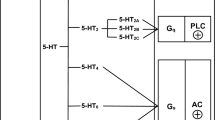
Abstract
A decade ago, central 5-HT receptors were classified into 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 types (Peroutka and Snyder, 1979). More recently, 5-HT3 receptors were recognized (Kilpatrick et al., 1987) and 5-HT4 sites have also been proposed (Dumuis et al., 1989). The 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 types have been divided into various subtypes on the basis of binding properties and 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 families have now been suggested by a number of groups (e.g. Schmidt and Peroutka, 1989). The 5-HT1C site, with which this chapter is mainly concerned, occurs very densely in the choroid plexus but is also widely distributed in the rest of the brain (Pazos et al., 1987). Although activation of other 5-HT1 subtype receptors stimulates cyclic AMP synthesis, activation of 5-HT1C sites stimulates phosphoinositide hydrolysis (Conn and Sanders-Bush, 1987a) which is a characteristic of 5-HT2 receptors. The 5-HT1C receptor also has both molecular biological and pharmacological similarities with 5-HT2 sites (Julius et al., 1988; Pritchett et al., 1988; Schmidt and Peroutka, 1989). Recent work suggests that its activation may have many behavioural and physiological effects and it could thus be implicated in a number of disorders of the central nervous system including anxiety.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asarch, K. E., Ransom, R. W. and Shih, J. S. (1985). 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B selectivity of two phenylpiperazine derivatives: evidence for 5-HT1B heterogeneity. Life Sci., 36, 1265–73.
Brewerton, T. D., Murphy, D. L., Mueller, E. A. and Jimerson, D. C. (1988). Induction of migraine like headaches by the serotonin agonist m-chlorophenylpiperazine. Clin. Pharm. Ther., 43, 605–9.
Charney, D. S., Woods, S. W., Goodman, W. K. and Heninger, G. R. (1987). Serotonin function in anxiety. II: Effects of the serotonin agonist mCPP in panic disorder patients and healthy subjects. Psychopharmacology, 92, 14–24.
Chopin, P. and Briley, M. (1987). Animal models of anxiety: the effects of compounds that modify 5-HT neurotransmission. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 8, 383–8.
Conn, P. J. and Sanders-Bush, E. (1987a). Relative efficacies of piperazines at the phosphoinositide hydrolysis — linked serotonergic (5-HT2 and 5-HT1C) receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 242, 552–7.
Conn, P. J. and Sanders-Bush, E. (1987b). Central serotonin receptors: effector systems, physiological roles and regulation. Psychopharmacology, 92, 267–77.
Curzon, G., Kennett, G. A., Shah, K. and Whitton, P. (1990). Behavioural effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine (m-CPP) a reported migraine precipitant. In Sandler, M. and Collins, G. (eds.), Migraine: a Spectrum of Ideas. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 173–8.
Dourish, C. T., Clark, M. L., Fletcher, A. and Iversen, S. D. (1989). Evidence that blockade of post-synaptic 5-HT1 receptors elicits feeding in satiated rats. Psychopharmacology, 97, 54–8.
Dourish, C. T., Hutson, P. H. and Curzon, G. (1986). Putative anxiolytics 8-OH-DPAT and buspirone and TVXQ 7821 are agonists at 5-HT1A autoreceptors in the raphe nuclei. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 7, 212–14.
Dumuis, A., Sebben, M. and Bockaert, J. (1989). BRL 24924: a potent agonist at a non-classical 5-HT receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in colliculi neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 162, 381–4.
Engel, G., Göthert, M., Hoyer, D., Schlicker, E. and Hillenbrand, K. (1986). Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol., 332, 1–7.
File, S. E. and Guardiola-Lemaitre, B. J. (1988). L-Fenfluramine in tests of dominance and anxiety in the rat. Neuropsychobiology, 20, 205–11.
Frances, H. (1988). Psychopharmacological profile of 1-(M-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl) piperazine (TFMPP). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 31, 37–41.
