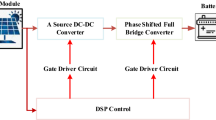
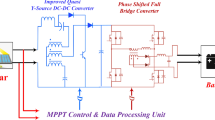
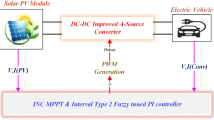
Abstract
Solar PV based charging of Electric vehicle (EV) charging circuit is presented in this research. To obtain the optimal performance of the solar photovoltaic system under Typical Test Circumstances, incremental conductance MPPT algorithm is employed. With a boost converter with a 400 V output, a 100 AH battery may be charged by a solar PV array. Then, the voltage is lowered to meet the needs of buck operation and a 220 V battery. Short-term storage capacity is shown to completely charge rapidly. The objective is accomplished by the appropriate application of the calculated parameters of the passive components (filter elements on the converters and inverters of the system). When power from solar photovoltaic panels is not available, electric cars are powered from the AC source. We use a PI (proportional plus integral) regulator with a 10 rad/s corner frequency. An H-bridge rectifier provides a DC–DC bidirectional converter with a 400 V dc output voltage. One thing to note is how fast the SOC of the battery is reached. The battery current and voltage are shown during charging and draining modes. During charging, it is evident that the current and voltage of grid are synchronized. It is believed that they are out of phase during discharge, signifying a opposite power movement. Power semiconducting components are controlled with switching frequency of 10 kHz PWM pulse. Electric vehicle on-board chargers are available for use in parking lots and residences. Less grid-based power needs and emission-free, quiet driving are hallmarks of solar PV connected electric vehicles (EVs).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu N, Chen O, Lu X, Liu J, Zhang J (2015) A charging strategy for PV-based battery switch station considering service availability and self-consumption of PV energy. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(8):4878–4889
Edenhofer O (2015) Climate change 2014: mitigation of climate change, vol 3. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Lucas A, Bonavitacola F, Kotsakis E, Fulli G (2015) Grid harmonic impact of multiple electric vehicle fast charging. Electr Power Syst Res 127:13–21
Tan L, Wu B, Yaramasu V, Rivera S, Guo X (2016) Effective voltage balance control for bipolar-DC-bus-fed EV charging station with three-level DC–DC fast charger. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63:4031–4041
Yong JY, Ramachandaramurthy VK, Tan KM, Mithulananthan N (2015) A review on the state-of-the-art technologies of electric vehicle, its impacts and prospects. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 49:365–385
Hu X, Zou C, Zhang C, Li Y (2017) Technological developments in batteries. IEEE Power Energy Mag 20–31
Goli P, Shireen W (2014) PV integrated smart charging of PHEVs based on DC link voltage sensing. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 5:1421–1428
Dharmakeerthi CH, Mithulananthan N, Saha TK (2012) Modeling and planning of EV fast charging station in power grid. In: Power and energy society general meeting, 2012 IEEE
Haghbin S et al (2013) Grid-connected integrated battery chargers in vehicle applications: review and new solution. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(2):459–473
Nafeh AE-SA (2011) An effective and safe charging algorithm for lead-acid batteries in PV systems. Int Energy Res 35(8):733–740
**aopeng C et al (2012) An overview of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. In: IPEC, 2012 conference on power & energy. IEEE
Karimi G, Li X (2013) Thermal management of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. Int J Energy Res 37(1):13–24
Botsford C, Szczepanek A (2009) Fast charging vs. slow charging: pros and cons for the new age of electric vehicles. EVS24, Stavanger, Norway
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumari, P., Kumar, S. (2024). Powering Electric Vehicles with Solar Panels with Both the G2V and V2G Charging Modes. In: Gupta, O.H., Padhy, N.P., Kamalasadan, S. (eds) Soft Computing Applications in Modern Power and Energy Systems. EPREC 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1107. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8007-9_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8007-9_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8006-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8007-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)