 370.
Gjostein, N.A., and Rhines, F.N. (1959) Absolute interfacial energies of [001] tilt and twist boundaries in copper. Acta Metallogr. 7, 319–330.
Gordon, R.S. (1973) Mass transport in the diffusional creep of ionic solids. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 56, 147–152.
Gordon, R.S. (1975) Ambipolar diffusion and its application to diffusion creep, in Mass Transport Phenomena in Ceramics, edited by A.R. Cooper and A.H. Heuer, Materials Science Research, vol. 7, pp. 445–464. Plenum Press, New York.
Gordon, R.S. (1985) Diffusional creep in polycrystalline solids, in Point Defects in Minerals, edited by R.N. Schrock, pp. 132–140. Amer. Geophys. Union, Geo-physical Mon. 31.
Gronsky, R. (1979) Direct imaging of grain boundaries, in Grain-Boundary Structure and Kinetics, edited by R.W. Balluffi, pp. 45–70. American Society of Metals, Metals Park, Ohio.
Gupta, D., Campbell, D.R., and Ho, P.S. (1978) Grain boundary diffusion, in Thin Films—Interdiffusion and Reactions, edited by J.M. Poate, K.N. Tu, and J.W. Mayer, pp. 161–242. Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Hagege, S., Carter, C.B., Cosandev, F., and Sass, S.L. (1982) The variation of grain boundary structural width with misorientation angle and boundary plane. Philos. Mag. A 45, 723–740.
Hall, E.L. (1982) Application of the analytical electron microscope to the study of grain-boundary chemistry. J. de Phys. 43, C6, 239–254.
Hallwig, D., Schactner, R., and Sockel, H.G. (1982) Diffusion of magnesium, silicon and oxygen in Mg2Si04 and formation of the compound in the solid state, in Reactivity of Solids, edited by K. Dryek, J. Habor and J. Nowotry, pp. 166–169. Proc. 9th Int. Symposium.
Harding, B.C., and Price, D.M. (1972) Cation self-diffusion in MgO up to 2350 °C. Philos. Mag. 26, 253–260.
Harrison, L.G. (1961) Influence of dislocations on diffusion kinetics in solids with particular reference to the alkali halides. Trans. Faraday Soc. 57, 1191–1199.
Hart, E.W. (1957) On the role of dislocations in bulk diffusion. Acta Metall. 5, 597.
Hasson, G.C., and Goux, C. (1971) Interfacial energies of tilt boundaries in aluminum. Experimental and theoretical determination. Scripta Metall. 5, 889–894.
Haul, R., and Dumbgen, G. (1962) Investigation of oxygen diffusion in Ti02, quartz and quartz glass by isotope exchange. Z. Electrochem. 66, 636–641.
Hay, R.S., and Evans, R. (1988) Intergranular distribution of pore fluid and the nature of high-angle grain boundaries in limestone and marble. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8959–8974.
Herring, C. (1950) Diffusional viscosity of a polycrystalline solid. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 437–445.
Hillert, M. (1965) On the theory of normal and abnormal grain growth. Acta Metall. 13, 227–238.
Hirota, K., and Komatsu, W. (1977) Concurrent measurement of volume, grain-boundary and surface diffusion coefficients in the system NiO-Al203. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 60,105–107.
Hobbs, B. E. (1984) Point defect chemistry of minerals under a hydrothermal environment. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 4026–4038.
Hobbs, B. E. (1985) The hydrolytic weakening effect in quartz, in Point Defects in Minerals, edited by R.N. Schrock, pp. 151–170. Amer. Geophys. Union, Geophysical Mon. 31.
Holt, J.B. (1964) Self-diffusion of oxygen in single-crystal beryllium oxide. J. Nucl.Mater. 11, 107–110.
Hoshino, K., and Peterson, N.L. (1983) Cation self-diffusion in Cr203. J. Amer.Ceram. Soc. 66, C202–C203.
Ichinose, H., and Ishida, Y. (1985) High resolution electron microscopy of grain boundaries in fee and bcc metals. J. de Phys. 46, C4-39–C4-49.