Frances, H., Lienard, C. and Fermanian, J. (1990). Improvement of the isolation-induced social behavioural deficit involves activation of the 5-HT1 receptors. Progr. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiat., 14, 91–102.
Fuller, R. W., Snoddy, H. D. and Cohen, M. L. (1984). Interactions of trazodone with serotonin neurons and receptors. Neuropharmacology, 23, 539–44.
Gleeson, S., Ahlers, S. T., Mansbach, R. S., Foust, J. M. and Barrett, J. E. (1989). Behavioural studies with anxiolytic drugs VI. Effects on punished responding of drugs interacting with serotonin receptor subtypes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 250, 809–17.
Gray, J. A. (1987). The Neuropsychology of Anxiety: An Enquiry into the Functions of the Septo-Hippocampal System. Oxford University Press, New York.
Green, A. R., Guy, A. P. and Gardner, C. R. (1984). The behavioural effects of RU 24969, a suggested 5-HT1 receptor agonist in rodents and the effect on the behaviour of treatment with antidepressants. Neuropharmacology, 23, 655–61.
Hamik, A. and Peroutka, S. J. (1989). 1-(m-Chlorophenyl)piperazine (mCPP) interactions with neurotransmitter receptors in the human brain. Biol. Psychiat., 25, 569–75.
Hamon, M., Cossery, J. M., Spampinato, U. and Gozlan, H. (1986). Are there selective ligands for 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptor binding sites in brain? Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 7, 336–7.
Hirose, A., Tsuji, R., Shimizu, H., Tatsuno, T., Tanaka, H., Kumasaka, Y. and Nakamura, M. (1990). Inhibition by 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin and SM-3997, a novel anxiolytic drug, of the hippocampal slow (RSA) activity mediated by 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol., 341, 8–13.
Hitchcott, P. K., File, S. E., Ekwuru, M. and Neal, M. J. (1990). Chronic diazepam treatment in rats causes long-lasting changes in central [3H]-5-hydroxytryptamine and [14C]-aminobutyric acid release. Br. J. Pharmacol., 99, 11–12.
Hoyer, D. (1988). Functional correlates of serotonin 5-HT1 recognition sites. J. Receptor Res., 8, 59–81.
Hutson, P. H., Donohoe, T. P. and Curzon, G. (1988). Infusion of the 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists RU 24969 and TFMPP into the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus causes hypophagia. Psychopharmacology, 95, 550–2.
Hutson, P. H., Sarna, G. S., O’Connell, M. T. and Curzon, G. (1989). Hippocampal 5-HT synthesis and release in vivo, is decreased by infusion of 8-OH-DPAT into the nucleus raphe dorsalis. Neurosci. Lett., 100, 276–80.
Jenck, F., Broekkamp, C. L. and Van Delft, A. M. L. (1989). Opposite control mediated by central 5-HT1A and non-5-HT1A (5-HT1B or 5-HT1C) receptors on periaqueductal gray aversion. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 161, 219–21.
Johnston, A. L. and File, S. E. (1986). 5-HT and anxiety: promises and pitfalls. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 24, 1467–70.
Julius, A., MacDermott, A. M., Axel, R. and Jessell, T. M. (1988). Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1C receptor. Science, 241, 558–64.
Kahn, R. S., Asnis, G. M., Wetzler, S. and Van Praag, H. M. (1988). Neuroendocrine evidence for serotonin receptor hypersensitivity in panic disorder. Psychopharmacology, 97, 360–4.
Kennett, G. A. and Curzon, G. (1988a). Evidence that mCPP may have behavioural effects mediated by central 5-HT1C receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol., 94, 137–47.
Kennett, G. A. and Curzon, G. (1988b). Evidence that hypophagia induced by mCPP and TFMPP requires 5-HT1B receptors; hypophagia induced by RU 24969 only requires 5-HT1B receptors. Psychopharmacology, 96, 93–100.
Kennett, G. A., Dourish, C. T. and Curzon, G. (1987). 5-HT1B agonists induce anorexia at postsynaptic site. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 141, 429–35.