Ikegami, T., Matsuda, S.-I., Moriyoshi, Y., and Suzuki, H. (1982) Normal grain growth in porous and dense compacts. J. Mater. Sci. 17, 2855–2860.
Jaoul, O., Froidevaux, D., Durham, W.B., and Michaut, M. (1980) Oxygen self- diffusion in forsterite: Implications for the high temperature creep mechanism. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 47, 613–624.
Jaoul, O., Houlier, B., and Abel, F. (1983) Study of lsO diffusion in magnesium orthosilicate by nuclear microanalysis. J. Geophys. Res. 88, 613–624.
Jaoul, O., Poumellec, M., Froidevaux, C., and Havette, A. (1981) Silicon diffusion in forsterite: A new constraint for understanding mantle deformation, in Anelasticity in the Earth, edited by F.D. Stacey, M.S. Paterson, and A. Nicholas, pp. 95–100. Amer. Geophys. Union, Geodynamics Ser. 4.
Joesten, R. (1983) Grain growth and grain boundary diffusion in quartz from the Christmas Mountains (Texas) contact aureole. Amer. J. Sci. 283A (Orville Volume) 233–254.
Joesten, R. (1985) A diffusion-compensation relation for normal grain growth and grain-boundary diffusion of oxygen in oxides. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 68, C62–C64.
Joesten, R., and Fisher, G.W. (1988) Kinetics of diffusion-controlled mineral growth in the Christmas Mountains (Texas) contact aureole. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 100, 714–732.
Johnson, D.L., and Berrin, L. (1967) Grain boundary diffusion in the sintering of oxides, in Sintering and Related Phenomena, Materials Science Research, vol. 6, edited by G.C. Kuczynski, N.A. Hooten, and N.F. Gibbon, pp. 445–566. Gordon and Breach, New York.
Kapadia, C.M., and Liepold, M.H. (1974) Grain growth in pure dense MgO. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 57, 41–42.
Karstensen, F. (1959) Uber die Diffusion in Germaniumkristallen, die eine Korngranze enthalten. Z. Naturforschung 14A, 1031–1039.
Kingery, W.D. (1974a) Plausible concepts necessary and sufficient for interpretation of ceramic grain boundary phenomena: I. Grain-boundary characteristics, struc¬ture and electrostatic potential. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 57, 1–8.
Kingery, W.D. (1974b) Plausible concepts necessary and sufficient for interpretation of ceramic grain boundary phenomena: II. Solute segregation, grain-boundary diffusion and general discussion. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 57, 74–83.
Kingery, W.D., Bowen, H.K., and Uhlmann, D.R. (1976) Introduction to Ceramics ( 2nd ed. ). Wiley, New York, 1032 pp.
Kronenberg, A.K., Kirby, S.H., Aines, R.D., and Rossman, G.R. (1986) Solubility and diffusional uptake of hydrogen in quartz at high water pressures: Implications for hydrolytic weakening. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 12713–12744.
Kronenberg, A.K., and Tullis, J. (1984) Flow strengths of quartz aggregates: Grain size and pressure effects due to hydrolytic weakening. J. Geophys. Res. 89,4281– 4297.
Lartigue, S., and Priester, L. (1985) Grain boundaries in polycrystalline alumina. J.de Phys. 46, C4, 101–106.
Lavine, J.P., and Losee, D.L. (1984) Monte Carlo treatment of impurity diffusion in polycrystalline films. J. Appl. Phys. 56, 924–926.
Le Claire, A.D. (1951) Grain boundary diffusion in metals. Philos. Mag. 42, 468–474.
Le Claire, A.D. (1963) The analysis of grain boundary diffusion measurements. Brit.J. Appl. Phys. 14, 351–356.
Le Claire, A.D. (1986) Diffusion in dislocations—“pipe diffusion”, in Solute-Defect Interaction, Theory and Experiment, edited by S. Saimoto, G.R. Purdy, and G.V. Kidson, pp. 251–270. Pergamon Press, Toronto.
Le Claire, A.D., and Rabinovitch, A. (1984) Mathematical analysis of diffusion in dislocations, in Diffusion in Crystalline Solids, edited by G.E. Murch and A.S. Nowick S., pp. 257–318. Academic Press, Orlando.
Lessing, P.A., and Gordon, R.S. (1977) Creep of polycrystalline alumina, pure and doped with transition metal impurities. J. Mater. Sci. 12, 2291–2302.
Levine, H.S., and MacCallum, C.J. (1960) Grain boundary and lattice diffusion in polycrystalline bodies. J. Appl. Phys. 31, 595–599.
Lindner, R. (1956) Silikatbildung durch Reaktion im Festen Zustand. Zeitssch. Phys.Che. NF 6, 129–142.
Lindner, R. (1957) Studies on solid state reactions with radiotracers. J. Chem. Phys. 23, 410–411.
Martin, G., and Perraillon, B. (1979) Measurements of grain boundary diffusion, in Grain-Boundary Structure and Kinetics, edited by R.W. Balluffi, pp. 239–296. American Society of Metals, Metals Park, Ohio.
McKenzie, D.R., Searcy, A.W., Holt, J.B., and Condit, R.H. (1971) Oxygen grain-boundary diffusion in MgO. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 54, 188–190.
McLaren, A.C. (1986) Some speculation on the nature of high-angle grain boundaries in quartz rocks, in Mineral and Rock Deformation: Laboratory Studies. The Paterson Volume, edited by B.E. Hobbs and H.C. Heard, pp. 233–245. Amer. Geophys. Union, Geophysical Mon. 36.
Merkle, K.L., Reddy, J.F., and Wiley, C.L. (1985) Grain boundary structure in NiO. J. de Phys. 46, C4, 95–100.
Mistier, R.E., and Coble, R.L. (1974) Grain-boundary diffusion and boundary widths in metals and ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 45, 1507–1509.
Moosa, A.A., and Rothman, S.J. (1985) Effect of yttrium additions on the oxidation of nickel. Oxidation of Metals 24, 133–148.
Morioka, M. (1981) Cation diffusion in olivine—II. Ni-Mg, Mn-Mg, Mg and Ca. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 45, 1573–1580.
Morrissey, K.J., and Carter, C.B. (1983) Dislocations in twin boundaries in A12O3, in Character of Grain Boundaries, edited by M.F. Yan and A.H. Heuer. Adv. Ceram. vol. 6, pp. 85–95. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Murch, G.E., and Rothman, S.J. (1985) Grain boundary diffusion at high densities of grain boundaries. Diffusion and Defect Data 42, 17–28.
Mykura, H., Bansal, P.S., and Lewis, M.H. (1980) Coincidence site lattice relations of MgO-CdO interfaces. Philos. Mag. 42, 225–233.
Nagy, K.L., and Giletti, B.J. (1986) Grain boundary diffusion of oxygen in a macro-perthitic feldspar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 1151–1158.
Oishi, Y., Ando, K., Kurokawa, H., and Hiro, Y. (1983) Oxygen self-diffusion in MgO single crystals. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 66, C60–C62.
Oishi, Y., Ando, K., Suga, N., and Kingery, W.D. (1983) Effect of surface condition on oxygen self-diffusion coefficients for single crystal A1203. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 66, C130–C131.
Osenbach, J.W., and Stubican, V. (1983) Grain-boundary diffusion of 51Cr in MgO and Cr-doped MgO. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 66, 191–195.
Ostyn, K.M., and Carter, C.B. (1983) Structure of interfaces in cubic oxides, in Character of Grain Boundaries, edited by M.F. Yan and A.H. Heuer. Adv. Ceram. vol. 6, pp. 44–58. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Paladino, A.E., and Kingery, W.D. (1962) Aluminum ion diffusion in aluminum oxide. J. Chem. Phys. 37, 957–962.
Passmore, E.M., Duff, R.H., and Vasilos, T. (1966) Creep of dense, polycrystalline magnesium oxide. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 49, 594–600.
Paterson, M.S. (1986) The thermodynamics of water in quartz. Phys. Chem. Mineral. 13, 245–255.