Kennett, G. A., Whitton, P. and Curzon, G. (1990). ID50 values of antagonists versus mCPP-induced hypophagia and 5-HT2-mediated head shakes indicate 5-HT1C sites mediate the hypophagia in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol., 99, 241P.
Kennett, G. A., Whitton, P., Shah, K. and Curzon, G. (1989). Anxiogenic like effects of mCPP and TFMPP in animal models are opposed by 5-HT1C receptor antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 164, 445–54.
Kilpatrick, G. J., Jones, B. J. and Tyers, M. B. (1987). Identification and distribution of 5-HT3 receptors in rat brain using radioligand binding. Nature, 330, 746–8.
King, B. H., Brazell, C., Dourish, C. T. and Middlemiss, D. N. (1989). MK-212 increases rat plasma ACTH concentration by activation of the 5-HT1C receptor subtype. Neurosci. Lett., 105, 1 74–6.
Klodzinska, A., Jaros, T., Chojnacka-Wojcik, E. and Maj, J. (1989). Exploratory hypoactivity induced by m-trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine. J. Neural. Transm. [P-D Sect]., 1, 207–18.
Leysen, J. E., Awouters, F., Kennis, L., Laduron, P. M., Vandenberk, J. and Janssen, P. A. J. (1981). Receptor binding profile of R41 468, a novel antagonist of 5-HT2 receptors. Life Sci., 28, 1015–22.
Lindvall-Axelsson, M., Nilsson, C., Owman, C. and Svensson, P. (1989). Involvement of 5-HT1C receptors in the production of CSF from the choroid plexus. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 9, suppl., S680.
Lucki, I. and Frazer, A. (1982). Behavioural effects of indole and piperazine type serotonin receptor agonists. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr., 8, 101.
Lucki, I., Ward, H. R. and Frazer, A. (1989). Effect of 1-(m-chlorophenyl)piperazine and 1-(m-trifluoromethylphenyl)piperazine on locomotor action. J. Pharmacol Exp. Ther., 249, 155–64.
McKearney, J. W. (1989). Apparent antinociceptive properties of piperazine-type serotonin agonists: trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine, chlorophenylpiperazine, and MK-212. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 32, 657–60.
Meert, T. F. and Colpaert, F. C. (1986). The effects of agonists and antagonists at putative 5-HT receptor subtypes in the shock-probe conflict test. Psychopharmacology, 89, S23.
Mendels, J. (1987). Clinical experience with serotonin reuptake inhibiting antidepressants. J. Clin. Psychiat., 48 (3 suppl.), 26–30.
Mueller, E. A., Murphy, D. L. and Sunderland, T. (1985). Neuroendocrine effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine, a serotonin agonist, in humans. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab., 61, 1179–84.
Neill, J. C. and Cooper, S. J. (1989). Selective reduction by serotonergic agonist of hypertonic saline consumption in rats: evidence for possible 5-HT1C receptor mediation. Psychopharmacology, 99, 196–201.
Nelson, D. R. and Thomas, D. R. (1989). [3H]-BRL 43694 (Granisetron), a specific ligand for 5-HT3 binding sites in rat brain cortical membranes. Biochem. Pharmacol., 38, 1693–5.
Nishikawa, T. and Scatton, B. (1986). Neuroanatomical site of the inhibitory influence of anxiolytic drugs on central serotonergic transmission. Brain Res., 371, 123–32.
Pazos, A., Probst, A. and Palacios, J. M. (1987). Serotonin receptors in the human brain — III: Autoradiographic map** of serotonin — I: receptors. Neuroscience, 21, 97–122.
Pei, Q., Zetterstrom, T. and Fillenz, M. (1989). Both systemic and local administration of benzodiazepine agonists inhibit the in vivo release of 5-HT from neural hippocampus. Neuropharmacology, 28, 1061–6.
Peroutka, S. J. and Snyder, S. H. (1979). Multiple serotonin receptors: differential binding of [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine, [3H] lysergic acid diethylamide and [3H] spiroperidol. Molec. Pharmacol., 16, 687–99.
Pritchett, D. B., Bach, A. W. J., Wozny, M., Taleb, O., Dal Toso, R., Shih, J. C. and Seeburg, P. H. (1988). Structure and functional expression of cloned rat serotonin 5HT-2 receptor. EMBO J., 7, 4135–40.
Samanin, R., Mennini, T., Ferraris, A., Bendotti, C., Borsini, F. and Garattini, S. (1979). m-Chlorophenylpiperazine: a central serotonin agonist causing powerful anorexia in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol., 308, 159–63.
Schmidt, A. W. and Peroutka, S. J. (1989). 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor ‘families’. FASEB J., 3, 2242–9.
Schoeffler, P. and Hoyer, D. (1989). Interaction of arylpiperazines with 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1C and 5-HT1D receptors: do discriminatory 5-HT1B receptor ligands exist? Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol., 339, 675–83.
Sharp, T., Bramwell, S. R. and Grahame-Smith, D. G. (1989). 5-HT1 agonists reduce 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat hippocampus in vivo as determined by brain microdialysis Br. J. Pharmacol., 96, 283–90.
Sills, M. A., Lucki, I. and Frazer, A. (1985). Development of selective tolerance to the serotonin behavioural syndrome and suppression of locomotor activity after repeated administration of either 5-MeODMT or mCPP. Life Sci., 36, 2463–9.
Sills, M. A., Wolfe, B. B. and Frazer, A. (1984). Determination of selective and non-selective compounds for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors subtypes in rat frontal cortex. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 231, 480–7.
Targum, S. D. and Marshall, L. E. (1989). Fenfluramine provocation of anxiety in patients with panic disorder. Psychiatry Res., 28, 295–306.
Tricklebank, M. D., Forler, C. and Fozard, J. R. (1984). The involvement of subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor and catecholaminergic systems in the behavioural response to 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 106, 271–82.
Tricklebank, M. D., Middlemiss, D. N. and Neill, J. (1986). Pharmacological analysis of the behavioural and thermoregulatory effects of the putative 5-HT1 receptor agonist RU 24969 in the rat. Neuropharmacology, 25, 877–86.
Tyers, M. B. (1989). A review of the evidence supporting the anxiolytic potential of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. In Bevan, P., Cools, A. R. and Archer, T. (eds.), Behavioural Pharmacology of 5-HT. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ, 353–9.
Van Woert, M. H., Rosenbaum, D. and Enna, S. J. (1982). Overview of pharmacological approaches to therapy for Tourette syndrome. Adv. Neurol., 35, 369–75.
Whitton, P. and Curzon, G. (1990). Anxiogenic-like effect of infusing 1-(3-chlorophenyl)piperazine (mCPP) into the hippocampus. Psychopharmacology, 100, 138–40.
Wozniak, K. M., Aulakh, C. S., Hill, J. L. and Murphy, D. L. (1989). Hyperthermia induced by mCPP in the rat and its modification by antidepressant treatment. Psychopharmacology, 97, 269–74.
Zohar, J., Insel, T. R., Zohar-Kadouch, P. C., Hill, J. L. and Murphy, J. L. (1988). Serotonergic responsivity in obsessive—compulsive disorder. Effects of chronic clomipramine treatment. Arch. Gen. Psychiat., 45, 167–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Copyright information
© 1991 Macmillan Publishers Limited
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Curzon, G., Gibson, E.L., Kennedy, A.J., Kennett, G.A., Sarna, G.S., Whitton, P. (1991). Anxiogenic and Other Effects of mCPP, a 5-HT, 1C Agonist. In: Briley, M., File, S.E. (eds) New Concepts in Anxiety. Palgrave, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-11847-2_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-11847-2_10
Publisher Name: Palgrave, London
Print ISBN: 978-1-349-11849-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-349-11847-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)