Perrow, J.M., Smeltzer, W.W., and Embury, J.D. (1968) The role of structural defects in the growth of nickel oxide films. Acta Metall. 16, 1209–1218.
Peterson, N.L. (1979) Grain-boundary diffusion—Structural effects, models, and mechanisms, in Grain-Boundary Structure and Kinetics, edited by R.W. Balluffi, pp. 209–236. American Society of Metals, Metals Park, Ohio.
Peterson, N.L. (1983) Diffusion mechanisms in grain boundaries in solids, in Character of Grain Boundaries, edited by M.F. Yan and A.H. Heuer. Adv. Ceram. vol. 6, pp. 236–256. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Poirier, J.-P. (1985) Creep of Crystals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 280 PP-
Porter, D.A., and Easterling, K.E. (1981) Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, Van Nostrand Reinhold (UK), Wokingham, Berks., UK, 446 pp.
Raj, R., and Ashby, M.F. (1971) On grain boundary sliding and diffusional creep. Trans. Met. Soc. A.I.M.E. 2, 1113–1127.
Reddy, K.P.R., and Cooper, A.R. (1982) Oxygen self-diffusion in sapphire. J. Amer.Ceram. Soc. 65, 634–638.
Reddy, K.P.R., and Cooper, A.R. (1983) Oxygen diffusion in MgO and alpha-Fe2O3. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 66, 664–666.
Reddy, K.P.R., Oh, S.M., Major, L.D., Jr., and Cooper, A.R. (1980) Oxygen diffusion in forsterite. J. Geophys. Res. 85, 322–326.
Reed, D.J., and Wuensch, B.J. (1980) Ion-probe measurement of oxygen self-diffusion in single crystal A1203. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 63, 88–92.
Ricoult, D.L., and Kohlstedt, D.L. (1983a). Structural width of low-angle grain boundaries in olivine. Phys. Chem. Mineral. 9, 133–138.
Ricoult, D.L., and Kohlstedt, D.L. (1983b) Low-angle grain boundaries in olivine, in Character of Grain Boundaries, edited by M.F. Yan and A.H. Heuer, Adv. Ceram. vol. 6, pp. 59–72. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Ruehle, M. (1982) Transmission electron microscopy studies of grain boundaries in ceramics. J. de Phys. 43, C6-115–C6-133.
Ruehle, M. (1984) TEM observations of grain boundaries in ceramics, in Electron Microscopy of Materials, edited by W. Krakow, D.A. Smith, and L.W. Hobbs, pp. 317–323. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 31. North-Holland, New York.
Ruehle M. (1985) Comparisons between observed and computed grain boundary structures and energies in ceramics. J. de Phys. 46, C4, 281–291.
Ruehle, M., and Sass, S.L. (1984) The detection of the change in mean inner potential at dislocations in grain boundaries in NiO. Philos. Mag. A 49, 759–782.
Ruoff, A.L., and Balluffi, R.W. (1963) Strain-enhanced diffusion in metals. II. Dislocation and grain-boundary short circuiting models. J. Appl. Phys. 34,1848– 1853.
Schactner, R., and Sockel, H.G. (1977) Study of diffusion in quartz by activation analysis, in Reactivity of Solids, edited by J. Wood, O. Lindquist, C. Helgeson, and N.G. Vannerburg, pp. 605–609. Proc. 8th Int. Symposium.
Shewmon, P.G. (1963) Diffusion in Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York, 203 pp.
Smeltzer, W.W., Haering, R.R., and Kirkaldy, J.S. (1961) Oxidation of metals by short circuit and lattice diffusion of oxygen. Acta. Metall. 9, 880–885.
Smith, C.S., and Guttman, L. (1953) Measurement of internal boundaries in three- dimensional structures by random sectioning. Amer. Inst. Min. Metallogr. Engineers Trans. 197, 81–87.
Spriggs, R.M., Brissette, L.A., and Vasilos, T. (1964) Grain growth in fully dense magnesia. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 47, 417–418.
Stocker, R.L., and Ashby, M.F. (1973) On the rheology of the upper mantle. Rev. Geophys. 11, 391–426.
Stubican, V.S., Huzinec, G., and Damjanovic, D. (1985) Diffusion of 51Cr in surface layers of magnesia, alumina and spinel. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 68, 181–184.
Stubican, V.S., and Osenbach, J.W. (1984) Influence of anisotropy and do** on grain-boundary diffusion in oxide systems. Solid State Ionics 12, 375–381.
Sun, C.P., and Balluffi, R.W. (1982) Secondary grain boundary dislocations in [001] twist boundaries in MgO, I. Intrinsic structures. Philos. Mag. A 46, 49–62.
Suzuoka, T. (1961) Lattice and grain boundary diffusion in polycrystals. Trans. Japan Inst. Met. 2, 25–33.
Tullis, J., and Yund, R.A. (1982) Grain growth kinetics of quartz and calcite aggregates. J. Geol. 90, 301–318.
Turnbull, D. (1951) Theory of grain boundary migration rates. Trans. A.I.M.E. 191, 661–665.
Underwood, E. E. (1972) The mathematical foundations of quantative stereology, in Stereology and Quantitative Metallography, edited by G. E. Pellissier and S.M. Purdy, pp. 3–37. ASTM STP 504, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia.
Underwood, E.E., Colcord, A.R., and Waugh, R.C. (1968) Quantative relation-ships for random microstructures, in Ceramic Microstructures, edited by R.M. Fulrath and J.A. Pask, pp. 25–52. Wiley, New York.
Vaudin, M.D., Ruehle, M., and Sass, S.L. (1983) Faceting of tilt boundaries in NiO.Acta Metall 31, 1109–1116.
Veblen, D.R. (1980) Anthophyllite asbestos: Microstructures, intergrown sheet silicates, and mechanisms of fiber formation. Amer. Mineral. 65, 1075–1086.
Veblen, D.R., and Buseck, P.R. (1981) Hydrous pyriboles and sheet silicates in pyroxenes and uralites: Intergrowth microstructures and reaction mechanisms. Amer. Mineral. 66, 1107–1134.
Verhoeven, J.D. (1975) Fundamentals of Physical Metallurgy. Wiley, New York. 567 pp.
Wang, H.A., and Kroeger, F.A. (1980) Chemical diffusion in polycrystalline A12O3. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 63, 613–619.
Whipple, R.T.P. (1954) Concentration contours in grain boundary diffusion. Philos. Mag. 45 (371), 1225–1236.
Weber, G.W., Bitler, W.R, and Stubican, V.S. (1977) Diffusion of 51Cr in MgO. J.Amer. Ceram. Soc. 60, 61–65.
Wuensch, B.J., and Yasilos, T. (1964) Grain boundary diffusion in MgO. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 47, 63–68.
Wuensch, B.J., and Vasilos, T. (1966) Origin of grain-boundary diffusion in MgO. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 49, 433–436.
Wuensch, B.J., and Vasilos, T. (1971) Diffusion of Ni2+ in high-purity MgO at high temperatures. J. Chem. Phys. 54, 1123–1129.
Wuensch, B.J., Steele, W.C., and Vasilos, T. (1973) Cation self-diffusion in single crystal MgO. J. Chem. Phys. 58, 5258–5266.
Yan, M.F., and Heuer, A.H. (editors) (1983) Character of Grain Boundaries, Adv.Ceram. vol. 6, 339 pp. American Ceramic Society, Columbus, Ohio.
Young, G., and Funderlich, R.E. (1973) On the grain-boundary diffusion theory of Fisher and Whipple. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 5151–5154.
Yund, R.A. (1983) Diffusion in feldspars, in Feldspar Mineralogy (2nd ed), Reviews in Mineralogy, vol. 2, edited by P.H. Ribbe, pp. 203–222, Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Joesten, R. (1991). Grain-Boundary Diffusion Kinetics in Silicate and Oxide Minerals. In: Ganguly, J. (eds) Diffusion, Atomic Ordering, and Mass Transport. Advances in Physical Geochemistry, vol 8. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-9019-0_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-9019-0_11
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-9021-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-9019-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive